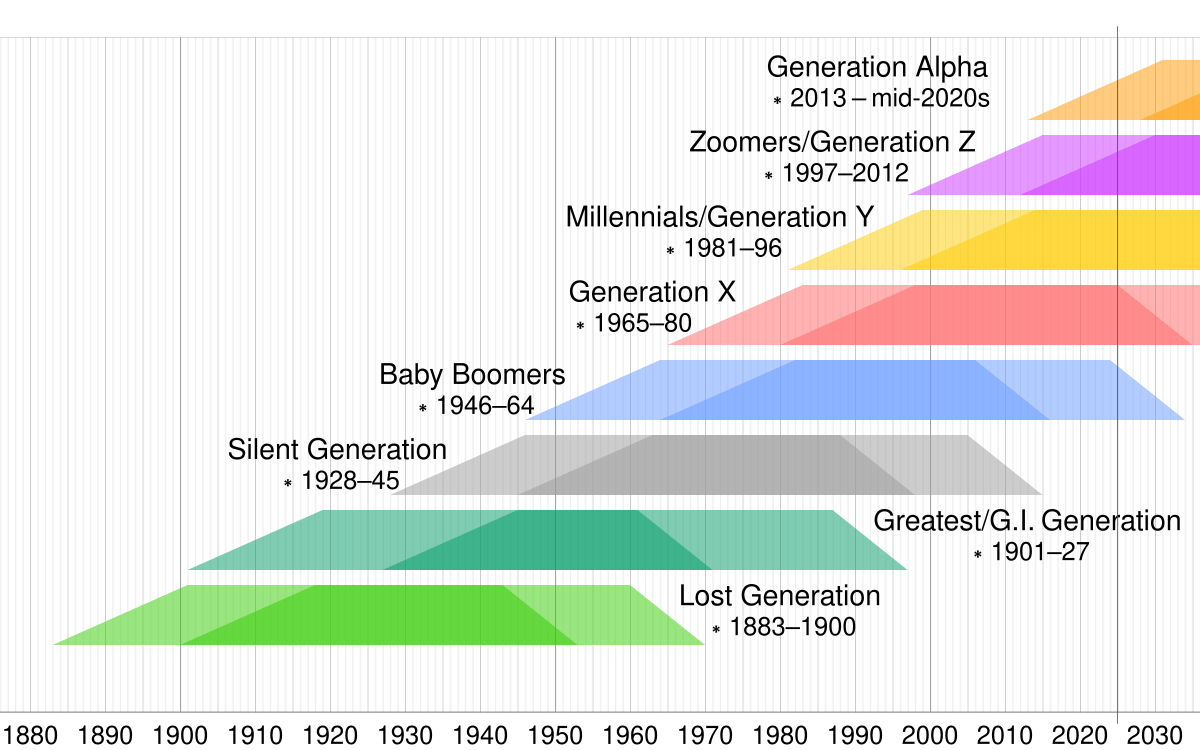
In the intricate tapestry of human history, generational differences serve as a fascinating lens through which to understand societal evolution and cultural shifts. To navigate the complexities of these variations, the "generation timeline chart" emerges as an invaluable tool. This chart is not just a representation of historical timelines but a reflection of the socio-cultural, economic, and technological transformations that have shaped each generation uniquely. By examining the "generation timeline chart," one gains insights into the distinct characteristics, values, and behaviors of each generation. This understanding is crucial for fostering intergenerational communication and collaboration in various domains, including family dynamics, workplace environments, and educational settings.
Delving into the "generation timeline chart," we uncover the rich narratives that have defined each cohort. These generational cohorts, from the Silent Generation to Generation Z, encompass a wide range of experiences influenced by historical events, technological advancements, and changing societal norms. Each generation is marked by pivotal moments that have left indelible imprints on their collective psyche. By tracing these timelines, we can appreciate the unique contributions and challenges each generation brings to the table.
The significance of the "generation timeline chart" extends beyond mere academic interest. It is a practical tool for organizations, educators, and policymakers seeking to address the diverse needs and expectations of different age groups. Understanding these generational distinctions enables the development of strategies that resonate with each cohort, fostering inclusivity and mutual respect. As we embark on this exploration, we aim to provide a comprehensive, user-friendly guide to navigating the complex yet fascinating world of generational timelines.
