Sternberg's Theory of Intelligence offers a comprehensive framework that redefines how we perceive intelligence beyond traditional metrics. This theory emphasizes the multifaceted nature of intelligence, particularly highlighting the crucial ability to analyze problems effectively. In a world increasingly driven by complex challenges and diverse problem-solving scenarios, understanding this aspect of intelligence is not just beneficial; it is essential.
In this article, we will delve deep into the intricacies of Sternberg's Theory of Intelligence, exploring its core components and the significant role of analytical abilities in problem-solving. We will also discuss the implications of this theory in educational settings, workplaces, and everyday life, providing insights into how we can apply these principles to enhance our cognitive capabilities.
Whether you are an educator, a student, or simply someone interested in the dynamics of intelligence, this exploration will equip you with valuable knowledge. Let’s embark on this journey to understand the critical aspects of intelligence as proposed by Robert Sternberg.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Sternberg's Theory
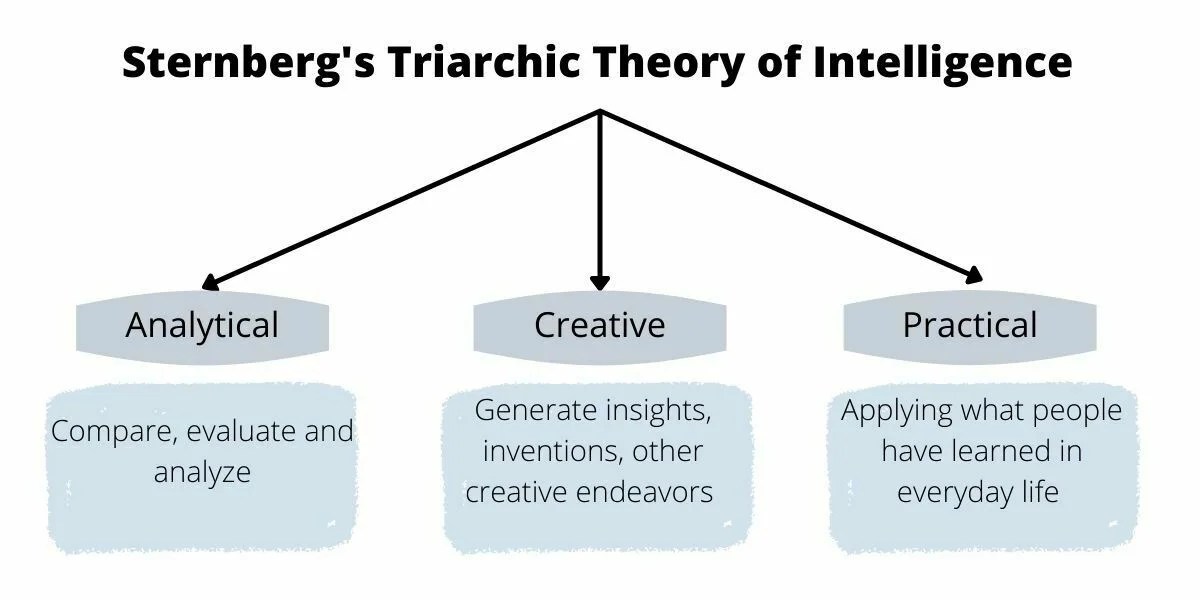
Robert Sternberg, a prominent psychologist, introduced his triarchic theory of intelligence in the 1980s. This theory breaks down intelligence into three primary components: analytical, creative, and practical intelligence. Each of these components plays a vital role in how individuals approach and solve problems.
Sternberg's approach challenges the conventional view of intelligence, which often relies heavily on standardized testing and IQ scores. Instead, he posits that intelligence is a broader construct, encompassing various skills and abilities that individuals utilize in different contexts.
Understanding this theory allows us to appreciate the diversity of cognitive processes and how they contribute to effective problem-solving. In the following sections, we will explore each component of Sternberg's theory in greater detail.
