Taxable income is a vital concept in personal finance and taxation that affects everyone who earns money. Understanding what constitutes taxable income can help you manage your finances better and ensure compliance with tax laws. In this article, we will explore the meaning of taxable income, how it is calculated, and its implications on your overall financial health.
Taxable income refers to the portion of your income that is subject to taxation by the government. This includes wages, salaries, bonuses, interest, rental income, and other forms of earnings. Knowing what qualifies as taxable income can help you optimize your tax situation and make informed decisions regarding deductions and credits.
As we delve deeper into the concept of taxable income, we will discuss various factors that can influence your taxable income, including deductions, exemptions, and credits. We will also examine common misconceptions about taxable income and provide you with resources to help you navigate the complexities of tax laws effectively.
Table of Contents
What is Taxable Income?
Taxable income is defined as the total income earned by an individual or entity that is subject to taxation. This can include various sources of income such as:
- Wages and salaries
- Business income
- Interest and dividends
- Rental income
- Capital gains
Understanding taxable income is crucial as it determines the amount of tax you owe to the government each year. It is important to differentiate between gross income and taxable income, as not all income is subject to tax.
How Taxable Income is Calculated
The calculation of taxable income involves several steps:
For example, if your gross income is $70,000 and you have $10,000 in deductions, your taxable income would be $60,000.
Factors Affecting Taxable Income
Several factors can impact your taxable income:
- Your filing status (single, married, head of household)
- The number of dependents you claim
- The types of income you receive
- Any deductions or credits for which you are eligible
Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions regarding your finances and tax obligations.
Common Deductions and Exemptions
Some common deductions include:
- Mortgage interest
- State and local taxes
- Charitable contributions
- Medical expenses (above a certain threshold)
Exemptions may include personal exemptions for yourself and dependents, which can further reduce your taxable income.
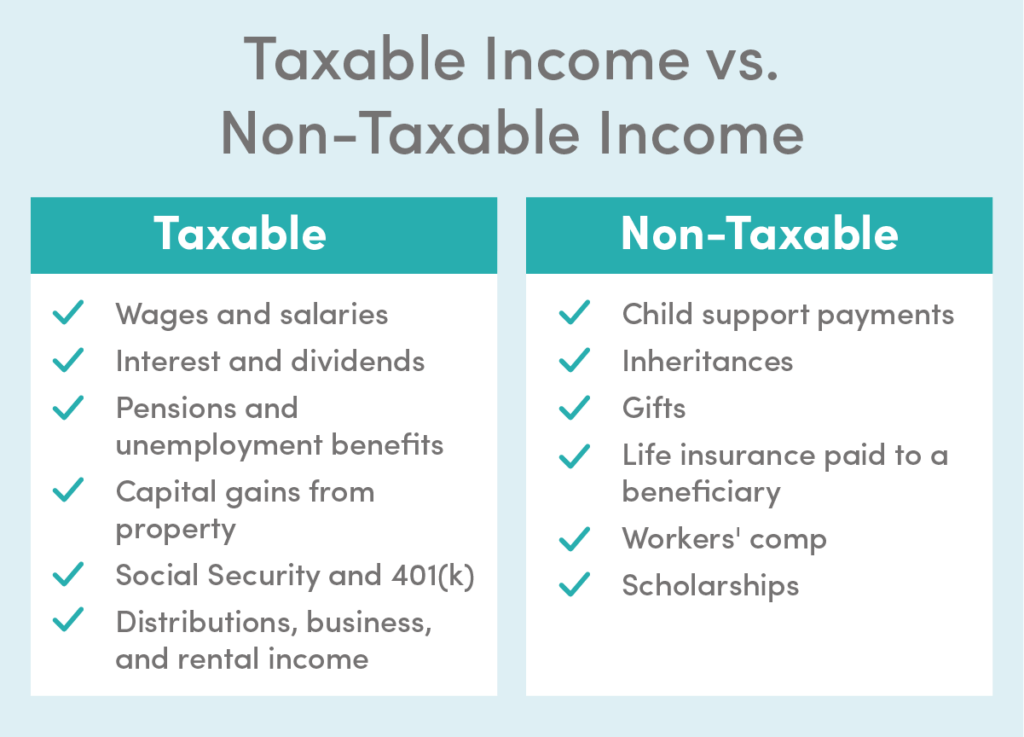
Taxable Income vs. Non-Taxable Income
It is essential to distinguish between taxable and non-taxable income:
- Taxable Income: Income that is subject to tax.
- Non-Taxable Income: Income that is exempt from tax, such as certain gifts, inheritances, and life insurance proceeds.
Understanding these distinctions can help you optimize your tax planning strategies.
Misconceptions About Taxable Income
Common misconceptions about taxable income include:
- All income is taxable.
- You cannot deduct any expenses.
- Only high-income earners pay taxes.
Addressing these misconceptions can empower individuals to better understand their tax obligations and plan accordingly.
Importance of Keeping Records
Maintaining accurate records is crucial for tax purposes. Good record-keeping practices can help you:
- Prepare your tax returns accurately.
- Support any deductions or credits you claim.
- Provide documentation in the event of an audit.
Consider using accounting software or hiring a professional to help manage your finances effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding taxable income is essential for effective tax planning and compliance. By knowing what constitutes taxable income, how it is calculated, and the factors that influence it, you can make informed decisions regarding your finances. Remember to keep accurate records and consult with a tax professional if needed.
We encourage you to leave a comment below, share this article with others, or explore our other resources on personal finance and taxation.
Thank you for reading! We hope to see you back here for more insightful articles.
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8ta3XmpmlnV2eu6S7zJ5loaydoQ%3D%3D