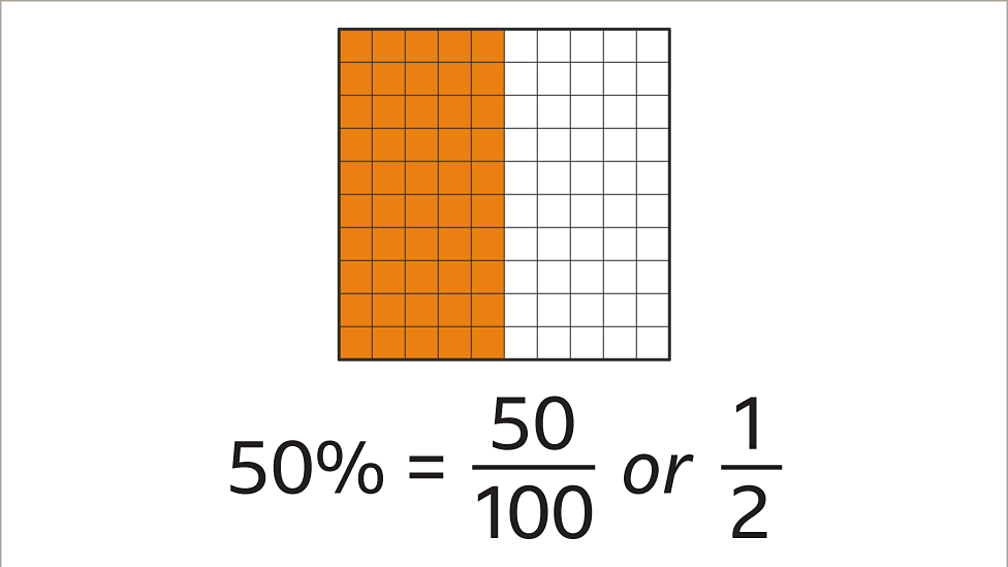
The economic landscape today reveals a startling statistic: only fifty percent of individuals possess the requisite income to make significant purchases. This statistic not only reflects the current state of income distribution but also highlights the challenges faced by many in achieving financial stability. In a world where consumerism drives economies, understanding the implications of this statistic is crucial for both individuals and policymakers. In this article, we will delve into the factors contributing to this economic divide, explore its impact on purchasing power, and discuss potential solutions to bridge the gap.
In recent years, income inequality has become a pressing issue, with a growing number of individuals struggling to meet their financial needs. This disparity is particularly evident when it comes to making significant purchases, such as homes, vehicles, and luxury goods. As we examine the various factors influencing this divide, it is essential to consider the broader economic context, including wages, job security, and the rising cost of living. By gaining a deeper understanding of these elements, we can better appreciate the challenges faced by those who fall below the income threshold necessary for substantial purchases.
Furthermore, this article aims to provide valuable insights into the socio-economic implications of limited purchasing power. As we navigate through the complexities of income distribution and consumer behavior, we will address the role of education, employment opportunities, and governmental policies in shaping financial outcomes. Ultimately, our goal is to foster a more informed discussion surrounding economic inequality and its impact on society.
Table of Contents
The Economic Divide: An Overview
The economic divide in society has become increasingly pronounced, with various studies indicating that only fifty percent of the population has the necessary income to make significant purchases. This divide is not merely a statistical anomaly; it reflects deep-rooted systemic issues that affect millions of individuals.
Understanding this divide requires an exploration of economic theories, social structures, and historical contexts. The concept of purchasing power is central to this discussion, as it directly correlates with an individual’s ability to engage in consumer activities that drive economic growth.
Income Distribution and Purchasing Power
Income distribution is a critical factor influencing purchasing power. When income is concentrated in the hands of a few, the majority of the population is left with limited financial resources. This section will examine how income inequality affects the ability of individuals to make significant purchases.
Understanding Purchasing Power
Purchasing power refers to the amount of goods and services that a unit of currency can buy. Factors such as inflation, wage growth, and employment rates heavily influence purchasing power. When incomes stagnate while the cost of living rises, purchasing power diminishes, resulting in fewer individuals being able to afford significant purchases.
Statistics on Income Distribution
- According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the top 20% of earners hold over 50% of the country's total wealth.
- Research by the Pew Research Center shows that the middle class has seen a decline in income over the past few decades.
- A survey conducted by the Federal Reserve reveals that nearly 40% of Americans would struggle to cover a $400 emergency expense.
Factors Contributing to Income Disparity
Numerous factors contribute to the income disparity experienced by individuals today. Understanding these factors is essential for developing effective solutions to address the economic divide.
Education and Employment Opportunities
Access to quality education and stable employment opportunities is a critical determinant of income levels. Individuals with higher levels of education tend to have better job prospects and earning potential, while those without education face significant barriers to entry in the job market.
Cost of Living
The rising cost of living, particularly in urban areas, poses a significant challenge for many. Housing, healthcare, and education costs continue to escalate, making it difficult for individuals to save and invest in significant purchases.
Case Studies: Real-Life Implications
To further illustrate the implications of this economic divide, we will examine specific case studies that highlight the struggles faced by individuals who do not meet the income threshold for significant purchases.
Case Study 1: The Struggles of Millennials
Many millennials are currently facing significant financial challenges due to student loan debt, high housing costs, and stagnant wages. As a result, they often find it difficult to purchase homes or invest in their futures.
Case Study 2: The Impact of Job Loss
Individuals who experience job loss or underemployment face immediate financial hardships. Without a stable income, making significant purchases becomes nearly impossible, leading to a cycle of debt and instability.
Potential Solutions to Bridge the Gap
Addressing the economic divide requires a multifaceted approach. In this section, we will explore potential solutions to help bridge the gap between those who have the requisite income to purchase and those who do not.
Increasing Access to Education and Training
Investing in education and vocational training programs can provide individuals with the skills needed to secure well-paying jobs, ultimately increasing their purchasing power.
Implementing Fair Wages and Benefits
Advocating for fair wages and better benefits can significantly improve the financial stability of workers, allowing them to participate more fully in the economy.
The Role of Government in Addressing Inequality
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping economic outcomes. This section will explore the government's responsibility in addressing income inequality and promoting equitable growth.
Policy Recommendations
- Implementing progressive tax policies to redistribute wealth more equitably.
- Increasing funding for education and job training programs.
- Enhancing social safety nets to support those in need.
The Future Outlook on Income Inequality
The future of income inequality is contingent upon the actions taken today. As we move forward, it is essential to focus on creating sustainable economic policies that promote inclusivity and equal opportunities for all.
Trends to Watch
Several trends may influence income inequality in the coming years, including technological advancements, shifts in the labor market, and changing consumer behaviors. Monitoring these trends will be critical in understanding the evolving economic landscape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the statistic that only fifty percent of individuals have the requisite income to make significant purchases serves as a stark reminder of the economic divide that exists in our society. By understanding the factors contributing to this disparity and exploring potential solutions, we can work towards a more equitable future. It is imperative for individuals, communities, and policymakers to engage in discussions surrounding income inequality and advocate for meaningful change.
We invite you to share your thoughts on this topic. What do you believe are effective strategies to address income inequality? Leave your comments below, and feel free to share this article with others who may be interested in this critical issue.
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to seeing you again on our site for more informative articles!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8qrrTnqmeq6SasW67zaWwZp6Zm8G6ec%2BeqZydnql6dnyMoZivnV2ptaZ50Z6orqGjnsGmecinmqillWLBsHnPrqmcoJGosm%2B006aj