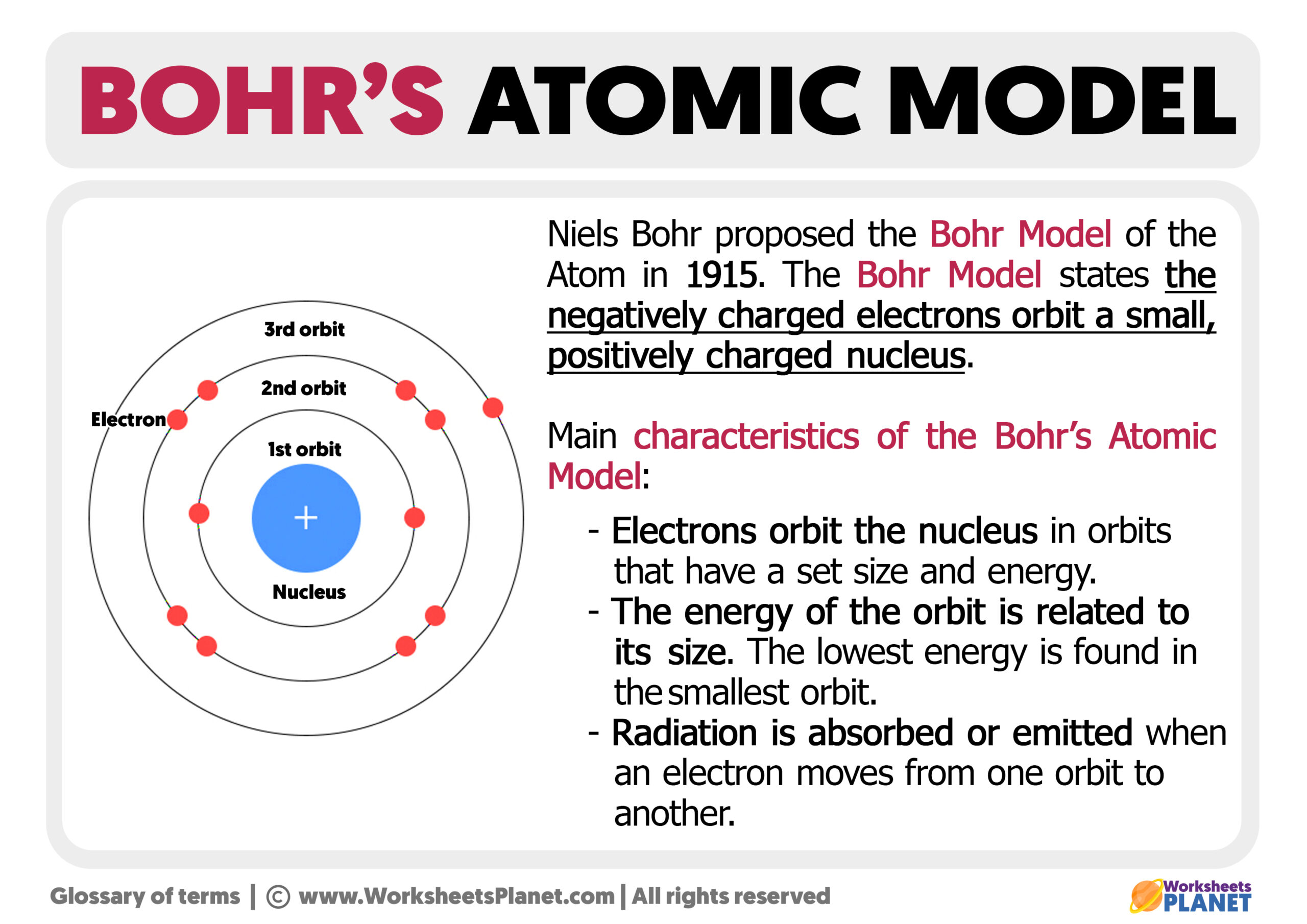
The atomic model of Niels Bohr represents a groundbreaking advancement in the field of atomic physics. Developed in the early 20th century, this model challenged existing notions about atomic structure and laid the groundwork for modern quantum mechanics. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of Bohr's atomic model, its historical context, and its lasting impact on scientific thought.
Bohr's model of the atom emerged during a time when scientists were grappling with the limitations of earlier atomic theories. It introduced the concept of quantized energy levels, which fundamentally changed the way we understand electron behavior in atoms. This innovative approach not only clarified the spectral lines observed in hydrogen but also provided insights into the behavior of more complex atoms.
As we delve into the details of Bohr's atomic model, we will examine its key components, including the postulates that underpin it, the implications for atomic structure, and the criticisms it faced. Furthermore, we will highlight the significance of Bohr's contributions to the field and how they continue to influence contemporary physics. Join us on this journey through the atomic world as we unpack Niels Bohr's revolutionary ideas.
