Sickle cell anemia is a significant health concern that affects children worldwide, leading to various complications and health issues. When a child is diagnosed with this condition, it is crucial for healthcare professionals, particularly nurses, to understand the appropriate tests and assessments needed to manage the illness effectively. In the following sections, we will explore the essential tests that nurses perform for children diagnosed with sickle cell anemia, providing a comprehensive overview of the condition and its implications.
In this article, we will delve into the symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and the critical role that nurses play in the management of sickle cell anemia. Understanding these components not only helps in the immediate care of affected children but also informs parents and caregivers about the necessary steps to support their health. With the increasing awareness of sickle cell anemia, it is essential to highlight the importance of early diagnosis and the tests involved in this process.
By the end of this article, readers will have a clearer understanding of which tests are crucial when a child is diagnosed with sickle cell anemia and why these tests are vital for effective management and treatment. Therefore, we invite you to join us on this informative journey as we explore the intricacies of sickle cell anemia and the pivotal role of nurses in managing this condition.
Table of Contents
Understanding Sickle Cell Anemia
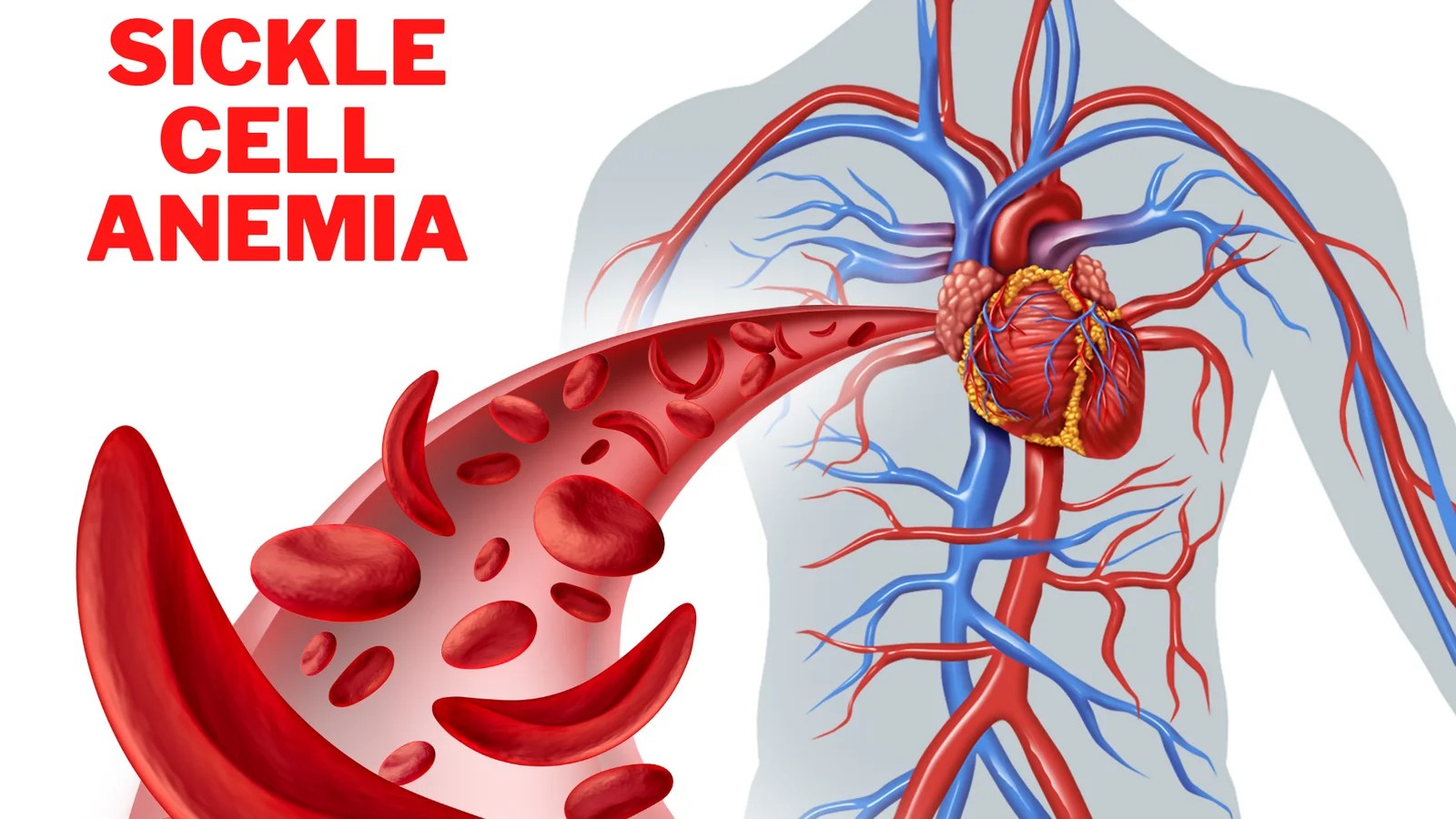
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic blood disorder characterized by the presence of abnormal hemoglobin, which can lead to the distortion of red blood cells into a sickle or crescent shape. This abnormality can cause various complications, including painful crises, increased risk of infections, and potential organ damage. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of this condition is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Symptoms of Sickle Cell Anemia
The symptoms of sickle cell anemia can vary widely among affected individuals and may include:
- Severe pain episodes, known as sickle cell crises
- Fatigue and weakness
- Frequent infections
- Delayed growth and development in children
- Vision problems
Diagnosis Procedures
Diagnosing sickle cell anemia typically involves a series of tests to confirm the presence of the disease. The following procedures are commonly undertaken:
- Blood tests to determine hemoglobin levels and types
- Hemoglobin electrophoresis to identify the specific type of hemoglobin
- Genetic testing for family members
