Accumulated depreciation is a crucial accounting concept that significantly impacts a company's financial statements and overall value. Understanding how much accumulated depreciation is at the end of the year can help businesses and investors make informed decisions regarding asset management and valuation. In this article, we will explore the definition of accumulated depreciation, how it is calculated, its implications for financial reporting, and more.
As companies invest in physical assets, these assets lose value over time due to wear and tear, obsolescence, and other factors. This loss in value is recorded as accumulated depreciation on the balance sheet, which impacts the net book value of the assets. Knowing how to calculate accumulated depreciation and interpret its significance is essential for accountants, financial analysts, and business owners.
In the following sections, we will delve deep into the topic of accumulated depreciation, including its calculation methods, examples, and its relevance in financial analysis. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of accumulated depreciation and its impact on financial reporting.
Table of Contents
1. Definition of Accumulated Depreciation
Accumulated depreciation refers to the total amount of depreciation expense that has been recorded against a fixed asset since its acquisition. It represents the wear and tear, deterioration, or obsolescence of an asset over time. This accounting practice allows companies to match the cost of an asset with the revenue it generates over its useful life, following the matching principle in accounting.
2. Calculation Methods of Accumulated Depreciation
There are several methods to calculate accumulated depreciation, each with its unique approach. The most common methods include:
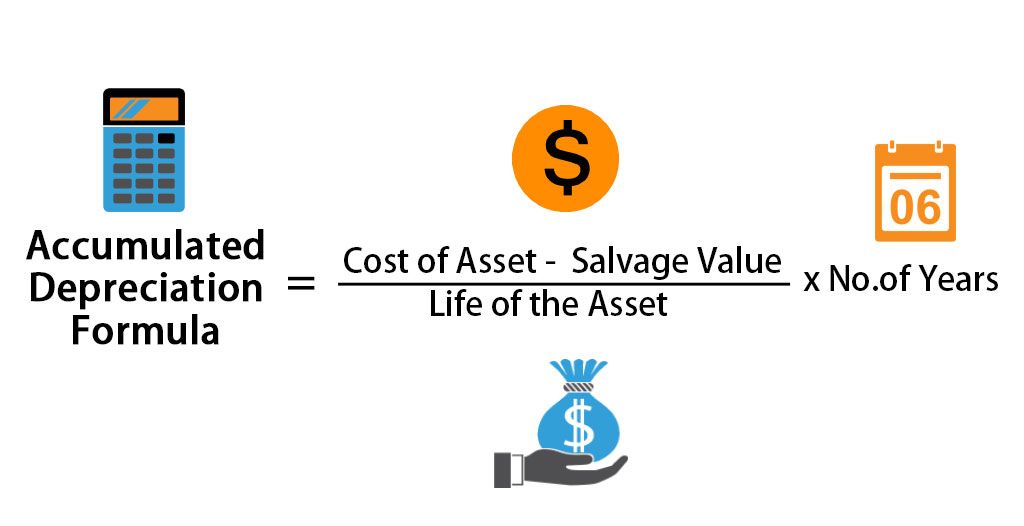
- Straight-Line Method: This method spreads the cost of the asset evenly over its useful life. The formula is:
- Declining Balance Method: This method calculates depreciation based on a fixed percentage of the asset's remaining book value each year.
- Units of Production Method: This method bases depreciation on the actual usage of the asset, making it ideal for machinery and equipment.
Straight-Line Method Example
For instance, if a company purchases a machine for $10,000 with a useful life of 5 years and no salvage value, the annual depreciation expense using the straight-line method would be:
Annual Depreciation Expense = (Cost - Salvage Value) / Useful Life = ($10,000 - $0) / 5 = $2,000
3. Implications of Accumulated Depreciation
Accumulated depreciation has several implications for businesses, including:
- Tax Implications: Depreciation expense is tax-deductible, which can reduce taxable income.
- Impact on Asset Valuation: As accumulated depreciation increases, the net book value of the asset decreases, affecting the overall valuation of the company.
- Cash Flow Considerations: While depreciation is a non-cash expense, it influences cash flow management and investment decisions.
4. Accumulated Depreciation in Financial Reporting
In financial reporting, accumulated depreciation is presented on the balance sheet as a contra asset account. It reduces the gross value of fixed assets to reflect their net book value. This practice ensures that financial statements provide a more accurate representation of a company's financial position.
5. Examples of Accumulated Depreciation
Let’s consider a common scenario to illustrate how accumulated depreciation is calculated:
Imagine a company that purchased a delivery truck for $50,000 with a useful life of 10 years and a salvage value of $5,000. Using the straight-line method, the annual depreciation expense would be:
Annual Depreciation Expense = (Cost - Salvage Value) / Useful Life = ($50,000 - $5,000) / 10 = $4,500
After three years, the accumulated depreciation would be:
Accumulated Depreciation = Annual Depreciation Expense x Number of Years = $4,500 x 3 = $13,500
6. Common Misconceptions about Accumulated Depreciation
There are several misconceptions about accumulated depreciation, including:
- Depreciation is a Cash Expense: Depreciation does not involve cash outflow; it is simply an accounting entry.
- All Assets Depreciate at the Same Rate: Different assets have varying useful lives and depreciation rates.
- Accumulated Depreciation Represents Current Market Value: Accumulated depreciation reflects the accounting value, not necessarily the market value.
7. Impact of Accumulated Depreciation on Asset Value
Accumulated depreciation directly impacts the book value of an asset. As depreciation accumulates, the reported value of fixed assets decreases, which can influence investor perceptions and company valuations. A high level of accumulated depreciation may indicate that an asset is nearing the end of its useful life, prompting management to consider replacement or upgrades.
8. Conclusion
In summary, accumulated depreciation is a vital concept in accounting that affects how assets are valued and reported on financial statements. Understanding the calculation methods, implications, and common misconceptions surrounding accumulated depreciation is essential for anyone involved in financial analysis or business management. By keeping track of accumulated depreciation, businesses can make informed decisions about asset management, tax implications, and overall financial health.
We encourage you to leave a comment with your thoughts on accumulated depreciation or share this article with others who may find it useful. For more in-depth articles on financial concepts, feel free to explore our website!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back here for more insightful content!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8t63LrpxmoJ%2Bseq7BwqFkoqtdlrCkwcyuo5qslZl6pbHPq5ycoZGptrC6jJqrZqyYmnqmusNmpp9lpJ2ybsXEmqlnoKSiuQ%3D%3D