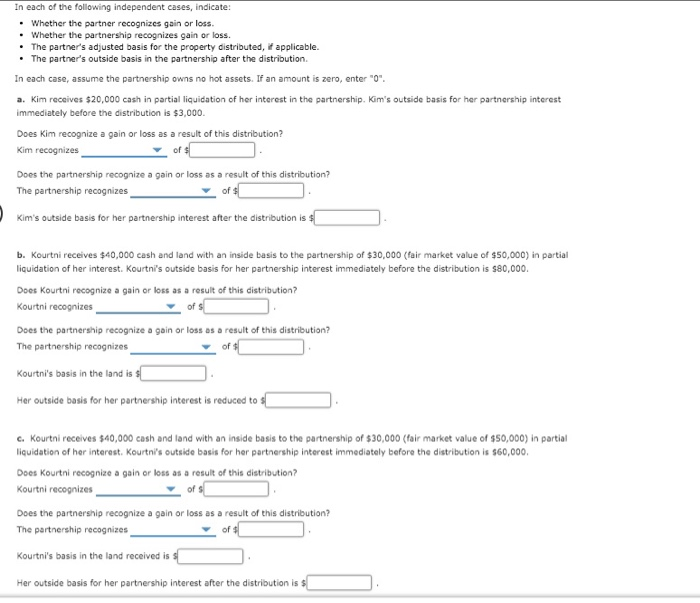
In the realm of partnership taxation, understanding the concept of outside basis is crucial, especially when it involves the distribution of land or property. The outside basis reflects a partner's investment in a partnership and is vital for evaluating tax implications upon distribution. This article aims to delve deep into the complexities of land and her outside basis in the partnership following a distribution, providing clarity and insight for partners navigating these waters.
The partnership structure often presents unique challenges and opportunities for its partners, particularly when it comes to contributions and distributions. The tax implications can significantly affect a partner's financial position, making it essential to grasp how these factors interrelate. In this article, we will explore the definitions, calculations, and impacts of outside basis on the distribution of land within a partnership. Additionally, we will discuss relevant case studies and examples to illustrate these concepts effectively.
By the end of this comprehensive guide, you will have a clear understanding of how outside basis functions in partnership distributions, particularly concerning land. Whether you are a seasoned partner or a newcomer to partnership taxation, this article will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate these complexities confidently.
Table of Contents
1. Definition of Outside Basis
Outside basis refers to the adjusted basis of a partner's interest in a partnership. This basis represents the amount that a partner has invested in the partnership, including cash contributions, property contributions, and any share of partnership liabilities. Understanding the outside basis is essential for determining the tax consequences of distributions and allocations within a partnership.
1.1 Components of Outside Basis
The outside basis comprises several components, including:
- Initial cash contributions
- Fair market value of property contributed
- Partner's share of partnership liabilities
- Adjustments for income, losses, and distributions
2. Importance of Outside Basis in Partnerships
The outside basis is significant for several reasons, including:
- Determining the taxability of distributions – A partner's outside basis is critical in assessing whether a distribution is taxable or non-taxable.
- Calculating gain or loss on the sale of partnership interest – The outside basis helps in determining the gain or loss when a partner sells their interest in the partnership.
- Assessing partnership liabilities – Understanding how liabilities affect outside basis can influence a partner's overall tax position.
3. Understanding Land Distribution in Partnerships
When land is distributed to a partner, it carries specific tax implications that must be understood. The distribution of land can significantly impact the outside basis and overall tax liability of the partner receiving the land.
3.1 Types of Land Distribution
There are generally two types of land distributions in partnerships:
- Liquidating Distributions: This occurs when a partner withdraws from the partnership, and their interest is liquidated, often involving the distribution of assets such as land.
- Non-Liquidating Distributions: This involves the distribution of land while the partner remains active in the partnership.
4. Calculating Outside Basis After Distribution
Calculating the outside basis after a distribution requires a systematic approach. Several factors influence this calculation, including the type of distribution and the partner's original basis.
4.1 Step-by-Step Calculation
The calculation typically follows these steps:
5. Case Studies on Land and Outside Basis
Examining real-life scenarios can provide insight into how outside basis functions in partnerships, particularly regarding land distribution.
5.1 Case Study 1: Liquidating Distribution of Land
In this case, Partner A decides to withdraw from the partnership and receives land valued at $100,000. Partner A's initial outside basis was $150,000, and there were no liabilities associated with the land. The calculation would be as follows:
- Initial Outside Basis: $150,000
- Less: Fair Market Value of Land Distributed: $100,000
- New Outside Basis: $50,000
5.2 Case Study 2: Non-Liquidating Distribution of Land
Partner B receives land valued at $80,000 while remaining active in the partnership. Partner B's initial outside basis was $120,000. The calculation is as follows:
- Initial Outside Basis: $120,000
- Less: Fair Market Value of Land Distributed: $80,000
- New Outside Basis: $40,000
6. Tax Implications of Outside Basis
The tax implications of outside basis can be significant, especially regarding distributions. Understanding how the outside basis interacts with distributions can help partners minimize tax liabilities.
6.1 Non-Taxable Distributions
In many cases, distributions can be non-taxable up to the amount of the partner's outside basis. This means that if a partner's outside basis is higher than the value of the distribution, they may not incur any immediate tax liability.
6.2 Taxable Distributions
However, if the distribution exceeds the outside basis, it may trigger taxable gain, leading to potential tax liabilities for the partner receiving the distribution.
7. Common Misconceptions About Outside Basis
There are several misconceptions surrounding outside basis that can lead to confusion among partners:
- Misconception 1: All distributions are automatically taxable.
- Misconception 2: Outside basis is the same as inside basis.
- Misconception 3: Partners cannot adjust their outside basis after distributions.
8. Conclusion and Call to Action
Understanding land and her outside basis in the partnership after distribution is essential for effective partnership management and tax planning. By recognizing the importance of outside basis, partners can make informed decisions that impact their financial positions positively. We encourage readers to take the next step by commenting below with questions or sharing this article with others who may benefit from this information. Additionally, explore other articles on our site for more insights into partnership taxation.
In conclusion, knowledge is power when it comes to navigating the complexities of partnership taxation. Staying informed about outside basis will help partners avoid pitfalls and maximize benefits in their partnerships.
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8ra3NnWSappRitaa%2BjKisrauZmbJursCsoKxlmaN6tbTEZqeaqqSjsrO%2Fx6KnZpmWqbKzedOhnGacmajBs7XBrquip55jtbW5yw%3D%3D