The relationship between output and the standard of living is a fundamental concept in economics that significantly influences how societies function and develop. As economies grow, the output, which refers to the total value of goods and services produced, plays a critical role in determining the quality of life for individuals within that society. In this article, we will explore how output impacts living standards, the factors that contribute to these dynamics, and what policies can be implemented to improve both output and the standard of living.
Understanding this relationship is essential for policymakers, economists, and individuals alike. It not only helps in assessing the current economic health of a nation but also provides insights into future growth trajectories and potential improvements in quality of life. By examining various dimensions, including productivity, income distribution, and social welfare, we can better appreciate how output correlates with living standards.
As we delve into this topic, we will highlight different metrics used to measure output and living standards, analyze how they interact, and discuss the implications for economic policy. This comprehensive examination aims to shed light on the complex interplay between production and quality of life, ultimately providing a deeper understanding of how to foster a prosperous society.
Table of Contents
Understanding Output
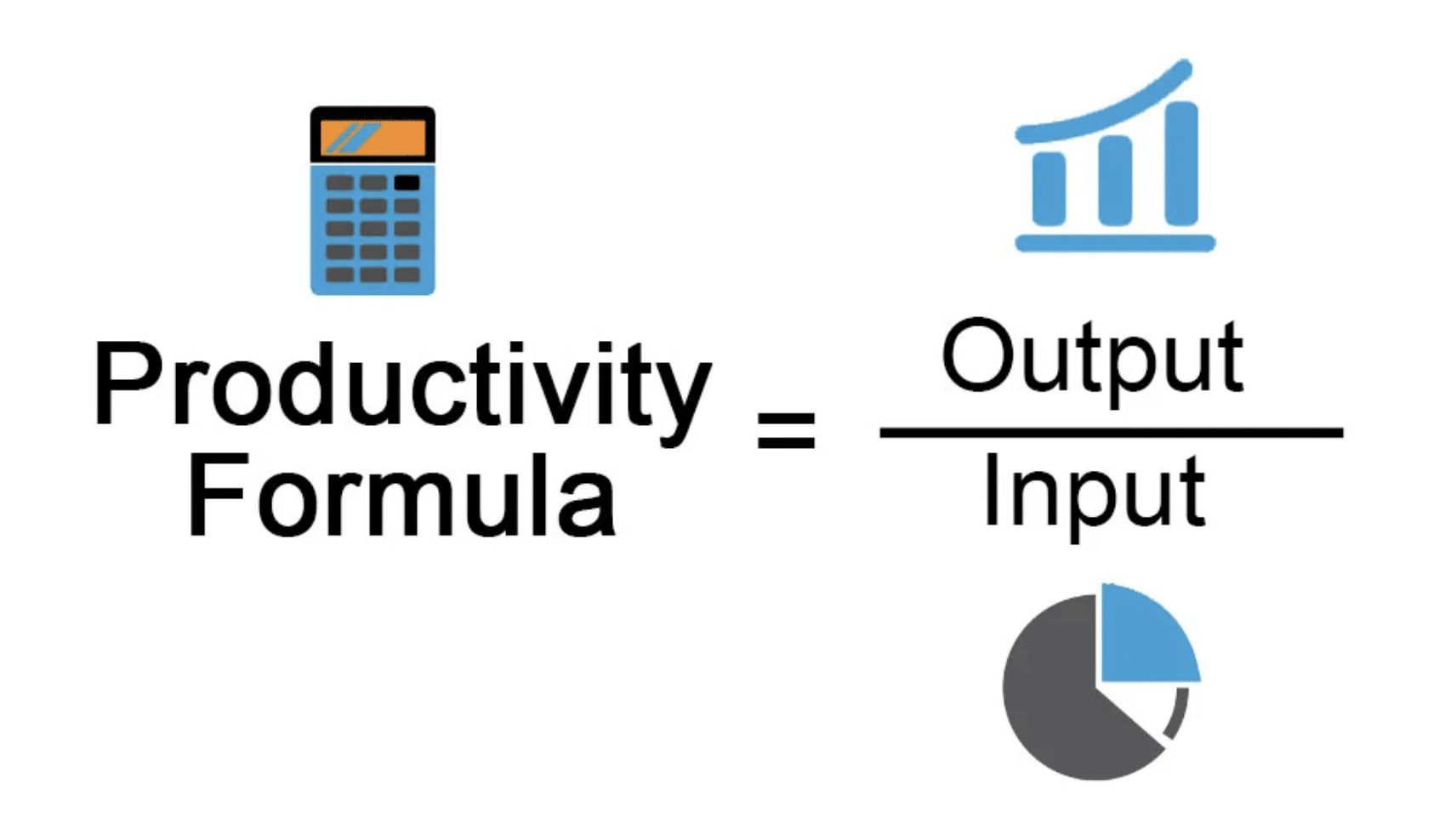
Output in economics refers to the total amount of goods and services produced in an economy over a specific period. It is a critical measure of economic performance and is often represented by Gross Domestic Product (GDP). The level of output indicates how efficiently resources are utilized and the capacity of an economy to generate wealth.
