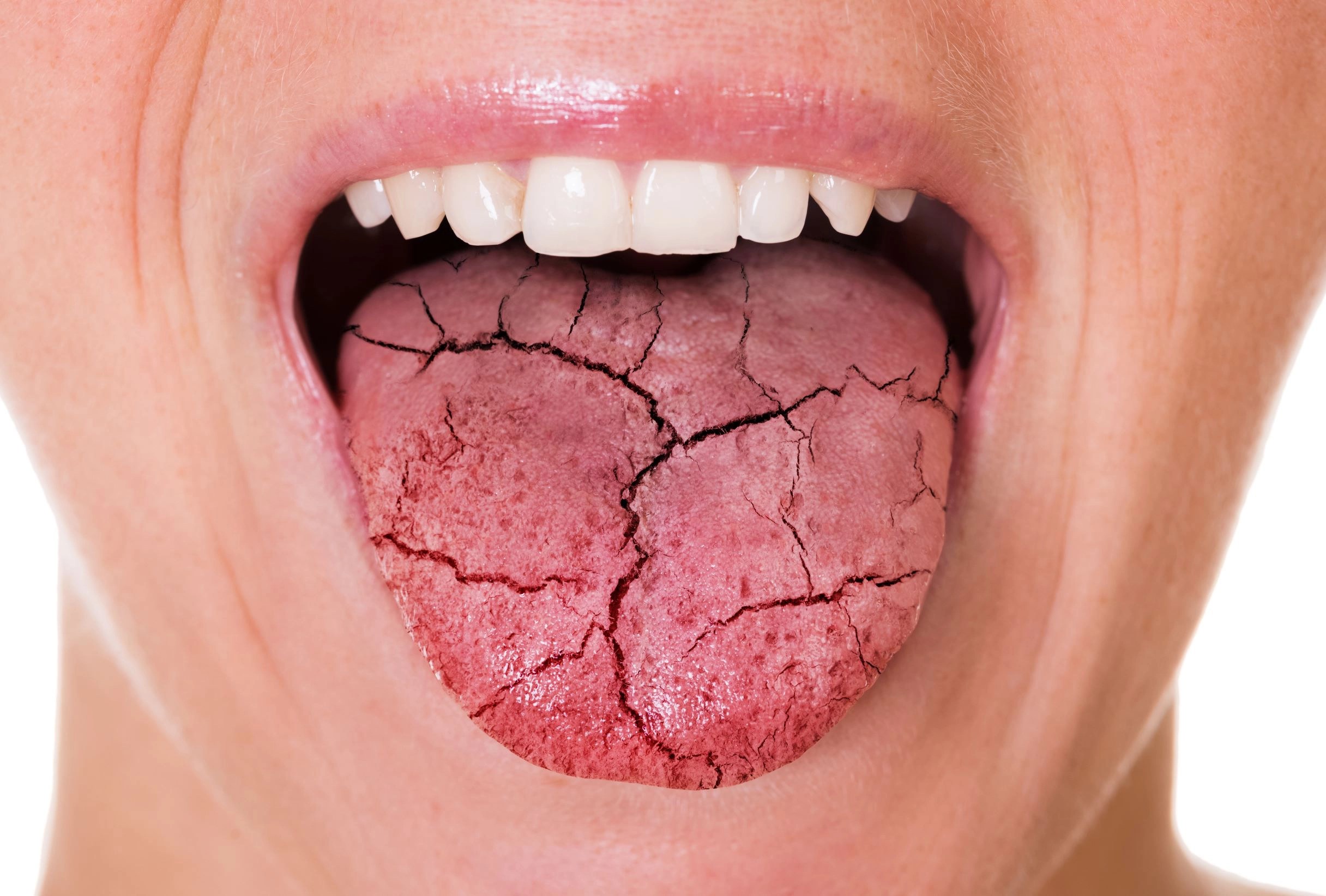
Xerostomia, commonly referred to as dry mouth, is a condition that significantly impacts an individual’s quality of life. It is characterized by a decrease in saliva production, leading to discomfort and potential complications such as difficulty swallowing, altered taste, and increased risk of dental caries. Nurses play a pivotal role in recognizing and interpreting this condition, which can be indicative of underlying health issues or medication side effects. In this article, we will delve into the implications of xerostomia, the nurse's interpretation of this condition, and its management.
