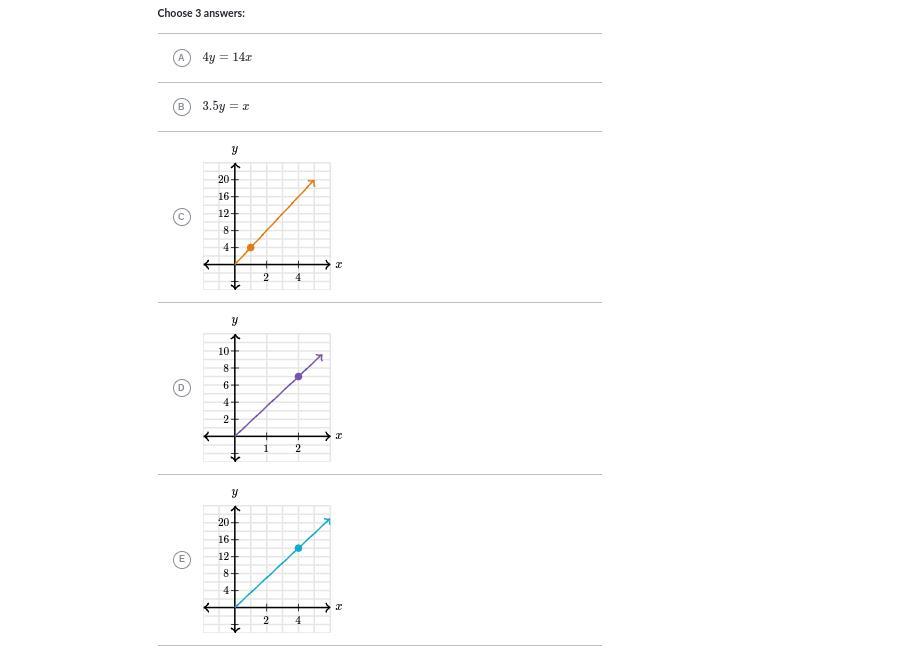
In the realm of physics and scientific experiments, a common question arises: which balloon ascended faster? This inquiry invites curiosity and exploration into the principles of buoyancy, gas laws, and the behavior of different gases when heated. Understanding the factors that influence balloon ascension can lead to fascinating insights into not just engineering, but also the fundamental laws of physics. In this article, we will explore the mechanics behind balloon ascension, compare various types of balloons, and delve into the principles that dictate their speed. This exploration will be particularly useful for educators, students, and anyone with a keen interest in science.
Our exploration will cover a breadth of topics, including the science behind buoyancy, the characteristics of different gases used in balloons, and practical experiments to observe balloon ascension firsthand. We’ll also discuss the various factors that can affect the speed of a balloon’s ascent, such as temperature, gas composition, and balloon material. By the end of this article, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of the factors at play when determining which balloon ascended faster.
So, whether you are a teacher looking for a classroom experiment, a student preparing for a science project, or simply an enthusiast eager to learn, this article is designed to provide valuable insights. Let’s embark on this scientific journey to uncover the mysteries of balloon ascension!
Table of Contents
1. Understanding Buoyancy
Buoyancy is the force that causes objects to float in a fluid, such as air or water. It is an essential concept for understanding how balloons ascend. The principle of buoyancy is based on Archimedes’ principle, which states that an object submerged in a fluid experiences an upward force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced.
When a balloon is filled with a gas that is less dense than the surrounding air, it will rise. The buoyant force acting on the balloon is greater than the gravitational force pulling it down. This difference in forces results in ascension. For example, helium is significantly less dense than air, which is why helium-filled balloons float.
1.1 Archimedes’ Principle
To further understand buoyancy, let’s break down Archimedes’ principle:
- An object submerged in a fluid experiences a buoyant force.
- The buoyant force is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
- If the weight of the object is less than the buoyant force, it will float.
1.2 Density and Ascension
Density plays a critical role in determining whether a balloon will ascend. The formula for density is:
Density = Mass/Volume
A balloon filled with a gas that has a lower density than the surrounding air will ascend. Conversely, if the gas inside the balloon is denser than the air, the balloon will not rise.