Furthermore, output can be categorized into two types:
- Real Output: This takes into account the inflation-adjusted value of goods and services, providing a more accurate reflection of an economy's health.
- Nominal Output: This measures the value at current market prices, not adjusted for inflation.
Understanding the differences helps in analyzing the economic growth rate and its implications for living standards.
Defining Standard of Living
The standard of living refers to the level of wealth, comfort, material goods, and necessities available to a certain socioeconomic class in a certain geographic area. It encompasses various factors including income, employment, class disparity, poverty rate, and housing affordability.
Common indicators used to assess the standard of living include:
- Income per capita
- Access to healthcare
- Educational attainment
- Life expectancy
- Overall economic stability
Measuring Output: Key Indicators
To gauge output accurately, economists typically rely on several key indicators:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): This is the total monetary value of all finished goods and services produced within a country's borders in a specific time frame.
- Productivity: This refers to the efficiency of production, often measured as output per hour worked.
- Employment Rates: A higher employment rate generally corresponds with greater output, as more individuals are contributing to production.
- Industrial Production Index: This measures the real output of manufacturing, mining, and utilities.
Impact of Output on Standard of Living
The relationship between output and standard of living can be observed through various channels:
- Income Growth: As output increases, it often leads to higher income levels for workers, thereby improving living standards.
- Job Creation: High output typically results in more job opportunities, reducing unemployment and enhancing overall welfare.
- Investment in Public Services: Increased output can allow governments to invest more in healthcare, education, and infrastructure, which directly contributes to a higher quality of life.
Factors Affecting Output
Several factors can significantly influence output levels in an economy:
1. Capital Investment
Investment in capital goods, such as machinery and technology, enhances productivity and, in turn, increases output.
2. Labor Force Skills
The skills and education of the workforce directly impact productivity levels, affecting overall output.
3. Technological Advancements
Innovation and advancements in technology can lead to more efficient production methods, resulting in higher output.
4. Economic Policies
Government regulations, taxation, and incentives can either promote or hinder economic output.
Policies for Improving Living Standards
To enhance the standard of living, policymakers can implement several strategies:
- Education and Training Programs: Investing in education helps develop a skilled workforce that can contribute to higher output.
- Infrastructure Development: Improving transportation and communication infrastructure facilitates better trade and productivity.
- Healthcare Access: Ensuring access to healthcare can improve the overall health of the workforce, leading to increased productivity.
Case Studies: Output and Living Standards
Examining specific countries can provide valuable insights into how output and living standards interact:
- Norway: With high output driven by oil production, Norway has one of the highest standards of living globally, supported by strong social welfare systems.
- United States: The U.S. has a high GDP but faces challenges regarding income inequality, impacting overall living standards.
- Bangladesh: Despite lower output levels, improvements in education and healthcare have significantly raised living standards in recent years.
Future Outlook: Sustainable Growth
As we look toward the future, achieving sustainable economic growth that enhances living standards will require a multifaceted approach:
- Emphasizing Sustainability: Focusing on renewable resources and sustainable practices can ensure long-term output growth without compromising future generations.
- Inclusive Policies: Crafting policies that address income inequality will be essential for improving living standards across all socioeconomic classes.
- International Cooperation: Global challenges such as climate change require collaborative efforts to ensure that growth is beneficial for all.
Conclusion
In summary, the connection between output and the standard of living is complex yet crucial for understanding economic development. By focusing on increasing output through investment, education, and sustainable practices, societies can improve quality of life for their citizens. It is imperative for policymakers and individuals to recognize this relationship and work towards fostering an environment where both output and living standards can flourish.
We encourage you to share your thoughts on this topic in the comments below and explore other articles on our site to further your understanding of economic principles.
Closing Thoughts
We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the relationship between output and the standard of living. As we continue to analyze these critical economic dynamics, we invite you to return for more informative content that enhances your understanding of how economies operate.
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8sMHTqaytZZGjsW7Ax55krKyRo7GivsNmpp9lnJ7DqrrGZ5%2BtpZw%3D