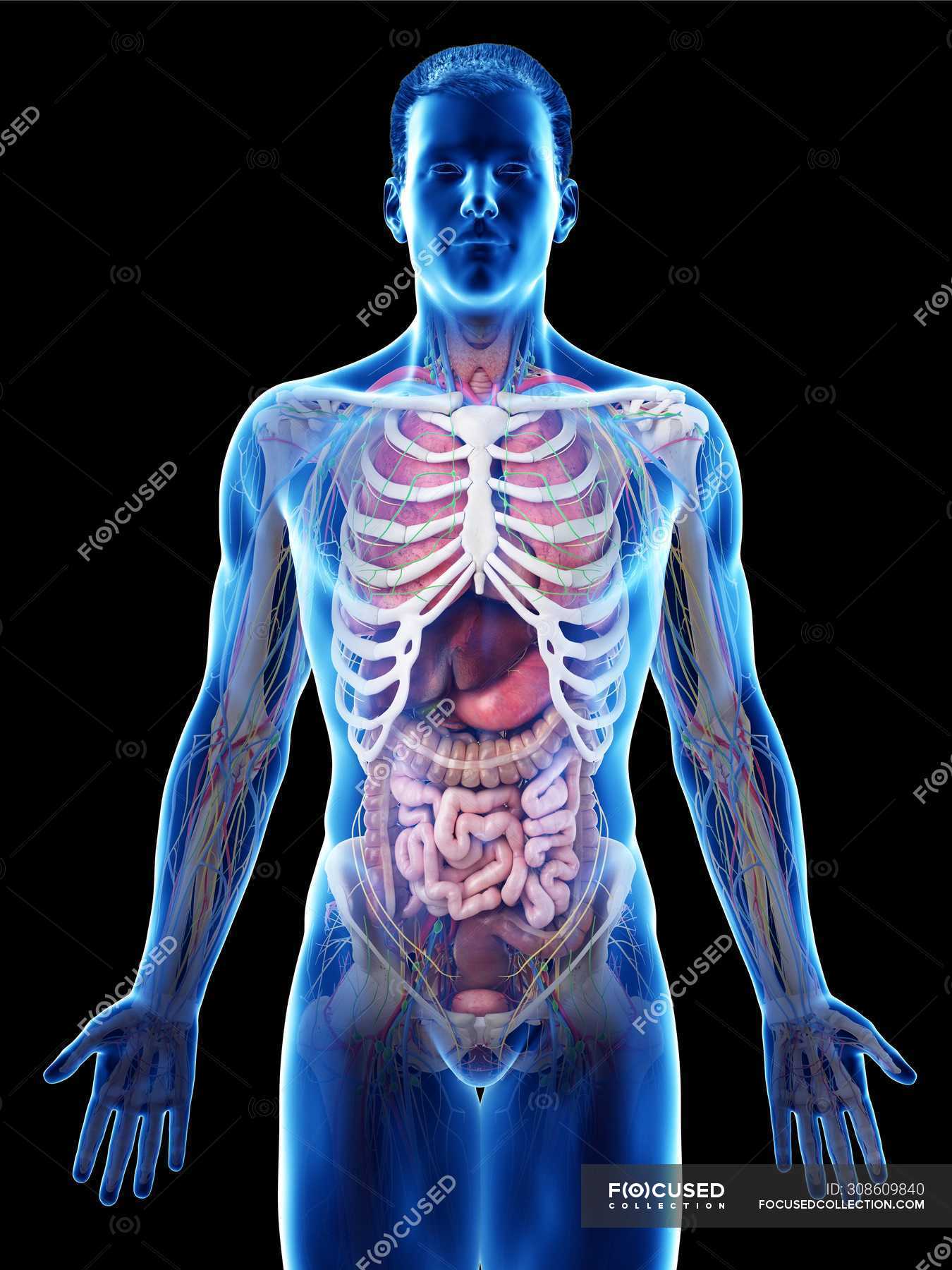
When we talk about a person's body, we are delving into an intricate system that defines not only our physical capabilities but also our overall health and well-being. The human body is a marvel of biological engineering, comprising numerous systems that work in harmony to sustain life. Understanding the complexities of our body can empower us to make informed health decisions, leading to a better quality of life.