Table of Contents
The Concept of Generations
The term "generation" refers to a cohort of people born and living around the same time, sharing similar cultural experiences and societal influences. This concept helps in understanding how historical events, technological advancements, and social changes impact the collective mindset and behavior of individuals within the same age group. Generations are often defined by sociologists and demographers to facilitate the study of societal shifts over time.
Generations are typically delineated by significant historical events or cultural shifts, which create a shared set of experiences for those born within a specific period. These shared experiences shape the values, beliefs, and behaviors of each generation, distinguishing them from those that come before or after. The study of generations allows for a deeper understanding of how societal norms evolve over time and how these changes influence individual and collective behavior.
Understanding the concept of generations is crucial in today's rapidly changing world. With each new generation, new challenges and opportunities arise, necessitating a continuous adaptation to the evolving social landscape. By examining the characteristics and defining moments of each generation, we can better appreciate the diverse perspectives and contributions that each brings to the broader societal fabric.
The Silent Generation (1928-1945)
The Silent Generation, born between 1928 and 1945, lived through some of the most tumultuous times in modern history, including the Great Depression and World War II. This generation is often characterized by its resilience, discipline, and a strong work ethic, shaped by the hardships and uncertainties of their formative years.
Members of the Silent Generation grew up during a period of economic hardship and global conflict, which instilled in them a sense of duty, loyalty, and a commitment to securing stable, long-term employment. They are often described as conservative and traditional, valuing security and stability over risk-taking and innovation. Family and community ties are central to their identity, and they place a high value on respect for authority and adherence to social norms.
Despite their name, the Silent Generation has made significant contributions to society. They played a crucial role in rebuilding post-war economies, advancing civil rights, and laying the groundwork for technological and cultural advancements that would follow. Their steadfast dedication to work and community has left a lasting legacy that continues to influence subsequent generations.
Baby Boomers (1946-1964)
Baby Boomers, born in the post-World War II era between 1946 and 1964, represent one of the largest and most influential generations in history. The term "Baby Boomer" is derived from the significant increase in birth rates following the war, reflecting a period of economic prosperity and societal optimism.
This generation grew up during a time of great change and innovation, including the civil rights movement, the advent of television, and the space race. These experiences fostered a spirit of idealism, individualism, and a desire for social progress. Baby Boomers are often associated with the counterculture movement of the 1960s, advocating for civil rights, gender equality, and environmental conservation.
As Baby Boomers entered the workforce, they transformed industries and economies, driving growth and innovation. Their influence is evident in the rise of consumerism, the expansion of suburban living, and the development of new technologies. Today, Baby Boomers continue to shape society, as they redefine aging and retirement, challenging traditional notions of what it means to grow older.
Generation X (1965-1980)
Generation X, born between 1965 and 1980, is often referred to as the "middle child" generation, sandwiched between the larger Baby Boomer and Millennial cohorts. This generation came of age during a time of significant social and economic change, including the rise of dual-income families, the advent of personal computing, and the end of the Cold War.
Generation X is characterized by its independence, adaptability, and entrepreneurial spirit. Having grown up in an era of shifting family dynamics and economic uncertainty, they value self-reliance and are often described as pragmatic and resourceful. This generation witnessed the transition from analog to digital technologies, making them adept at navigating the rapidly changing technological landscape.
In the workforce, Generation X is known for its strong work ethic and commitment to work-life balance. They are often seen as the bridge between traditional and modern workplace practices, embracing technological advancements while valuing personal connections and collaboration. As they move into leadership roles, Generation X continues to influence organizational culture and drive innovation.
Millennials (1981-1996)
Millennials, also known as Generation Y, were born between 1981 and 1996. This generation is defined by its digital nativity, having grown up during the rise of the internet, social media, and mobile technology. Millennials are known for their tech-savviness, diversity, and desire for meaningful work and experiences.
This generation came of age during a time of rapid technological advancement and globalization, shaping their worldview and expectations. Millennials value diversity and inclusivity, advocating for social justice and environmental sustainability. They prioritize work-life balance and seek careers that align with their values and provide opportunities for personal and professional growth.
Millennials have transformed traditional industries with their embrace of technology and innovation. They are driving the shift towards remote work, gig economy, and digital entrepreneurship. As the largest generation in the workforce today, Millennials continue to influence workplace culture, consumer behavior, and societal norms.
