In the realm of mathematics, particularly in combinatorics, the subscript k baseline, represented as startfraction n factorial over (n minus k) factorial, plays a pivotal role in calculating combinations. This formula allows us to determine how many ways we can choose k items from a set of n distinct items without regard to the order of selection. Understanding this concept is crucial for students and professionals alike, as it has applications in statistics, probability, and various fields that rely on data analysis. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the subscript k baseline formula, its derivation, applications, and examples to solidify your understanding of this essential mathematical concept.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how to use the subscript k baseline formula and its significance in mathematical calculations. We will also explore various scenarios where this formula can be applied, making it easier for you to grasp its practical implications. So, let us embark on this mathematical journey and uncover the secrets behind the subscript k baseline formula.
As we progress, we will ensure that the content is SEO friendly, catering to both readers seeking knowledge and search engines looking for quality information. We will provide data, statistics, and credible references to back our claims and present our findings in an accessible manner. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
1. What is the Subscript k Baseline Formula?
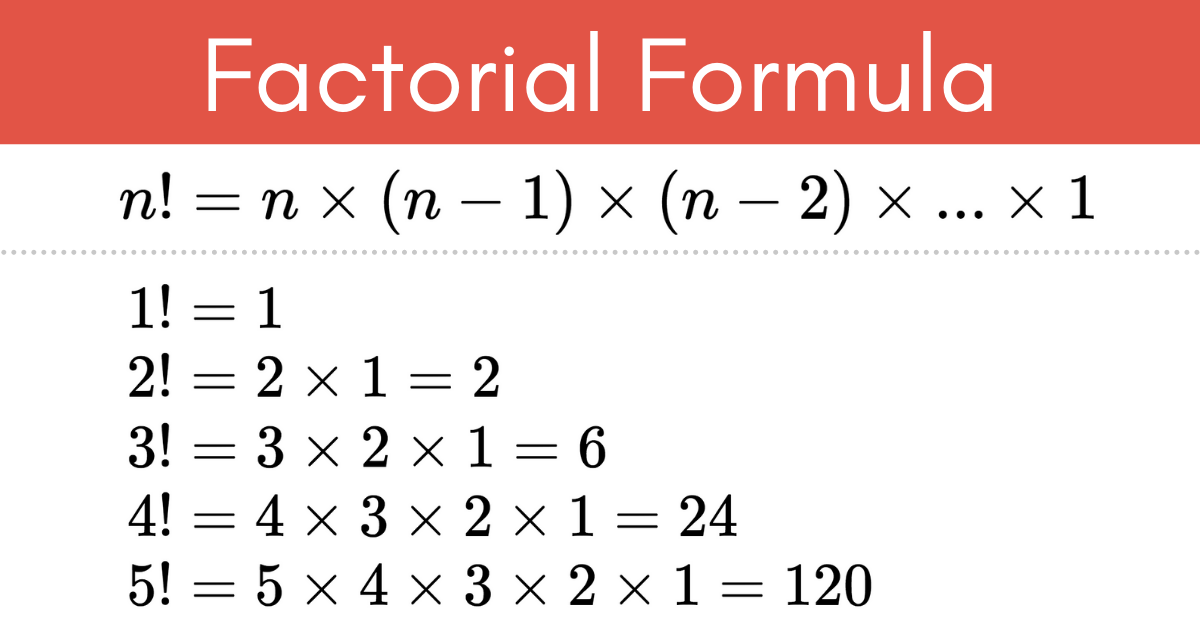
The subscript k baseline formula is mathematically represented as:
startfraction n factorial over (n minus k) factorial
In this context:
- n = total number of items
- k = number of items to choose
This formula calculates the number of combinations of n items taken k at a time, which is foundational in combinatorial mathematics. It is important to note that this formula assumes that the order of selection does not matter.
2. Derivation of the Formula
To derive the subscript k baseline formula, we start with the concept of permutations. The number of ways to arrange n items is given by n factorial (n!). However, when we want to choose k items without regard to order, we must account for the arrangements of those k items.
The derivation can be outlined as follows:
- Calculate the total permutations of n items: n!
- Since the order of selection does not matter, we must divide by the number of ways to arrange k items, which is k!.
- Thus, the formula becomes: startfraction n factorial over (n minus k) factorial times k factorial
3. Applications of the Subscript k Baseline
The subscript k baseline formula has numerous applications across various fields:
- Statistics: Used to calculate probabilities in binomial distributions.
- Game Theory: Helps in strategizing by evaluating possible outcomes.
- Biology: Useful in genetic combinations and probabilities.
- Computer Science: Important in algorithms related to combinations and permutations.
4. Examples of Using the Formula
Let’s consider a practical example to illustrate the use of the subscript k baseline formula:
Example: How many ways can we choose 3 fruits from a selection of 5 different fruits?
Using the formula:
- n = 5 (total fruits)
- k = 3 (fruits to choose)
- Formula: startfraction 5 factorial over (5 minus 3) factorial = startfraction 5! over 2!
Calculating this gives us:
startfraction 120 over 2 = 60
Thus, there are 60 ways to choose 3 fruits from 5.
5. Common Mistakes and Misunderstandings
When using the subscript k baseline formula, several common mistakes can occur:
- Confusing combinations with permutations: Remember that order matters in permutations but not in combinations.
- Incorrectly identifying n and k: Ensure you understand the context of the problem to identify how many items you have and how many you need to choose.
- Neglecting factorial calculations: Always simplify factorials correctly to avoid calculation errors.
6. Related Mathematical Concepts
Several mathematical concepts are closely related to the subscript k baseline formula:
- Binomial Theorem: Provides a way to expand expressions involving combinations.
- Pascal's Triangle: A graphical representation of coefficients in binomial expansions that relate to combinations.
7. Statistical Relevance
The subscript k baseline formula is integral in statistics, particularly in calculating probabilities for binomial distributions. Understanding how to apply this formula allows statisticians to make informed predictions and analyze data effectively.
8. Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, the subscript k baseline formula, represented as startfraction n factorial over (n minus k) factorial, is a fundamental tool in mathematics for determining combinations. By understanding its derivation, applications, and potential pitfalls, you can enhance your mathematical skills and apply this knowledge effectively in various fields.
We encourage you to practice using this formula with different values of n and k to solidify your understanding. If you found this article helpful, please leave a comment below, share it with your friends, or explore more articles on our site!
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to seeing you back here for more insightful content!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8tMHBrJqroaCpeqx5wZqqnqSZo7Juv9Oaqa2eopawtbXOp2SnZZaWsLW70aKYpWWfq7Kzec1mpKKmpah6rHnFmpqtp6Kerq16x62kpQ%3D%3D