The body serves as a vessel for our experiences, emotions, and interactions. As we explore the various components of a person's body, we will uncover the significance of anatomy, the importance of maintaining health, and how our bodies reflect our lifestyle choices. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the human body's structure, functions, and the factors influencing its well-being.
In this article, we will break down the essential elements of the human body into several sections, including its anatomy, health implications, and tips for maintaining optimal health. We will also discuss the impact of lifestyle choices and external factors on our physical well-being. So, let's embark on this enlightening journey to understand the importance of a person's body.
Table of Contents
1. Anatomy of the Human Body
The human body is composed of various systems that work together to maintain life. Understanding these systems is crucial for recognizing how our bodies function and respond to different stimuli.
Major Body Systems
- Muscular System: Responsible for movement and stability.
- Skeletal System: Provides structure and protection for vital organs.
- Nervous System: Controls and coordinates body activities.
- Circulatory System: Transports nutrients and oxygen through the blood.
- Respiratory System: Facilitates breathing and gas exchange.
- Digestive System: Breaks down food and absorbs nutrients.
2. Muscular System
The muscular system consists of over 600 muscles that allow for movement and function. Muscles are categorized into three types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac.
Functions of the Muscular System
- Facilitating movement of the body.
- Maintaining posture and body position.
- Generating heat to maintain body temperature.
3. Skeletal System
The skeletal system is made up of 206 bones in the adult human body. It provides structure, support, and protection for vital organs.
Components of the Skeletal System
- Long Bones: Found in arms and legs, provide strength and support.
- Short Bones: Provide stability and support with little movement.
- Flat Bones: Protect vital organs (e.g., skull, ribs).
4. Nervous System
The nervous system controls body functions by transmitting signals between different body parts. It is essential for communication within the body.
Parts of the Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS): Comprises the brain and spinal cord.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Connects the CNS to limbs and organs.
5. Circulatory System
The circulatory system plays a vital role in transporting blood, nutrients, and oxygen throughout the body.
Key Components of the Circulatory System
- Heart: Pumps blood throughout the body.
- Blood Vessels: Arteries, veins, and capillaries that carry blood.
- Blood: Carries oxygen, nutrients, and waste products.
6. Respiratory System
The respiratory system is essential for gas exchange, allowing oxygen to enter the body and carbon dioxide to be expelled.
Major Organs of the Respiratory System
- Nose: Filters, warms, and moistens air.
- Lungs: Main organs for gas exchange.
- Diaphragm: Muscle that aids in breathing.
7. Digestive System
The digestive system breaks down food and absorbs nutrients necessary for energy and growth.
Process of Digestion
- Ingestion: Taking in food through the mouth.
- Digestion: Breaking down food into smaller components.
- Absorption: Nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream.
- Excretion: Waste is eliminated from the body.
8. Maintaining Health and Well-being
Maintaining a healthy body involves regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient rest. Here are some tips for optimal health:
Tips for a Healthy Lifestyle
- Engage in regular physical activity (at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week).
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Get sufficient sleep (7-9 hours per night).
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques or hobbies.
Conclusion
Understanding the importance of a person's body is essential for making informed health decisions. From the anatomy of various systems to the significance of maintaining health, every aspect plays a vital role in our overall well-being. By incorporating healthy habits into our daily lives, we can enhance our physical capabilities and improve our quality of life. We encourage readers to share their thoughts, experiences, or questions in the comments section below, and to explore more articles on our site for further insights into health and wellness.
Final Thoughts
We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the complexities of a person's body. Remember that taking care of your body is a lifelong journey. We invite you to return for more informative content on health and well-being in the future.
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8sLKMmmSpnaKovK%2B%2FjJumnbFencGuuA%3D%3D