2. Components of Sternberg's Theory
Sternberg identifies three main components of intelligence, which are essential for analyzing problems:
- Analytical Intelligence: The ability to analyze, evaluate, and compare information.
- Creative Intelligence: The capacity to innovate and generate new ideas or approaches.
- Practical Intelligence: The skill to implement solutions in real-world scenarios effectively.
2.1 Analytical Intelligence
Analytical intelligence is perhaps the most recognized aspect of Sternberg's theory. It involves critical thinking, logical reasoning, and the ability to dissect complex problems into manageable parts. This form of intelligence is often assessed through traditional tests and academic performance.
2.2 Creative Intelligence
Creative intelligence goes beyond conventional reasoning. It involves thinking divergently and generating innovative solutions. Individuals with high creative intelligence can approach problems from unique angles, leading to breakthroughs that analytical thinkers might overlook.
2.3 Practical Intelligence
Practical intelligence is about applying knowledge to real-world situations. This component emphasizes the importance of context and experience in problem-solving, showcasing how individuals navigate everyday challenges effectively.
3. The Role of Analytical Intelligence
Analytical intelligence is crucial in various domains, particularly in academic and professional settings. It encompasses several key skills:
- Problem identification
- Data analysis
- Logical reasoning
- Critical thinking
Individuals with strong analytical intelligence can break down complex issues, evaluate evidence, and draw logical conclusions. This ability is particularly valued in fields such as science, mathematics, and engineering, where precise analysis is essential for success.
4. Practical Intelligence: Real-World Applications
Practical intelligence plays a significant role in everyday life. It allows individuals to apply their knowledge and skills in practical situations. Examples include:
- Managing personal finances
- Navigating social interactions
- Problem-solving in the workplace
People with high practical intelligence are adept at recognizing opportunities and challenges in their environments, enabling them to make informed decisions that lead to successful outcomes.
5. Creative Intelligence: Thinking Outside the Box
Creative intelligence is not just about artistic ability; it encompasses innovative thinking across various domains. This component is vital for:
- Generating novel ideas
- Finding unique solutions to problems
- Adapting to new situations effectively
Individuals with high creative intelligence can approach problems from unconventional angles, leading to unique solutions that may not be apparent through analytical methods alone.
6. Educational Implications of Sternberg's Theory
Sternberg's theory has profound implications for education. Traditional educational systems often emphasize analytical intelligence, neglecting creative and practical aspects. By incorporating all three components into teaching methodologies, educators can foster a more holistic approach to learning.
Strategies include:
- Encouraging problem-solving projects that require creative thinking
- Incorporating real-world scenarios in lessons to enhance practical intelligence
- Using diverse assessment methods to evaluate all aspects of intelligence
7. Applications in the Workplace
In the workplace, understanding and applying Sternberg's theory can lead to improved team dynamics and productivity. Employers can benefit from recognizing the diverse intelligences within their teams:
- Assigning roles based on individual strengths
- Encouraging collaboration between analytical and creative thinkers
- Fostering an environment that values innovative solutions
By leveraging the strengths of each intelligence component, organizations can enhance problem-solving capabilities and drive success.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, Sternberg's Theory of Intelligence provides valuable insights into the multifaceted nature of human intelligence. The ability to analyze problems is just one aspect of a broader cognitive framework that includes creative and practical intelligence. By understanding and appreciating these components, we can enhance our problem-solving skills and apply them effectively in various aspects of life.
We encourage you to reflect on your own strengths and consider how you can cultivate each type of intelligence in your personal and professional endeavors. Share your thoughts in the comments below, and feel free to explore more articles on this topic.
Thank you for reading! We hope to see you back here for more insightful discussions on intelligence and cognitive processes.
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8qrqMrKueqp6XsrOz0maroZ2fp8Zuu8VmoKeslaG5qrPEp5qeZaSdsm6twaKjoqypYsGwecCnmKWxqpp6sb7Om6OepaNirq%2BwjaGrpqQ%3D