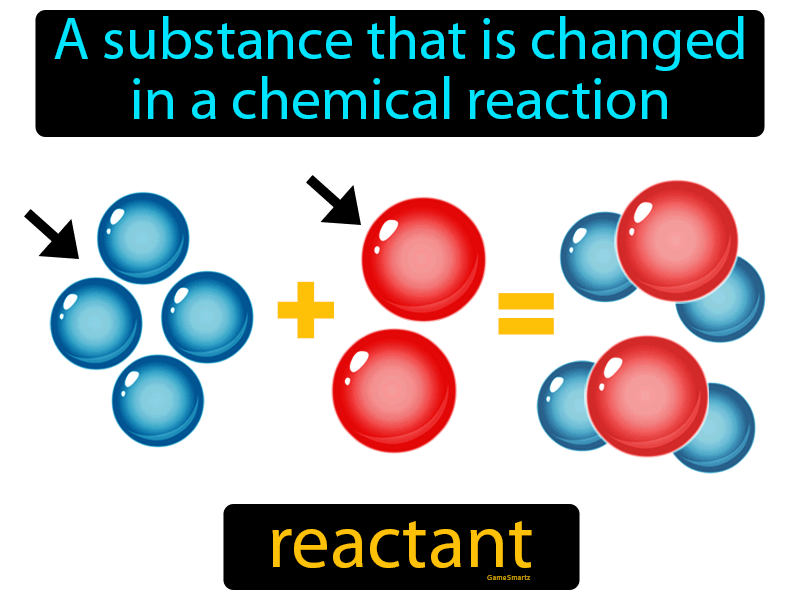
Reactants are fundamental components in the realm of chemistry, serving as the starting substances in chemical reactions. In a chemical equation, reactants are transformed into products through various processes, driving the changes that occur in matter. This article delves into the intricacies of reactants, their types, and their significance in both theoretical and practical applications. By the end of this comprehensive guide, you will have a clearer understanding of what reactants are and their role in everyday chemical reactions.
In the world of chemistry, the term "reactant" refers to any substance that undergoes a change during a chemical reaction. These substances interact with one another, leading to the formation of new products. The study of reactants is essential not only for chemists but also for anyone interested in the science that governs our physical world. This article aims to provide insights into the various aspects of reactants, including their definitions, types, and examples.
Whether you are a student, an educator, or simply a curious individual, understanding reactants can enhance your knowledge of chemical processes and their implications in various fields, such as biology, environmental science, and materials science. Let us dive deeper into the fascinating world of reactants and discover their vital role in shaping our understanding of chemistry.
Table of Contents
What Are Reactants?
In chemistry, reactants are substances that participate in a chemical reaction. They are the starting materials that react to form products. The interaction between reactants involves breaking and forming chemical bonds, leading to the rearrangement of atoms. Understanding reactants is crucial for anyone studying chemistry, as they are the foundation upon which reactions are built.
Characteristics of Reactants
- Reactants can be elements or compounds.
- The physical state of reactants (solid, liquid, gas) can influence the reaction.
- Reactants can undergo various types of reactions, including synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, and double replacement.
Types of Reactants
Reactants can be classified into several categories based on their nature and behavior in chemical reactions. Understanding these types helps in predicting the outcomes of various reactions.
1. Organic Reactants
Organic reactants contain carbon and are typically involved in reactions that produce organic compounds. Examples include hydrocarbons, alcohols, and carboxylic acids.
2. Inorganic Reactants
Inorganic reactants do not primarily contain carbon and include a wide range of substances such as salts, metals, and minerals. These reactants are often involved in reactions that do not produce organic compounds.
3. Gaseous Reactants
Many chemical reactions involve gaseous reactants, such as oxygen and hydrogen, which play crucial roles in combustion and respiration processes.
4. Aqueous Reactants
Aqueous reactants are substances dissolved in water. They are common in reactions involving electrolytes and are essential in biological processes.
Reactants in Chemical Equations
A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction, showcasing the relationship between reactants and products. In these equations, reactants are typically written on the left side, while products are placed on the right side.
Balancing Chemical Equations
Balancing chemical equations is crucial to ensure that the law of conservation of mass is upheld. This means that the number of atoms of each element must be the same on both sides of the equation.
Example of a Chemical Reaction
Consider the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen to form water:
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
In this reaction, hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) are the reactants, while water (H2O) is the product.
Role of Reactants in Daily Life
Reactants play a vital role in numerous everyday processes. From cooking to cleaning, understanding the role of different reactants can enhance our daily experiences.
Cooking
Many cooking processes involve chemical reactions, such as the Maillard reaction, where amino acids and reducing sugars react to create complex flavors and browning in cooked foods.
Cleaning Products
Household cleaning products often contain reactants that react with dirt and stains, breaking them down to make surfaces clean. For example, bleach (sodium hypochlorite) reacts with organic materials to eliminate stains.
Common Examples of Reactants
Here are some common examples of reactants and the reactions they undergo:
- Hydrogen and oxygen gas: React to form water.
- Carbon dioxide and water: React through photosynthesis to produce glucose and oxygen.
- Sodium and chlorine: React to form sodium chloride (table salt).
Impact of Reactants on the Environment
The use and disposal of reactants can significantly impact the environment. Understanding these effects is crucial for developing sustainable practices.
Pollution from Chemical Reactants
Many industrial processes release harmful reactants into the environment, contributing to air and water pollution. Awareness of these impacts is essential for regulatory measures and environmental protection.
Green Chemistry
Green chemistry focuses on designing chemical products and processes that minimize the use and generation of hazardous substances, promoting safer reactants and sustainable practices.
Safety Considerations When Handling Reactants
Safety is paramount when working with chemical reactants. Here are some important safety considerations:
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and goggles.
- Understand the properties of the reactants you are working with, including their reactivity and potential hazards.
- Store reactants properly to prevent accidents, such as spills or reactions with incompatible substances.
Conclusion
In summary, reactants are essential components in chemical reactions that form the basis of various processes in nature and industry. Understanding reactants allows us to appreciate the complexities of chemistry and its applications in our daily lives. We encourage you to explore more about chemical reactions and their implications in various fields. If you found this article informative, please leave a comment, share it with others, or check out more articles on our site!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back for more engaging content on chemistry and science!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8s7HAnKuapqSoe6nAzKU%3D