The Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM) theory is a psychological framework that explains how people process persuasive messages. In an era where communication is paramount, understanding the mechanisms behind persuasion can significantly impact marketing, education, and interpersonal communication. This article delves into the intricacies of the ELM theory, exploring its core components, applications, and the various ways it identifies persuasive pathways. By examining both the central and peripheral routes of persuasion, we will uncover how individuals can be influenced by different types of messages.
Understanding the ELM theory is essential for anyone looking to master the art of persuasion, whether in marketing campaigns, public speaking, or everyday conversations. The theory suggests that people process information differently depending on their motivation and ability to engage with the message. As we navigate through this article, we will highlight the practical implications of ELM and how it can be applied effectively in various contexts.
As we explore the depths of the ELM theory, we will provide insights into its relevance and importance in today's fast-paced information society. By the end of this article, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of how the ELM theory identifies blank ways by influencing attitudes and behaviors through its dual-process model of persuasion.
Table of Contents
Introduction to the Elaboration Likelihood Model
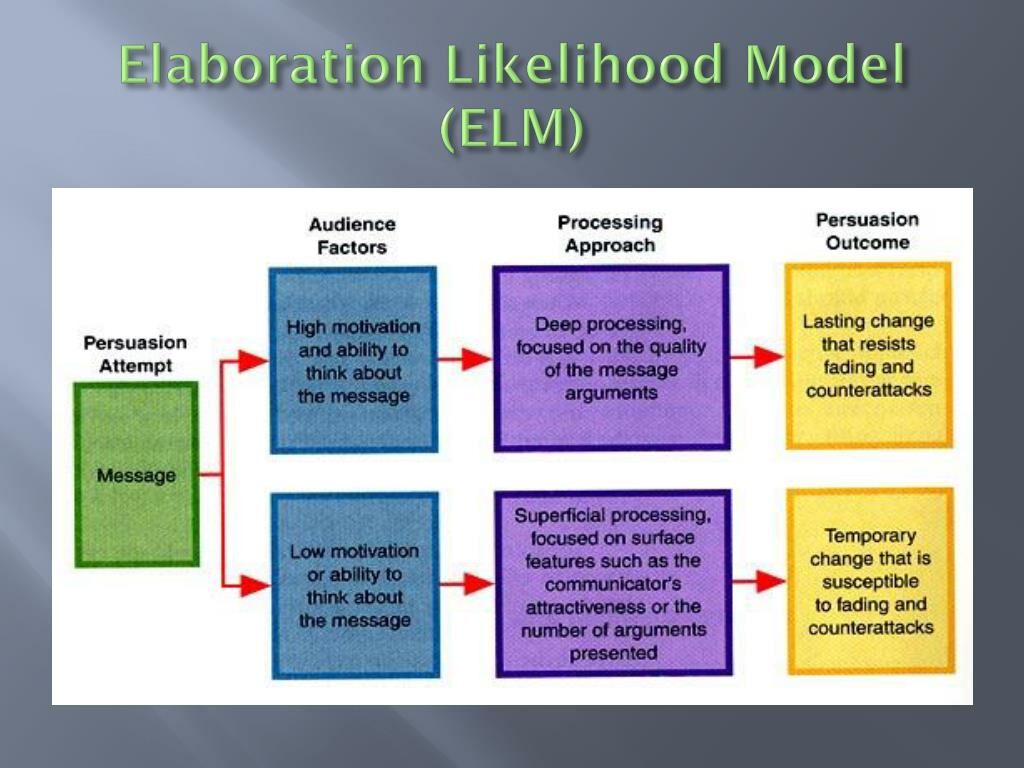
The Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM) was developed by Richard E. Petty and John Cacioppo in the 1980s as a means to explain the different ways individuals process persuasive information. At its core, ELM posits that there are two primary routes through which persuasion occurs: the central route and the peripheral route. These routes are determined by the audience's motivation and ability to engage with the message.
Understanding ELM is particularly relevant in our information-saturated world, where individuals are constantly bombarded with messages vying for their attention. By recognizing how different strategies can influence persuasion, marketers, educators, and communicators can tailor their approaches to achieve desired outcomes.
Core Components of ELM Theory
The Elaboration Likelihood Model consists of several key components that help to elucidate how persuasive messages are processed. These include:
- Elaboration: Refers to the extent to which an individual thinks about or analyzes a message.
- Motivation: The desire or willingness to engage with the message, which can be influenced by personal relevance or interest.
- Ability: The cognitive capacity to process the information, which can be affected by distractions or complexity.
Understanding Elaboration
Elaboration is a crucial factor in determining which route of persuasion will be taken. High elaboration leads to a deeper processing of the message, while low elaboration results in superficial processing.
Factors Influencing Motivation and Ability
Several factors can influence a person's motivation and ability to process persuasive messages, including:
- Personal relevance of the topic
- Level of distraction in the environment
- Complexity of the message
The Central Route of Persuasion
The central route is characterized by high elaboration, where individuals carefully consider the arguments presented in the message. This route is often employed when the audience is motivated and able to process the information. Key aspects of the central route include:
- Strong arguments: Persuasive messages that contain well-reasoned and logical arguments are more likely to lead to attitude change.
- Long-lasting change: Attitude changes resulting from the central route tend to be more stable and enduring.
- Critical thinking: Individuals engaging with the central route employ critical thinking and analytical skills.
The Peripheral Route of Persuasion
In contrast, the peripheral route involves low elaboration, where individuals rely on cues outside the message content to form their attitudes. This route is often activated when individuals are either not motivated or unable to engage deeply with the content. Key elements of the peripheral route include:
- Heuristics: Individuals may rely on mental shortcuts or heuristics to make quick decisions.
- Superficial cues: Factors such as the attractiveness of the communicator, emotional appeals, or social proof can influence attitudes.
- Temporary change: Attitudes formed via the peripheral route are often less stable and may change easily over time.
Applications of ELM Theory
The Elaboration Likelihood Model has diverse applications across various fields, including marketing, health communication, and public relations. Some of the notable applications include:
- Advertising: Advertisers can tailor their messages based on the target audience's motivation and ability to process information.
- Public health campaigns: Understanding how to effectively communicate health messages can lead to better public health outcomes.
- Political communication: Politicians can craft their messages to resonate with voters, depending on their engagement levels.
The Impact of ELM on Decision Making
The ELM theory also sheds light on how persuasion affects decision-making processes. Understanding the routes of persuasion can help individuals make informed choices by recognizing the factors influencing their attitudes.
Case Studies Illustrating ELM in Action
Case studies provide real-world examples of how the ELM theory operates in practice. For instance, research in consumer behavior has shown that messages with strong arguments are more effective in persuading consumers when they are highly involved with the product category.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
In conclusion, the Elaboration Likelihood Model theory identifies blank ways by outlining the processes through which individuals engage with persuasive messages. By understanding the central and peripheral routes of persuasion, marketers, educators, and communicators can craft messages that resonate with their audiences. The practical applications of ELM are vast, and its insights can significantly enhance persuasive efforts across various domains.
We invite you to share your thoughts in the comments below, explore more articles on our site, and join our community of learners eager to understand the nuances of persuasion.
Final Thoughts
Thank you for taking the time to explore the Elaboration Likelihood Model theory with us. We hope this article has provided valuable insights and encouraged you to think critically about the messages you encounter daily. We look forward to seeing you again soon!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8tbTEZpylmZKkv6LAyKilZqSZoLKttceopp1lnaSxpriMrZ%2Bep6KueqqwxKerop6ZmsBursuapaSXj5SsoKuMsJiyq12Xxm%2B006aj