The importance of understanding xerostomia cannot be overstated, as it is often overlooked in clinical settings. Patients may not report dry mouth unless specifically asked, leading to a lack of appropriate interventions. As healthcare providers, nurses must be equipped with the knowledge to assess oral health comprehensively and to recognize the signs and symptoms of xerostomia. Through this article, we aim to enhance awareness and provide valuable insights into the nursing perspective on xerostomia.
In this extensive discussion, we will cover various aspects of xerostomia, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. We will also explore the nurse's role in patient education and support, emphasizing the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to managing this condition. Let’s embark on this informative journey to better understand xerostomia and its implications for nursing practice.
Table of Contents
What is Xerostomia?
Xerostomia is defined as a subjective feeling of oral dryness due to reduced or absent saliva flow. This condition can arise from various factors, including medical conditions, medications, or lifestyle choices. It is essential to recognize that xerostomia is distinct from salivary gland dysfunction, although they are often interrelated.
Understanding Saliva and Its Importance
Saliva plays a critical role in maintaining oral health. Its functions include:
- Facilitating digestion
- Protecting teeth from decay
- Neutralizing acids produced by bacteria
- Assisting in taste sensation
- Moistening food for easier swallowing
Without adequate saliva, individuals may experience significant oral discomfort and increased susceptibility to infections and dental issues.
Causes of Xerostomia
Xerostomia can be caused by a myriad of factors, some of which include:
- Medications: Many common medications, including antihistamines, antidepressants, and diuretics, can lead to dry mouth as a side effect.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, Sjögren's syndrome, and autoimmune disorders can impair salivary gland function.
- Radiation Therapy: Patients undergoing radiation treatment for head and neck cancers may experience damage to salivary glands.
- Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake or excessive fluid loss can result in decreased saliva production.
Understanding the underlying causes of xerostomia is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Symptoms of Xerostomia
Individuals with xerostomia may report a variety of symptoms, including:
- Persistent dry mouth
- Difficulty swallowing
- Altered taste sensation
- Burning sensation in the mouth
- Increased thirst
- Halitosis (bad breath)
These symptoms can significantly impact daily activities, including eating, speaking, and social interactions.
Diagnosis of Xerostomia
The diagnosis of xerostomia typically involves a comprehensive assessment that includes:
- Medical History: A thorough review of the patient's medical history, including medications and existing health conditions.
- Clinical Examination: A clinical examination of the oral cavity to assess signs of dryness and other related conditions.
- Salivary Testing: Salivary flow rates may be measured to evaluate the severity of xerostomia.
Accurate diagnosis is essential for determining the appropriate management strategies.
Nurse's Role in Xerostomia Management
Nurses play a vital role in the management of xerostomia by:
- Identifying patients at risk for xerostomia
- Performing oral assessments and documenting findings
- Educating patients about the condition and self-care strategies
- Coordinating care with other healthcare professionals
By taking an active role in xerostomia management, nurses can help improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
Treatment Options for Xerostomia
Treatment for xerostomia often involves a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches, including:
- Saliva Substitutes: Over-the-counter saliva substitutes can provide temporary relief from dry mouth.
- Medications: Prescription medications, such as pilocarpine, may stimulate saliva production.
- Hydration: Encouraging adequate fluid intake is essential for managing xerostomia.
- Oral Care Products: Using fluoride toothpaste and mouthwashes specifically designed for dry mouth can help protect dental health.
These treatment options should be tailored to the individual patient's needs and preferences.
Patient Education and Support
Education is a fundamental component of managing xerostomia. Nurses should provide patients with information on:
- Understanding xerostomia and its causes
- Self-care strategies to alleviate symptoms
- Importance of oral hygiene to prevent complications
- When to seek further medical advice
Empowering patients with knowledge can enhance their ability to manage xerostomia effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, xerostomia is a condition that can greatly affect an individual's quality of life. Nurses play a crucial role in interpreting this condition and implementing effective management strategies. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for xerostomia, healthcare providers can offer comprehensive care to those affected. It is essential for patients to be educated about their condition and involved in their own care. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of xerostomia, do not hesitate to seek advice from your healthcare provider.
We invite you to share your thoughts in the comments below, or explore our other articles for more information on related topics.
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back on our site for more insightful health-related articles!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8onnCpaCepqRitrR5zairnpxdqbxutMCvnGawlae8tMDOpqCaZaSdsm661KuqnmWZo8Gmvs%2BrnK2rXam1qr%2BMraZmpZWWu2%2B006aj