Tests Nurses Perform
When a child is diagnosed with sickle cell anemia, nurses play a critical role in performing and coordinating the necessary tests. The primary test that a nurse will perform includes:
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) is often the first test performed to assess the patient's overall health and to detect a variety of disorders, including anemia. This test evaluates red blood cell count, hemoglobin levels, and other important parameters.
Hemoglobin Electrophoresis
This test is essential for diagnosing sickle cell anemia and differentiating it from other hemoglobinopathies. It helps identify the specific type of hemoglobin present in the blood, which is crucial for treatment decisions.
Nursing Role in Management
Nurses are at the forefront of managing sickle cell anemia, providing care and support to both patients and their families. Their responsibilities include:
- Administering medications as prescribed
- Monitoring vital signs and symptoms
- Educating families about managing sickle cell anemia
- Coordinating with multidisciplinary teams for comprehensive care
Treatment Options
Treatment for sickle cell anemia focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. Common treatment options include:
- Pain management through medications
- Hydroxyurea to reduce the frequency of pain crises
- Blood transfusions for severe anemia
- Bone marrow or stem cell transplant in eligible patients
Support for Families
Supporting families of children with sickle cell anemia is crucial for their emotional and psychological well-being. Resources available include:
- Support groups for parents and caregivers
- Educational materials on managing sickle cell anemia
- Access to mental health professionals
Conclusion
In conclusion, when a child is diagnosed with sickle cell anemia, nurses play an integral role in performing essential tests such as the Complete Blood Count and Hemoglobin Electrophoresis. Understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is vital for effective management. We encourage readers to engage with this topic by leaving comments, sharing this article, or exploring further resources related to sickle cell anemia management.
Thank you for taking the time to learn about this important health issue. We hope this article has provided valuable insights and encourages a comprehensive understanding of sickle cell anemia and the critical role of nursing in its management.
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8onnCoaClnF2ewG6wyJqep6ejmrFuw8itn2armZi4rbGMnJylpF2Wu6a5yJpksKCZmLVuwMSsq2avmaG5bsDHnmSnraKosm%2B006aj