DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the hereditary material in all known living organisms. It serves as the blueprint for life, encoding the genetic instructions necessary for the growth, development, reproduction, and functioning of every organism on Earth. Understanding DNA is not just a scientific pursuit; it has profound implications for medicine, genetics, and even forensic science. In this article, we will explore what DNA is, its structure and function, its role in heredity, and why it is vital for life as we know it.
As we delve into the intricacies of DNA, we will address key concepts such as its composition, the significance of genetic variation, and the impact of modern genetic research. With advancements in technology, our understanding of DNA has evolved, leading to breakthroughs in fields like personalized medicine and genetic engineering. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of DNA and its essential role in biology.
This exploration of DNA will also touch upon ethical considerations and the potential consequences of genetic manipulation, highlighting the importance of responsible science. Let’s embark on this journey of discovery to unravel the mysteries of DNA!
Table of Contents
What is DNA?
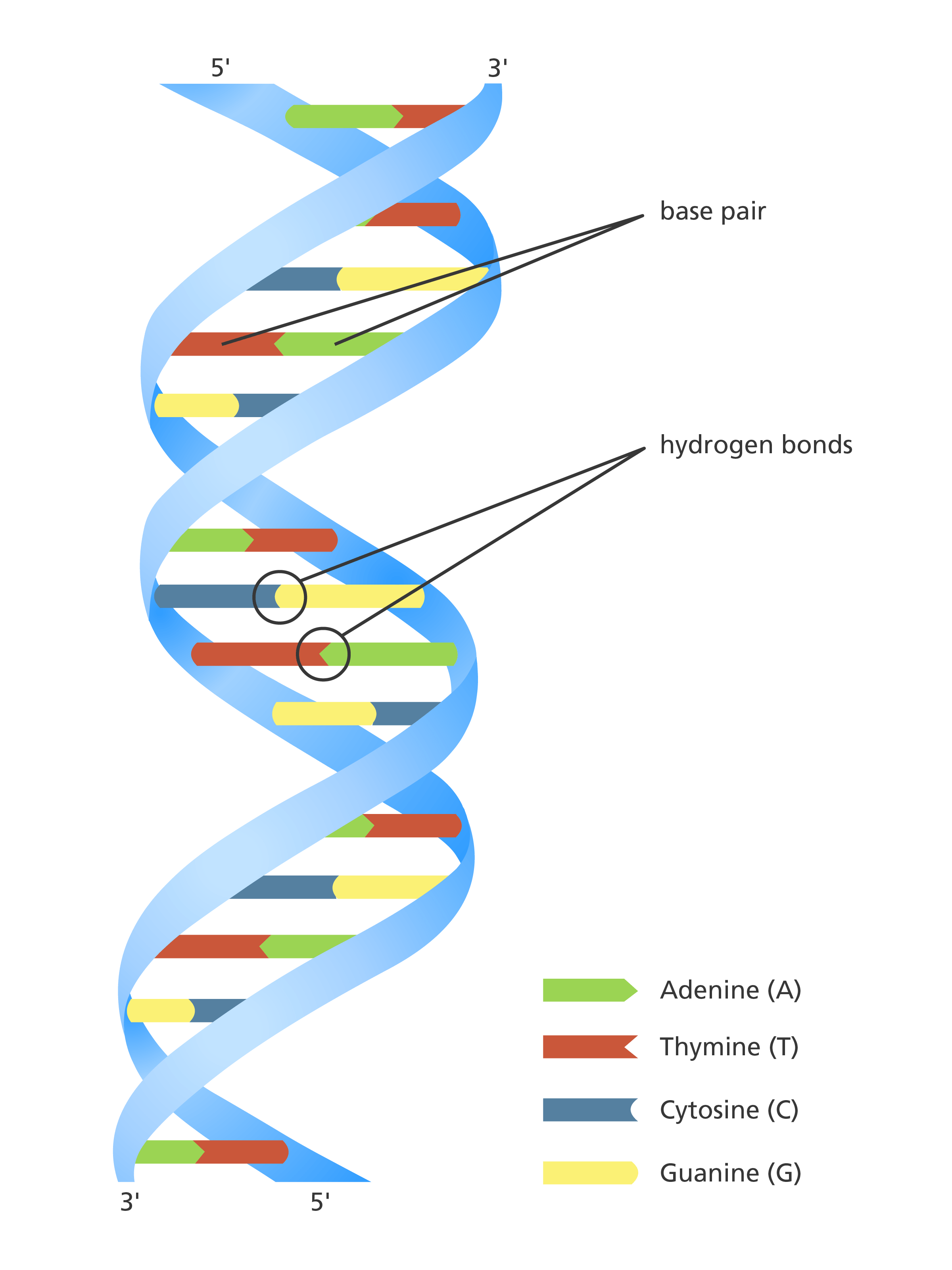
DNA, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that contains the instructions an organism needs to develop, live, and reproduce. DNA is structured as a double helix, resembling a twisted ladder, with each rung composed of pairs of nitrogenous bases. It is found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells, where it functions as the carrier of genetic information.