Table of Contents
Biography of Niels Bohr
Niels Bohr was born on October 7, 1885, in Copenhagen, Denmark. He was a physicist who made significant contributions to our understanding of atomic structure and quantum mechanics. Bohr's educational background included studying at the University of Copenhagen, where he earned his doctorate in 1911. He worked closely with other renowned physicists of his time, including J.J. Thomson and Ernest Rutherford.
Throughout his career, Bohr received numerous accolades, including the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922 for his work on the structure of atoms and radiation emanating from them. His research not only advanced scientific knowledge but also influenced philosophical discussions about the nature of reality and observation in quantum mechanics.
| Data | Details |
|---|---|
| Name | Niels Bohr |
| Date of Birth | October 7, 1885 |
| Place of Birth | Copenhagen, Denmark |
| Nobel Prize | Physics, 1922 |
| Field of Study | Atomic Physics, Quantum Mechanics |
| Date of Death | November 18, 1962 |
Key Postulates of Bohr's Atomic Model
Bohr's atomic model is built upon several key postulates that distinguish it from earlier models. These postulates include:
- Quantization of Angular Momentum: Electrons orbit the nucleus in specific, quantized energy levels, with angular momentum being quantized as well.
- Stable Orbits: Electrons can occupy stable orbits without radiating energy, which was a significant departure from classical physics.
- Energy Emission and Absorption: An electron can transition between energy levels by absorbing or emitting a photon of light corresponding to the energy difference between the levels.
- Hydrogen Atom Spectrum: Bohr's model successfully explained the spectral lines of hydrogen, providing a mathematical framework for predicting the wavelengths of emitted light.
Understanding Quantum Jumps
One of the most revolutionary aspects of Bohr's atomic model is the concept of quantum jumps. When an electron transitions between energy levels, it does so instantaneously, effectively "jumping" from one orbit to another without occupying the intervening space. This phenomenon can be illustrated as follows:
- When an electron absorbs energy, it jumps to a higher energy level.
- When an electron releases energy, it falls back to a lower energy level, emitting a photon in the process.
This concept not only explains the discrete lines observed in atomic spectra but also integrates the principles of quantum mechanics into the understanding of atomic behavior.
Spectral Lines and Their Significance
The spectral lines produced by atoms, especially hydrogen, provided crucial evidence supporting Bohr's atomic model. When hydrogen gas is energized, it emits light at specific wavelengths, leading to the appearance of distinct spectral lines. Bohr's model accounted for these lines through the quantized energy levels of the electron. The significance of spectral lines includes:
- Identification of Elements: Each element has a unique spectral fingerprint, allowing scientists to identify elements in distant stars and galaxies.
- Understanding Atomic Structure: The analysis of spectral lines has deepened our understanding of atomic structure and electron configurations.
- Applications in Technology: Spectroscopy, the study of spectral lines, is used in various fields, including chemistry, astronomy, and even medicine.
Limitations of Bohr's Model
While Bohr's atomic model was groundbreaking, it also faced limitations. Some of the notable criticisms include:
- Multi-electron Atoms: Bohr's model primarily explained hydrogen and failed to accurately predict the spectra of more complex atoms with multiple electrons.
- Electron Behavior: The model treated electrons as particles in fixed orbits, neglecting the wave-particle duality established by later quantum theories.
- Quantum Mechanics Integration: Bohr's model did not fully integrate the principles of quantum mechanics, leading to the development of more advanced models, such as the quantum mechanical model.
The Legacy of Niels Bohr
Niels Bohr's contributions to atomic physics have left a lasting legacy. His pioneering work laid the groundwork for the development of quantum mechanics and influenced a generation of physicists. Bohr's model not only revolutionized our understanding of atomic structure but also sparked philosophical discussions about the nature of reality and observation in the quantum realm.
Furthermore, Bohr's principles have found applications in various fields, including chemistry, material science, and technology. His legacy continues to inspire researchers and students alike, highlighting the importance of questioning established scientific paradigms.
Influence on Modern Physics
Bohr's atomic model has had a profound influence on modern physics. Subsequent developments in quantum mechanics, such as the Schrödinger equation and Heisenberg's uncertainty principle, built upon the foundation laid by Bohr. These advancements have led to a more comprehensive understanding of atomic and subatomic particles, as well as their interactions.
Additionally, the principles of Bohr's model are applied in various technologies, including lasers, semiconductors, and quantum computing. The understanding of energy levels and electron transitions remains a crucial aspect of modern scientific research and innovation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the atomic model of Niels Bohr has profoundly transformed our understanding of atomic structure and behavior. Through its key postulates and the introduction of concepts such as quantum jumps, Bohr's model provided clarity to the complexities of atomic physics. Despite its limitations, Bohr's contributions have paved the way for advancements in quantum mechanics and have left an enduring legacy in the field.
We invite you to share your thoughts on Bohr's atomic model in the comments below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into the fascinating world of physics and science.
Thank you for joining us on this exploration of Niels Bohr's atomic model. We look forward to seeing you again soon!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmpqefp7JuvMCipa1nkam8rrXCZqSonJWherCyjKegnqSjYq%2BwtNFnn62lnA%3D%3D