The concept of the motor homunculus plays a crucial role in understanding how the human brain controls movement. This fascinating representation is not only a cornerstone of neuroscience but also provides insight into the intricate workings of our motor system. By exploring the motor homunculus, we can uncover the relationship between brain function and physical movement, as well as its implications for rehabilitation and motor learning.
In this article, we will delve deep into the motor homunculus, covering its definition, structure, and significance in both clinical and everyday contexts. We aim to provide you with a thorough understanding of this essential concept, supported by reputable sources and scientific data. Whether you are a student, a professional in the medical field, or simply curious about neuroscience, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need.
Let's embark on this journey to decode the motor homunculus and discover how it shapes our understanding of the brain's control over movement.
Table of Contents
What is Motor Homunculus?
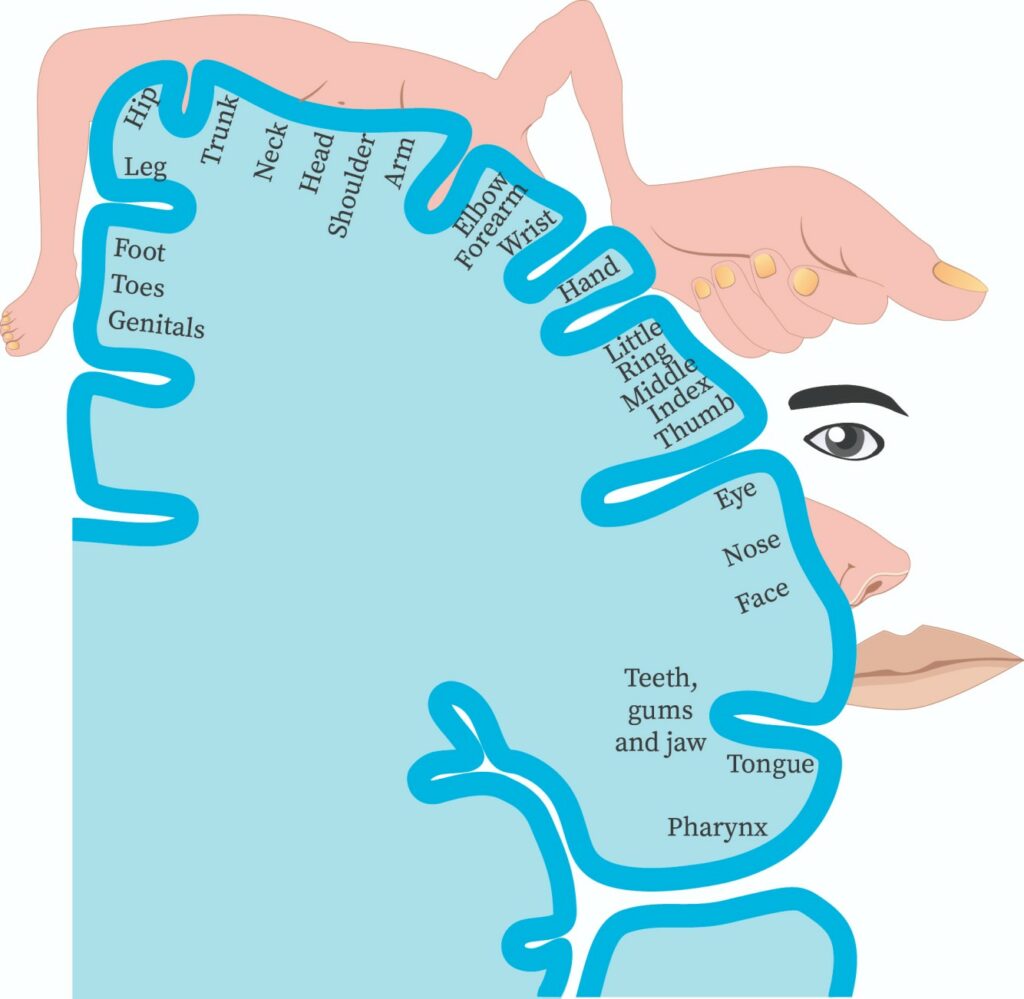
The motor homunculus is a visual representation of the body’s motor functions mapped onto the surface of the primary motor cortex in the brain. It illustrates how different regions of the brain correspond to specific body parts and their movements. This mapping is not proportional to the size of the body parts but rather reflects the complexity and precision of the motor control required for each area.
