Amnesia is a complex neurological condition that affects memory retention and recall, often resulting in significant challenges for those who suffer from it. The brain scans of people with amnesia are most likely to show damage to the hippocampus, a critical area for memory processing. Understanding the relationship between the hippocampus and amnesia not only sheds light on the condition itself but also has broader implications for how we understand memory and cognition in the human brain.
This article will delve into the intricacies of amnesia, exploring its types, causes, and effects on individuals. We will examine brain imaging studies that have highlighted the connection between the hippocampus and memory deficits. Additionally, we will discuss potential treatments and therapies that may aid those affected by amnesia, emphasizing the importance of ongoing research in this field. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how amnesia manifests in the brain and its implications for patients and healthcare providers alike.
As we navigate through this complex topic, it is essential to consider the experiences of individuals with amnesia and the challenges they face daily. The insights gained from studying the brain scans of these individuals not only enhance our scientific knowledge but also foster empathy and understanding towards those living with memory disorders. Join us as we explore the fascinating intersection of neurology, psychology, and human resilience.
Table of Contents
Understanding Amnesia
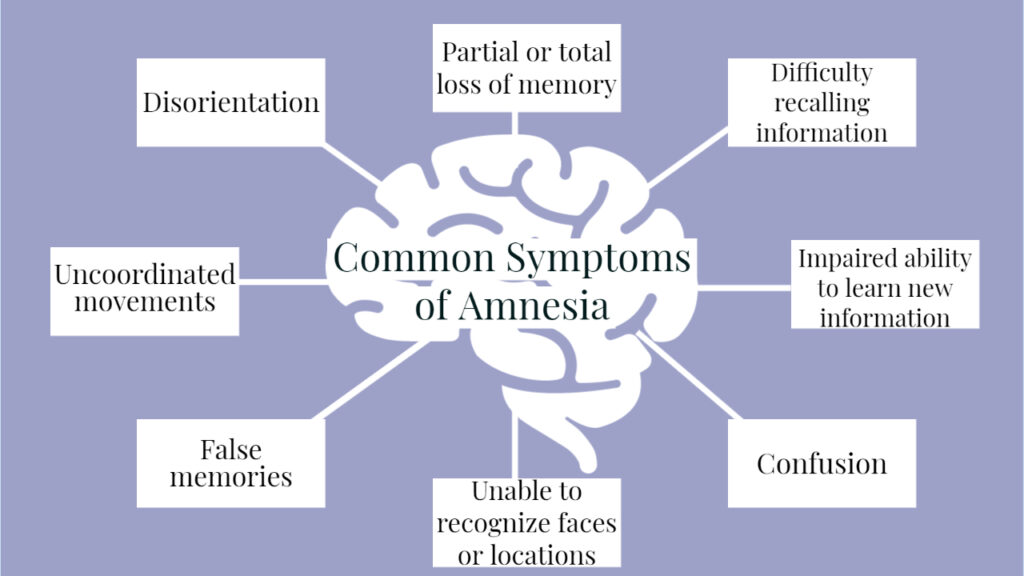
Amnesia is defined as a loss of memory that can occur due to various factors, including brain injury, psychological trauma, or degenerative diseases. It can manifest in different ways, affecting an individual's ability to recall past experiences or form new memories. The experience of amnesia can be profoundly disorienting for individuals and their loved ones, making it crucial to understand the underlying mechanisms at play.
Types of Amnesia
Amnesia can be classified into several types, each with distinct characteristics:
- Anterograde Amnesia: This type affects a person’s ability to form new memories after the onset of amnesia. Individuals can recall events and facts from before the condition but struggle to retain new information.
- Retrograde Amnesia: Retrograde amnesia involves the loss of pre-existing memories, often affecting events or information that occurred shortly before the onset of the condition. In some cases, long-term memories may also be impacted.
- Transient Global Amnesia: This is a temporary form of amnesia that can last for several hours. Individuals may experience sudden memory loss and confusion, but they usually recover completely.
- Childhood Amnesia: This refers to the inability to recall memories from early childhood, which is a common experience for many people as they grow older.
Causes of Amnesia
Various factors can lead to amnesia, including:
- Brain Injury: Trauma to the head, such as concussions or strokes, can damage areas of the brain responsible for memory processing.