Generation Z (1997-2012)
Generation Z, born between 1997 and 2012, is the first truly digital-native generation, having never known a world without the internet or smartphones. This generation is characterized by its comfort with technology, diversity, and social consciousness.
Having grown up in a hyper-connected world, Generation Z is adept at navigating digital platforms and leveraging technology for communication, learning, and entertainment. They are highly visual and prefer multimedia content over traditional text-based information. This generation values authenticity, transparency, and social responsibility, often using their digital presence to advocate for social and environmental causes.
In the workforce, Generation Z is known for its entrepreneurial mindset and desire for flexibility and autonomy. They are driving the demand for remote work, digital collaboration, and innovative technologies. As they enter adulthood, Generation Z is poised to shape the future of industries and redefine societal norms.
Generation Alpha (2013-Present)
Generation Alpha, born from 2013 onwards, represents the newest cohort of individuals entering the world. As the children of Millennials, this generation is expected to be the most technologically advanced and educated yet. They are growing up in a world of artificial intelligence, automation, and augmented reality, where technology is seamlessly integrated into every aspect of life.
Generation Alpha is characterized by its early exposure to technology and digital media, shaping their learning and communication styles. They are expected to be highly adaptable, creative, and collaborative, leveraging technology to solve complex problems and create new opportunities.
As Generation Alpha grows and matures, they will inherit a world facing significant challenges, including climate change, economic inequality, and political instability. Their ability to navigate these issues and drive positive change will be crucial in shaping the future of society.
Understanding Generational Characteristics
Generational characteristics are shaped by a complex interplay of historical events, cultural influences, and technological advancements. These characteristics define the values, beliefs, and behaviors of each generation, influencing how they interact with the world and each other.
Each generation is marked by defining moments and cultural shifts that leave lasting imprints on their collective identity. These shared experiences create generational cohorts with distinct characteristics, ranging from the resilience and discipline of the Silent Generation to the tech-savviness and social consciousness of Generation Z.
Understanding these generational characteristics is crucial for fostering effective communication and collaboration across age groups. By recognizing the diverse perspectives and contributions of each generation, we can build more inclusive and harmonious communities, workplaces, and societies.
Impact of Technology on Generations
Technology has played a pivotal role in shaping generational experiences and characteristics. From the advent of television and personal computing to the rise of the internet and mobile technology, each generation has been influenced by the technological advancements of their time.
The Silent Generation and Baby Boomers witnessed the emergence of television and mass media, transforming how information was disseminated and consumed. Generation X experienced the rise of personal computing and the internet, revolutionizing communication and access to information. Millennials and Generation Z grew up in a digital world, with technology integrated into every aspect of their lives, shaping how they learn, work, and connect with others.
Understanding the impact of technology on generations is crucial for navigating the digital age. By recognizing how technology influences behavior and expectations, we can develop strategies that harness its potential while addressing its challenges, fostering a more connected and informed society.
Generational Values and Beliefs
Generational values and beliefs are shaped by the historical, cultural, and technological contexts in which individuals are born and raised. These values and beliefs influence how generations perceive the world and make decisions, shaping their interactions with others and their contributions to society.
Each generation has distinct values and beliefs that reflect their unique experiences and defining moments. The Silent Generation values stability and security, while Baby Boomers prioritize individualism and social progress. Generation X is known for its independence and adaptability, while Millennials value diversity, inclusivity, and work-life balance. Generation Z prioritizes authenticity, transparency, and social responsibility.
Understanding these generational values and beliefs is essential for fostering mutual respect and collaboration across age groups. By recognizing the diverse perspectives and priorities of each generation, we can build more inclusive and harmonious communities, workplaces, and societies.
Intergenerational Communication and Collaboration
Effective intergenerational communication and collaboration are crucial for building cohesive and inclusive communities, workplaces, and societies. By understanding the unique characteristics and values of each generation, we can bridge generational gaps and foster mutual understanding and respect.
Intergenerational communication involves recognizing and appreciating the diverse perspectives and experiences of different age groups. By embracing open dialogue and active listening, we can build trust and rapport across generations, facilitating collaboration and innovation.