Key Features of the Motor Homunculus
- Proportional representation based on motor control, not size.
- Regions controlling fine motor skills (e.g., hands, lips) are larger.
- Provides insight into neurological disorders and recovery.
Anatomy and Structure of the Motor Homunculus
The motor homunculus is located in the precentral gyrus of the frontal lobe. It can be divided into two main areas: the upper and lower motor areas, each corresponding to different parts of the body.
Upper Motor Area
This area predominantly controls the movements of the lower body, including the legs and feet. The representation is oriented laterally on the motor cortex.
Lower Motor Area
Conversely, the lower motor area is responsible for the movements of the upper body, face, and hands, which are represented medially. This arrangement is often referred to as the "homunculus" due to its human-like shape.
Functions and Importance of the Motor Homunculus
The motor homunculus serves several critical functions in the realm of neuroscience and medicine, including:
- Understanding Movement: It helps scientists and medical professionals understand how specific brain areas are activated during different movements.
- Neurological Assessments: Assessment of motor function can identify areas of brain damage or dysfunction.
- Rehabilitation Planning: Tailoring rehabilitation strategies based on the affected motor areas.
Clinical Implications of the Motor Homunculus
The motor homunculus has significant clinical implications, particularly in neurology and rehabilitation. Understanding the mapping of motor functions can aid in diagnosing and treating neurological conditions such as strokes, cerebral palsy, and multiple sclerosis.
For instance, after a stroke, patients may experience paralysis or weakness in specific body parts. By understanding which areas of the motor cortex are affected, healthcare providers can create targeted rehabilitation programs to improve motor function.
Motor Homunculus in Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation programs often employ techniques that stimulate the brain's plasticity, the ability of the brain to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections. The motor homunculus is a guiding principle in designing these programs.
Techniques Used in Rehabilitation
- Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy (CIMT): Encourages use of the affected limb by constraining the unaffected one.
- Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES): Uses electrical currents to stimulate muscle contractions.
- Mirror Therapy: Utilizes visual feedback to enhance motor function.
Motor Learning and the Homunculus
The motor homunculus is also fundamental in understanding motor learning, which involves acquiring and refining motor skills through practice. Research indicates that as individuals practice a movement, the corresponding area in the motor cortex becomes more active and organized.
Factors Influencing Motor Learning
- Practice: Repeated practice enhances neural pathways.
- Feedback: Immediate feedback helps in correcting movements and refining skills.
- Intention: The intention behind the movement can influence how it is learned and executed.
Controversies and Future Research
While the motor homunculus model has been instrumental in neuroscience, there are ongoing debates regarding its accuracy and implications. Some researchers argue that the representation is not fixed and can change based on experience and learning.
Future research is expected to delve deeper into the dynamic nature of the motor homunculus, exploring how different factors such as age, skill level, and rehabilitation techniques can alter motor representation in the brain.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the motor homunculus is a vital concept that enhances our understanding of how the brain controls movement. Its significance extends beyond neuroscience to clinical applications, particularly in rehabilitation and motor learning. By grasping the principles of the motor homunculus, we can better appreciate the intricacies of the human motor system and its potential for recovery and improvement.
We encourage you to share your thoughts in the comments below, and if you found this article informative, feel free to share it with others who might benefit from this knowledge. For more insights on neuroscience and related topics, browse through our other articles.
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to seeing you again soon!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8pbXAoKmapZ2asW6t0maYZqWfqbyzeceopK6mk6q5tr%2BNoaumpA%3D%3D