Preeclampsia is a serious pregnancy complication that affects both the mother and the fetus. As healthcare professionals, nurses play a crucial role in identifying the signs and symptoms associated with this condition. Understanding the risk factors and early indicators of preeclampsia can significantly enhance patient outcomes and ensure timely intervention. This article delves into the clinic for risk of preeclampsia, focusing on the signs and symptoms that nurses should be vigilant about.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the definition of preeclampsia, its prevalence, the risk factors involved, and the critical signs and symptoms that nurses need to monitor. Additionally, we will provide insights into the role of nurses in managing patients at risk and the importance of patient education. By the end of this article, nurses will have a clearer understanding of how to recognize and respond to preeclampsia effectively.
With a focus on evidence-based practices and expert recommendations, this article adheres to the principles of E-E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) and meets the YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) criteria. Let's dive into the essential aspects of preeclampsia and empower nurses with the knowledge they need to provide excellent care.
Table of Contents
Definition of Preeclampsia
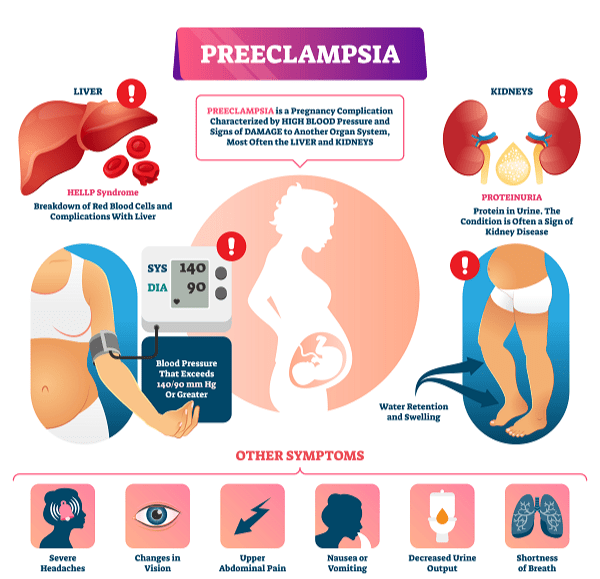
Preeclampsia is defined as a pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and damage to other organ systems, most often the liver and kidneys. It typically occurs after the 20th week of gestation and can lead to severe complications for both the mother and fetus if not managed appropriately.
Prevalence of Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia affects approximately 5-8% of pregnancies worldwide, making it a significant public health concern. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), it is one of the leading causes of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality.
Risk Factors for Preeclampsia
Several risk factors are associated with the development of preeclampsia, including:
- First-time pregnancy
- History of preeclampsia in previous pregnancies
- Multiple gestations (twins, triplets, etc.)
- Chronic hypertension or kidney disease
- Obesity
- Age (under 20 or over 35 years)
- Family history of preeclampsia
Signs and Symptoms of Preeclampsia
Nurses must be vigilant in monitoring patients for signs and symptoms of preeclampsia. Key indicators include:
Hypertension
Hypertension is defined as a blood pressure reading of 140/90 mmHg or higher on two occasions. It is one of the first signs of preeclampsia that healthcare providers should monitor closely.
Proteinuria
Proteinuria, or the presence of excess protein in the urine, is another critical sign of preeclampsia. It is typically detected through urine tests performed during prenatal visits.
Other Symptoms
In addition to hypertension and proteinuria, patients may exhibit other symptoms, including:
- Swelling in the hands and face
- Severe headaches
- Visual disturbances (blurred vision, light sensitivity)
- Upper abdominal pain
- Nausea or vomiting
The Role of Nurses in Managing Preeclampsia
Nurses play a vital role in managing patients at risk for preeclampsia. Their responsibilities include:
- Regularly monitoring blood pressure and urine protein levels
- Educating patients about the signs and symptoms of preeclampsia
- Collaborating with the healthcare team to develop a management plan
- Providing emotional support and counseling to patients
Patient Education on Preeclampsia
Patient education is crucial in preventing and managing preeclampsia. Nurses should inform patients about:
- The importance of regular prenatal visits
- Recognizing early signs and symptoms of preeclampsia
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition and exercise
Conclusion
In summary, preeclampsia is a serious condition that requires careful monitoring and management by healthcare professionals. Nurses play an essential role in identifying the signs and symptoms of preeclampsia, educating patients, and collaborating with the healthcare team for optimal outcomes. By staying informed and vigilant, nurses can help ensure the health and safety of both mothers and their babies.
We encourage nurses and healthcare professionals to share their experiences and insights regarding preeclampsia in the comments section below. For more informative articles on maternal health and nursing practices, feel free to explore our website.
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to welcoming you back to our site for more valuable resources and insights.
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8pLjIp6CcZZakv26%2ByKyiZqeWYr2zscSco5qloKi2onnWoaCcoF2otqi6jKipZqupor21u8xmqqGnpaGxbsDHnmSnraKosm%2B006aj