Structure of DNA
The structure of DNA is fundamental to its function. It consists of two long strands of nucleotides, which are the building blocks of DNA. Each nucleotide comprises three components: a phosphate group, a sugar molecule (deoxyribose), and a nitrogenous base. There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA:
- Adenine (A)
- Thymine (T)
- Cytosine (C)
- Guanine (G)
The bases pair specifically (A with T and C with G) through hydrogen bonds, forming the rungs of the double helix. This complementary base pairing is essential for the accurate replication of DNA during cell division.
Function of DNA
DNA carries the genetic information necessary for the synthesis of proteins, which are crucial for the structure and function of cells. The process of protein synthesis involves two main steps:
This flow of genetic information is often referred to as the central dogma of molecular biology. Furthermore, DNA is also involved in the regulation of gene expression, ensuring that genes are turned on or off as needed for the organism's development and response to environmental changes.
DNA and Heredity
DNA plays a critical role in heredity, the process by which traits are passed from parents to offspring. Each parent contributes half of their DNA to their children, resulting in a unique combination of genes. This genetic inheritance is responsible for the diversity of traits observed in populations.
Furthermore, the study of genetics has revealed how traits are inherited through dominant and recessive alleles, leading to various phenotypes. For example, if a child inherits a dominant allele for a trait, that trait will manifest, regardless of the other allele inherited from the other parent.
Genetic Variation and Its Importance
Genetic variation is essential for the evolution and adaptation of species. It arises from mutations, gene flow, and sexual reproduction. These variations provide a pool of traits that can be acted upon by natural selection, enabling populations to adapt to changing environments.
Some key points about genetic variation include:
- Mutations are random changes in the DNA sequence that can lead to new traits.
- Gene flow occurs when genes are transferred between populations, increasing genetic diversity.
- Sexual reproduction results in offspring with combinations of genes from both parents, contributing to variation.
Without genetic variation, populations would be more susceptible to diseases and environmental changes, potentially leading to extinction.
Modern Genetic Research and Its Implications
Advancements in genetic research have revolutionized our understanding of DNA and its applications. Techniques such as CRISPR-Cas9 allow scientists to edit genes with precision, opening up possibilities for treating genetic disorders, improving crops, and even combating diseases.
Some notable applications of modern genetic research include:
- Gene Therapy: A technique that modifies genes to cure genetic disorders.
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring medical treatment based on an individual's genetic makeup.
- Forensic Science: Using DNA profiling to solve crimes and identify individuals.
These advancements raise ethical questions about the manipulation of genetic material and the potential for unintended consequences.
Ethical Considerations in Genetic Research
The power of modern genetic research comes with significant ethical considerations. Issues such as genetic privacy, the potential for designer babies, and the implications of gene editing in humans demand careful consideration.
Some ethical questions include:
- Should parents be allowed to choose traits for their children through genetic engineering?
- How do we ensure the privacy of genetic information?
- What are the potential long-term impacts of gene editing on ecosystems?
As we navigate these complex issues, it is crucial to engage in discussions that balance scientific advancement with ethical responsibility.
Conclusion
In summary, DNA is a fundamental molecule that encodes the genetic information necessary for life. Its structure and function are intricately linked, enabling the processes of heredity, variation, and evolution. Modern genetic research continues to expand our understanding of DNA, offering exciting possibilities while also posing ethical challenges that must be addressed.
We encourage you to leave your thoughts in the comments below, share this article with others, and explore more about the fascinating world of genetics!
Thank you for joining us on this informative journey through the world of DNA, and we hope to see you back here for more engaging content!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8orrDZpunmV2ewG6vwKWjnpxencGuuA%3D%3D