- Psychological Trauma: Severe emotional stress or trauma can result in dissociative amnesia, where individuals block memories associated with distressing events.
- Degenerative Diseases: Conditions like Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia can lead to progressive memory loss over time.
- Substance Abuse: Chronic alcohol abuse and certain drugs can impair cognitive function and memory retention.
Brain Scans and Amnesia
Brain scans, particularly MRI and CT scans, play a critical role in diagnosing and understanding amnesia. These imaging techniques allow researchers and clinicians to visualize the brain's structure and identify any abnormalities. Studies have shown that the brain scans of people with amnesia often reveal damage to specific regions associated with memory processing.
The Importance of MRI and CT Scans
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scans are commonly used to assess brain structure. These imaging techniques help in identifying physical abnormalities in the brain, including lesions, atrophy, or other forms of damage that may contribute to memory impairment.
Findings from Imaging Studies
Research has indicated a strong correlation between damage to the hippocampus and various forms of amnesia. Studies utilizing brain imaging have found that individuals with anterograde amnesia often exhibit significant atrophy in the hippocampus. This supports the notion that the hippocampus plays a vital role in memory formation and retrieval.
The Role of the Hippocampus
The hippocampus is a small, seahorse-shaped structure located in the medial temporal lobe of the brain, and it is crucial for forming new memories and navigating spatial environments.
How the Hippocampus Functions
The hippocampus is involved in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory. It acts as a temporary storage site before information is transferred to other brain regions for long-term storage. Damage to the hippocampus can disrupt this process, leading to difficulties in forming new memories.
Clinical Implications of Hippocampal Damage
Understanding the role of the hippocampus in amnesia has significant clinical implications. It informs treatment approaches and rehabilitation strategies for individuals with memory disorders. Therapies focusing on cognitive exercises and memory training can help enhance the functioning of the hippocampus and improve memory outcomes.
Treatment Options for Amnesia
While there is no one-size-fits-all treatment for amnesia, several options may help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
- Cognitive Rehabilitation: This involves structured activities designed to improve memory and cognitive function through practice and repetition.
- Medication: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to address underlying conditions contributing to memory loss, such as depression or anxiety.
- Psychotherapy: Therapeutic approaches, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, can help individuals cope with the emotional impact of amnesia.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide emotional support and practical strategies for managing amnesia.
Case Studies in Amnesia
Examining specific case studies of individuals with amnesia can provide valuable insights into the condition and its effects on daily life. These studies illustrate the diverse experiences of individuals living with memory disorders and the challenges they face.
Case Study 1: The Man with a Memory of Three Seconds
One notable case is that of a man known as "Clive Wearing," who suffers from profound anterograde and retrograde amnesia. After a viral infection affected his brain, he was left with only a few seconds of memory. His case highlights the role of the hippocampus and the importance of emotional memories, as he retains the ability to recognize his wife despite his memory loss.
Case Study 2: The Woman Who Couldn't Remember Her Past
Another case involves a woman who experienced retrograde amnesia following a traumatic incident. She lost all memories of her life before the event, illustrating the psychological impact of trauma on memory. Her recovery process involved therapeutic interventions aimed at gradually recalling memories while coping with the emotional aftermath of her experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the brain scans of people with amnesia are most likely to show damage to the hippocampus, underscoring its critical role in memory processing. By understanding the types, causes, and effects of amnesia, as well as the implications of hippocampal damage, we can better support individuals affected by this complex condition. Ongoing research and advancements in treatment options offer hope for those living with memory disorders, emphasizing the importance of compassion and understanding in addressing their unique challenges.
We encourage you to share your thoughts in the comments below, connect with others who are interested in this topic, and explore related articles on our site for further reading.
Thank you for joining us in this exploration of amnesia and its impact on the human experience. We look forward to welcoming you back for more insightful discussions in the future.
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8tbTEZpmrmZmjerSvwKeqZqeWYr2mu8%2BlnGavmam1bq3Mp5ysoZFirrOxjKamrKxdobasscuyZK2nXai1sMOMnZimmZeaerW7jK2fnmaYqbqt