2. The Science of Gases
Gases behave according to specific laws, particularly when subjected to changes in temperature and pressure. Two notable gas laws relevant to balloons are Boyle’s Law and Charles’s Law.
2.1 Boyle’s Law
Boyle’s Law states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume when temperature is constant. This means that as a gas expands, its pressure decreases. In the context of a balloon:
- As a balloon rises and encounters lower atmospheric pressure, it expands.
- This expansion causes the balloon to become lighter and increases its buoyancy.
2.2 Charles’s Law
Charles’s Law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature when pressure is constant. This law explains why hot air balloons rise:
- When air inside the balloon is heated, it expands.
- This decrease in density allows the balloon to ascend.
3. Types of Balloons
There are various types of balloons, each with distinct characteristics that affect their ascension speed. Below are the two most common types:
3.1 Helium Balloons
Helium balloons are filled with helium gas, which is lighter than air. As a result, they tend to ascend quickly:
- Helium is non-flammable and safe to use.
- Helium balloons can rise to significant altitudes, making them popular for celebrations and decorations.
3.2 Hot Air Balloons
Hot air balloons use heated air to achieve lift. The principles of buoyancy and gas laws come into play:
- The air inside the balloon is heated, causing it to expand and become less dense than the cooler air outside.
- As a result, hot air balloons ascend steadily and can be controlled by regulating the temperature of the air inside.
4. Factors Affecting Ascension Speed
Several factors can influence the speed at which a balloon ascends. Understanding these factors is crucial for conducting experiments and making predictions about balloon behavior.
4.1 Temperature
Temperature significantly affects the density of gases. Warmer gases are less dense, which allows balloons to rise faster. In experiments, heating the gas inside a balloon can lead to increased ascension speed.
4.2 Gas Composition
The type of gas used in the balloon also affects its ascent:
- Helium balloons rise faster than air-filled balloons due to their lower density.
- Mixing gases can alter buoyancy and, consequently, ascent speed.
5. Experiments to Test Balloon Ascension
Conducting experiments can be a fun and educational way to observe the principles of buoyancy and gas laws in action. Here are a couple of simple experiments you can try:
5.1 Helium vs. Air Balloons
Materials needed:
- One helium balloon
- One air-filled balloon
Procedure:
- Release both balloons simultaneously and observe their ascent.
- Take note of which balloon ascends faster and discuss the reasons behind the results.
5.2 Hot Air Balloon Experiment
Materials needed:
- Plastic bottle
- Balloon
- Heat source (like warm water)
Procedure:
- Fill the plastic bottle with warm water and place the deflated balloon over the opening.
- Observe as the air inside the balloon heats up and expands, causing it to rise.
6. Real-World Applications
The principles of balloon ascension have far-reaching applications beyond mere experiments. Here are a few examples:
6.1 Meteorological Balloons
Meteorologists use weather balloons to collect data about atmospheric conditions. These balloons ascend to high altitudes, gathering valuable information on temperature, pressure, and humidity.
6.2 Recreational Hot Air Ballooning
Hot air ballooning has become a popular recreational activity, allowing individuals to enjoy scenic views while experiencing the principles of buoyancy firsthand.
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, the question of which balloon ascended faster is influenced by a variety of factors, including gas composition, temperature, and the principles of buoyancy and gas laws. Helium balloons tend to ascend more quickly than air-filled balloons, while hot air balloons demonstrate the fascinating interplay of heat and buoyancy. By conducting simple experiments, anyone can observe these principles in action and gain a deeper understanding of the science behind balloon ascension.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences regarding balloon experiments in the comments below. If you found this article informative, feel free to share it with others or explore more articles on our website!
You Might Also Like
Because I Wanted To Know If It Was True: Unraveling The Mystery Behind LizzieExploring The Variety Of Exotic Fruits Around The World
The Time Of This Sale Is: Your Ultimate Guide To Time-Limited Sales
The Table To Show The Difference In The Value Of The Accounts For Each
A Client Visits A Health Care Facility Reporting Amenorrhea For 10 Weeks
Article Recommendations

ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8tK3MnmShnZmctbV51qGgnKBdl66tuM6opWaZo5iyr7DEnWSfmaOpsrN5wqGmqKuVYn5urc2srp6qXZi1sLvSnmRqZpipuq0%3D