Rounding numbers is a fundamental mathematical skill that simplifies calculations and helps us communicate quantities more effectively. In this article, we will explore the concept of rounding to the nearest tenth, using 3.14 for pi as our reference point. We will specifically look at measurements of 2.6 ft, 7.0 ft, 10.5 ft, and 31.4 ft, demonstrating how to apply rounding in practical scenarios.
By understanding how to round numbers accurately, you can enhance your mathematical skills and make more informed decisions in daily life, whether you're dealing with finances, construction, or measurements in various fields. Rounding is especially important in fields that require precision, such as engineering, architecture, and science. Let's dive deeper into the principles of rounding to the nearest tenth.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of rounding to the nearest tenth, including practical examples and applications. We will break down the process step-by-step, ensuring that you have a clear grasp of how to round numbers effectively. Let's get started!
Table of Contents
What is Rounding?
Rounding is the process of adjusting the digits in a number to make it simpler and easier to work with while keeping its value close to the original number. When rounding to the nearest tenth, we focus on the digit in the tenths place and consider the digit immediately to its right (the hundredths place) to determine whether to round up or down.
Understanding Tenths and Hundredths
In a decimal number, the tenths place is the first digit to the right of the decimal point, while the hundredths place is the second digit. For example, in the number 2.6, the digit 6 is in the tenths place, and there is no digit in the hundredths place, which can be considered as 0.
Importance of Rounding
Rounding is essential for various reasons:
- Simplification: Rounding makes complex numbers easier to understand and work with.
- Estimation: It allows for quick estimations in calculations without needing precise figures.
- Communication: Rounding helps convey information clearly, especially in reports and presentations.
- Precision: In fields like science and engineering, rounding can help represent measurements accurately without unnecessary detail.
How to Round to the Nearest Tenth
To round a number to the nearest tenth, follow these steps:
Examples of Rounding
Let's apply these rules to the given measurements:
Example 1: Rounding 2.6 ft
The tenths place is 6 and there is no digit in the hundredths place (considered as 0). Since 0 is less than 5, we keep the tenths digit as it is. Therefore, 2.6 ft rounded to the nearest tenth is:
2.6 ft
Example 2: Rounding 7.0 ft
The tenths place is 0, and there is no digit in the hundredths place. Since there is nothing to round up, 7.0 ft remains:
7.0 ft
Example 3: Rounding 10.5 ft
The tenths place is 5, and since the hundredths place is not specified, we consider it as 0. Here, we round up the tenths place by 1. Therefore, 10.5 ft rounded to the nearest tenth becomes:
10.5 ft
Example 4: Rounding 31.4 ft
The tenths place is 4, and the hundredths place is 0. Since 0 is less than 5, we keep the tenths digit the same. Thus, 31.4 ft rounded to the nearest tenth is:
31.4 ft
Using Pi in Rounding
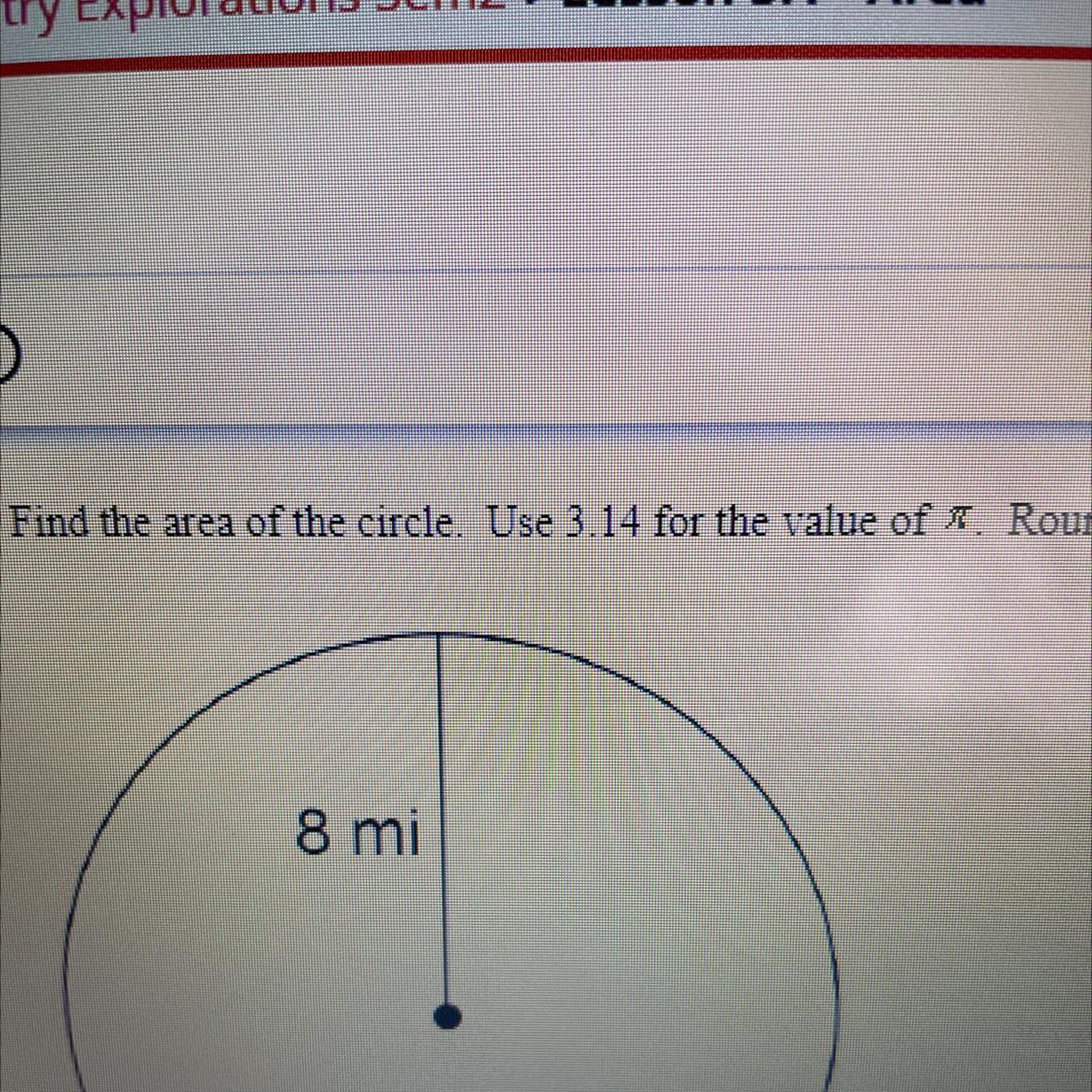
Pi (π) is approximately 3.14, and it often appears in calculations involving circles. When rounding calculations that involve pi, it's crucial to consider how rounding affects the outcome. For example, if you need to calculate the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 2.6 ft using the formula C = πd, you would use 3.14 for pi.
Calculating the circumference:
C = 3.14 × 2.6 ft = 8.164 ft
Now, rounding 8.164 to the nearest tenth, we check the hundredths place (6), which is greater than 5, so we round up:
C = 8.2 ft
Practical Applications of Rounding
Rounding is used in various fields, including:
- Finance: Rounding amounts to the nearest cent for easier transactions.
- Construction: Rounding measurements for cutting materials.
- Statistics: Rounding data points for clearer analysis.
- Cooking: Rounding ingredient measurements for simplicity.
Common Mistakes in Rounding
Some common mistakes to avoid when rounding include:
- Failing to identify the correct place value.
- Rounding down when the hundredths digit is 5 or greater.
- Overlooking decimals entirely in measurements.
- Inconsistently applying rounding rules across different calculations.
Conclusion
In summary, rounding to the nearest tenth is a valuable skill that enhances our ability to handle numbers in various situations. By understanding how to round effectively, you can simplify calculations, communicate more clearly, and avoid common mistakes.
We encourage you to practice rounding numbers in your daily life, especially when working with measurements or financial figures. Feel free to leave a comment below with your thoughts or questions, and don't forget to share this article with others who may benefit from it!
Thank you for reading! We hope you found this article helpful and informative. Be sure to check back for more insightful content.
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8orrSsJyrZaSkerW0xGalnpmimsC1edOepa2gXarApnmSamtmnp%2BnerG1jGttZp6kYoRxecWtZGpoZWKztXmSamtmnqRjtbW5yw%3D%3D