In the workplace, intergenerational collaboration is essential for driving organizational success and innovation. By leveraging the unique strengths and contributions of each generation, we can create diverse and dynamic teams that thrive in a rapidly changing world.
Generations in the Workplace
Generational diversity in the workplace presents both challenges and opportunities for organizations. Understanding the unique characteristics and preferences of each generation is crucial for fostering a positive and productive work environment.
The Silent Generation and Baby Boomers bring experience, discipline, and a strong work ethic, while Generation X offers independence, adaptability, and entrepreneurial spirit. Millennials value diversity, inclusivity, and work-life balance, while Generation Z brings tech-savviness, creativity, and social consciousness.
By recognizing and embracing generational diversity, organizations can harness the unique strengths and contributions of each cohort, driving innovation and success. Effective management of generational differences involves fostering open communication, providing opportunities for growth and development, and creating inclusive and supportive work environments.
Challenges and Opportunities in Managing Generations
Managing generational differences in the workplace presents both challenges and opportunities for organizations. Understanding the unique characteristics and preferences of each generation is crucial for fostering a positive and productive work environment.
One of the key challenges in managing generations is addressing the diverse needs and expectations of different age groups. Each generation has distinct values, beliefs, and work styles, which can lead to misunderstandings and conflicts if not effectively managed.
However, generational diversity also presents opportunities for organizations to harness the unique strengths and contributions of each cohort. By fostering open communication and collaboration across generations, organizations can drive innovation and success, creating dynamic and inclusive work environments that thrive in a rapidly changing world.
Future Trends in Generational Studies
As the world continues to evolve, generational studies will play an increasingly important role in understanding societal shifts and shaping the future. Emerging trends and technologies will continue to influence generational characteristics and interactions, necessitating ongoing research and adaptation.
One of the key future trends in generational studies is the impact of technology on communication, learning, and work. As new technologies continue to emerge and reshape the digital landscape, understanding their influence on generational behavior and expectations will be crucial for navigating the digital age.
Another important trend is the increasing diversity and inclusivity of future generations. As societies become more interconnected and globalized, understanding the diverse perspectives and contributions of different age groups will be essential for fostering mutual respect and collaboration.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a generation timeline chart?
A generation timeline chart is a visual representation that outlines the different generational cohorts, their birth years, and defining characteristics. It helps in understanding the unique experiences and influences that shape each generation.
2. How are generations defined?
Generations are typically defined by significant historical events or cultural shifts that create a shared set of experiences for individuals born within a specific period. Sociologists and demographers use these markers to facilitate the study of societal changes over time.
3. Why is understanding generational differences important?
Understanding generational differences is important for fostering effective communication, collaboration, and inclusivity across age groups. It helps in appreciating the diverse perspectives and contributions of each generation, building more cohesive communities and workplaces.
4. How does technology impact generational characteristics?
Technology plays a crucial role in shaping generational characteristics by influencing how individuals communicate, learn, and work. Each generation is marked by the technological advancements of their time, which shape their expectations and behaviors.
5. What are the key challenges in managing generational diversity in the workplace?
Key challenges in managing generational diversity include addressing the diverse needs and expectations of different age groups, fostering effective communication and collaboration, and creating inclusive work environments that leverage the strengths of each generation.
6. What are the future trends in generational studies?
Future trends in generational studies include the impact of emerging technologies on communication and work, increasing diversity and inclusivity of future generations, and the ongoing need for adaptation to societal changes and challenges.
Conclusion
The "generation timeline chart" serves as a valuable tool for understanding the complexities of generational differences and their impact on society. By examining the distinct characteristics and defining moments of each generation, we gain insights into the diverse perspectives and contributions that shape our world.
Understanding generational differences is crucial for fostering effective communication and collaboration across age groups, building more inclusive and harmonious communities, workplaces, and societies. As we continue to navigate the rapidly changing world, embracing generational diversity will be essential for driving innovation, success, and social progress.
In conclusion, the "generation timeline chart" offers a comprehensive guide to understanding the rich narratives and shared experiences that define each generational cohort. By recognizing the unique strengths and challenges of each generation, we can build a more connected and informed society, equipped to address the complex issues and opportunities of the future.
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmrK2TmLK0v4yepaChnpp8qLHNnqmarJmku27AyKacpaGemnqktMCrq2egpKK5