Understanding the structure of government is crucial to comprehending how our nation operates. The question "which branch of government works in this building?" often arises when discussing specific government buildings, such as courthouses, legislative halls, or the White House. Each building typically houses a distinct branch of government, playing a vital role in upholding democracy and the rule of law. In this article, we will explore the three branches of government—executive, legislative, and judicial—and identify which branch operates in various key government buildings. Additionally, we will provide insights into the functions and responsibilities of each branch, ensuring that readers gain a comprehensive understanding of our government system.
The U.S. government is divided into three branches to ensure a system of checks and balances. This separation of powers is fundamental to the Constitution and prevents any single branch from becoming too powerful. Each branch has its own responsibilities and operates independently, yet they must work together to govern effectively. In this article, we will delve deeper into each branch and discuss prominent buildings associated with them.
In the following sections, we will provide a thorough exploration of the branches of government, including their roles, key buildings, and the significance of those structures. By the end of this article, readers will have a well-rounded understanding of which branch of government works in various government buildings and the importance of these institutions in maintaining democracy.
Table of Contents
Introduction to the Three Branches of Government
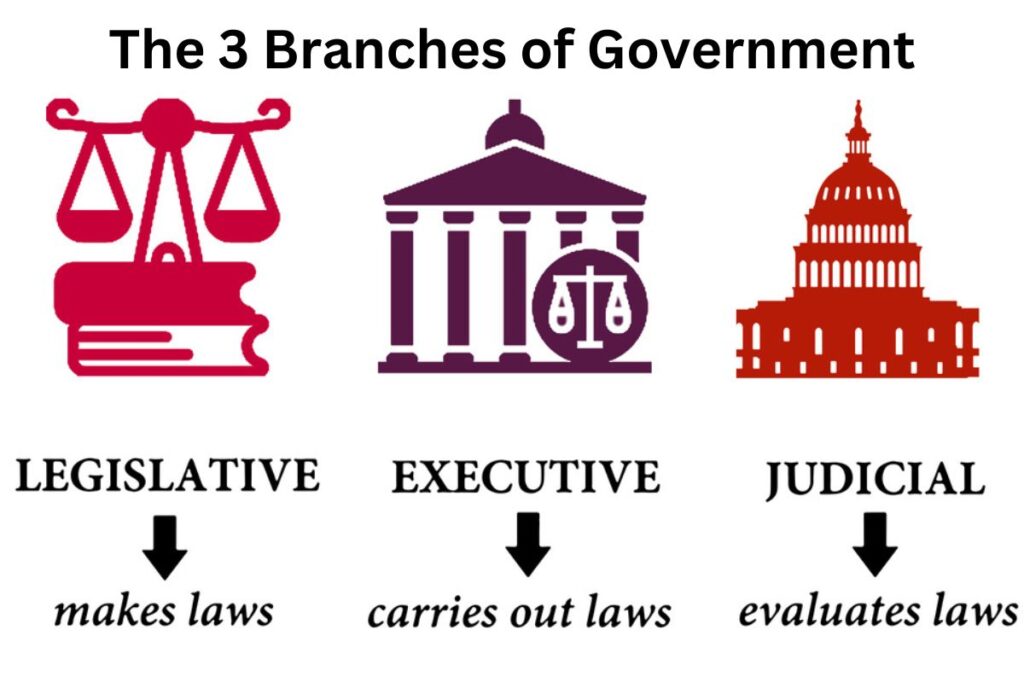
The United States government is structured around three branches: the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. This framework was established by the Constitution to create a system of checks and balances, ensuring that no single branch could dominate the others. Each branch has distinct powers and responsibilities, allowing for a balanced approach to governance.
The executive branch is responsible for enforcing laws, the legislative branch creates laws, and the judicial branch interprets laws. Understanding the roles of these branches helps citizens engage more effectively in the democratic process and promotes accountability within government institutions.
The Executive Branch
The executive branch is headed by the President of the United States and is responsible for implementing and enforcing the laws passed by Congress. This branch includes the Vice President, the Cabinet, and various federal agencies.
Key Buildings of the Executive Branch
Several important buildings represent the executive branch of government:
- The White House: The official residence and workplace of the President.
- The Eisenhower Executive Office Building: Houses the offices of the Vice President and other key staff.
- Federal Agencies: Various federal buildings across the country where agencies like the Department of Justice and Department of Defense operate.
Functions and Responsibilities of the Executive Branch
The primary functions of the executive branch include:
- Enforcing federal laws and regulations.
- Conducting foreign policy and diplomacy.
- Managing national defense and military operations.
- Administering federal programs and services.
The Legislative Branch
The legislative branch is responsible for making laws. It is comprised of two chambers: the House of Representatives and the Senate. Together, they form the United States Congress.
Key Buildings of the Legislative Branch
The legislative branch operates primarily out of the following buildings:
- The United States Capitol: The home of Congress, where both the House and Senate meet to discuss and pass legislation.
- The House of Representatives Office Buildings: Facilities that house the offices of Representatives.
- The Senate Office Buildings: Similar facilities for Senators to conduct their business.
Functions and Responsibilities of the Legislative Branch
The legislative branch has several key functions:
- Drafting and passing legislation.
- Approving the federal budget and government spending.
- Overseeing and investigating executive actions.
- Ratifying treaties and confirming presidential appointments.
The Judicial Branch
The judicial branch is responsible for interpreting the laws and ensuring justice. It consists of the Supreme Court and lower federal courts.
Key Buildings of the Judicial Branch
Important buildings associated with the judicial branch include:
- The Supreme Court Building: The home of the highest court in the land, where significant legal decisions are made.
- Federal Courthouses: Local court buildings where federal cases are heard.
Functions and Responsibilities of the Judicial Branch
The judicial branch performs several essential functions:
- Interpreting federal laws and the Constitution.
- Resolving disputes between states or individuals.
- Ensuring that laws comply with the Constitution.
- Protecting individual rights and liberties.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding which branch of government works in various government buildings is vital for grasping the broader workings of our democracy. The executive branch enforces laws, the legislative branch creates them, and the judicial branch interprets them. Each branch operates within its own designated buildings, contributing to a balanced and effective government. As citizens, it is crucial to stay informed and engaged with these institutions to uphold our democratic values. We encourage you to leave a comment below, share this article with others, or explore more content on our site!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back soon for more insightful articles about government and civic engagement!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8uLTInJ9mmqKWu6S0jKidZp%2Bfq7Kzusyepa1lp6S%2FrL%2BMoqVmrJiewG6u1KKjnaGenHupwMyl