Parkinson's disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects movement control. It is characterized by tremors, stiffness, and difficulty with balance and coordination. As the disease progresses, it poses significant challenges not only to patients but also to healthcare providers, especially nurses. Understanding how nurses can effectively care for patients with Parkinson's disease is crucial for improving patient outcomes and enhancing their quality of life.
The role of nurses in managing Parkinson's disease extends beyond administering medications; it involves comprehensive care strategies that include patient education, emotional support, and coordination with other healthcare professionals. This article will delve into the actions that nurses can take to demonstrate effective and compassionate care for patients with Parkinson's disease, along with the importance of their role in the multidisciplinary healthcare team.
Moreover, as we explore this topic, we will emphasize the importance of expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness in nursing practice. By the end of this article, healthcare professionals and caregivers will gain valuable insights into best practices for managing Parkinson's disease, ensuring that they can provide the highest level of care for their patients.
Table of Contents
What is Parkinson's Disease?
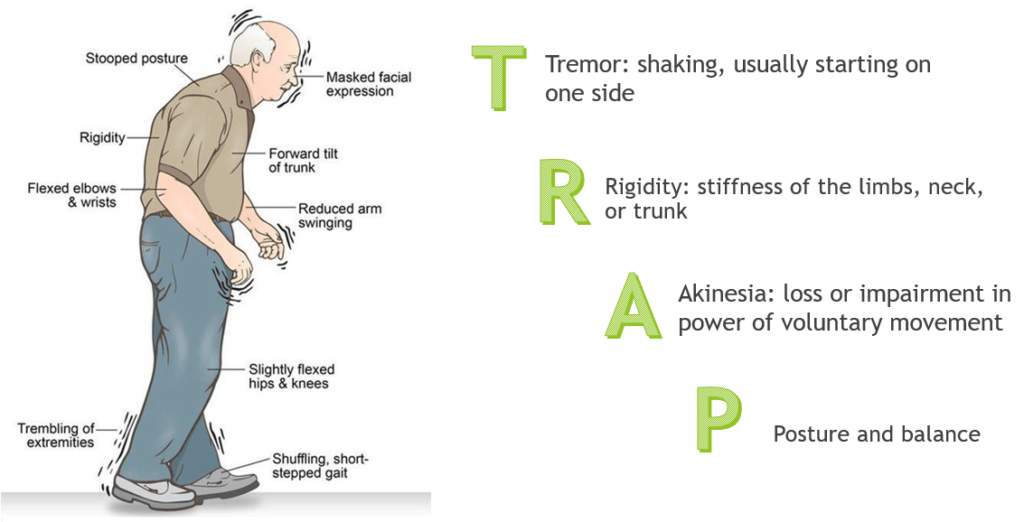
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects movement. It occurs when nerve cells in the brain, particularly those that produce dopamine, begin to die. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in coordinating smooth and controlled movements. As dopamine levels decrease, individuals may experience symptoms such as:
- Tremors or shaking, particularly at rest
- Muscle rigidity and stiffness
- Bradykinesia (slowness of movement)
- Postural instability and balance issues
While the exact cause of Parkinson's disease remains unclear, several risk factors have been identified, including age, genetic predisposition, and environmental factors. The disease typically affects individuals over the age of 60, but younger-onset Parkinson's can occur as well.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Diagnosing Parkinson's disease involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's medical history, symptoms, and a neurological examination. There is currently no definitive test for Parkinson's, making clinical judgment vital. Common symptoms include:
- Tremors in the hands, arms, legs, or face
- Changes in speech or writing
- Difficulty initiating movements
- Fatigue and sleep disturbances
Healthcare providers may utilize imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans, to rule out other conditions. Early diagnosis is essential for implementing timely interventions and treatments, which can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
The Nursing Role in Parkinson's Care
Nurses play a critical role in the care of patients with Parkinson's disease. Their responsibilities encompass various aspects, including:
- Monitoring patient progress and symptoms
- Administering medications as prescribed
- Providing education on disease management and lifestyle modifications
- Facilitating communication between patients and other healthcare professionals
By understanding the complexities of Parkinson's disease, nurses can advocate for their patients, ensuring they receive appropriate care and support throughout their journey.
Patient Education and Support
Educating patients and their families about Parkinson's disease is an essential component of nursing care. Effective patient education can empower individuals to take an active role in managing their condition. Key topics for education include:
- Understanding the disease process and expected progression
- Medication management and adherence
- Exercise and physical therapy options
- Nutritional considerations and dietary adjustments
Nurses can also provide emotional support, helping patients cope with the psychological impact of a chronic illness. Support groups and counseling services can be beneficial for both patients and caregivers.
Interdisciplinary Team Approach
An interdisciplinary approach to Parkinson's care is vital for addressing the multifaceted needs of patients. Nurses collaborate with various healthcare professionals, including:
- Neurologists and movement disorder specialists
- Physical and occupational therapists
- Dietitians and nutritionists
- Psychologists or psychiatrists for mental health support
This collaborative effort ensures that patients receive holistic care that addresses their physical, emotional, and social needs.
Effective Nursing Interventions
Specific nursing interventions tailored to the needs of patients with Parkinson's disease can significantly enhance their quality of life. Some effective interventions include:
- Encouraging regular physical activity to improve mobility and balance
- Assisting with daily activities to maintain independence
- Implementing fall prevention strategies in the home environment
- Monitoring medication side effects and interactions
These interventions not only help manage symptoms but also promote overall well-being and independence for patients.
Emotional Support and Coping Strategies
Living with Parkinson's disease can lead to feelings of anxiety, depression, and frustration. Nurses can play a crucial role in providing emotional support and helping patients develop coping strategies. Recommended approaches include:
- Encouraging open communication about feelings and concerns
- Promoting mindfulness and relaxation techniques
- Connecting patients with support groups and community resources
- Offering counseling or therapy referrals when necessary
By addressing the emotional aspects of the disease, nurses can help patients maintain a positive outlook and improve their overall quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Parkinson's disease presents numerous challenges, both for patients and healthcare providers. Nurses play a vital role in managing the complexities of this condition through education, support, and effective interventions. By utilizing an interdisciplinary approach and focusing on the holistic needs of patients, nurses can significantly impact their quality of life. If you have experiences or insights related to Parkinson's disease, feel free to leave a comment below or share this article with others who may benefit from it.
Thank you for reading! We invite you to explore more articles on our site for additional information and resources regarding Parkinson's disease and other health-related topics.
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8sa3RpKCnq5%2BjwG6wyKycmquVYsSptcKhZJqbpJ68r3nBsmStoJViu7a%2B0p5knZ2dpLu0wNGaq56rXam1pnnCqKmrnZOpe6nAzKU%3D