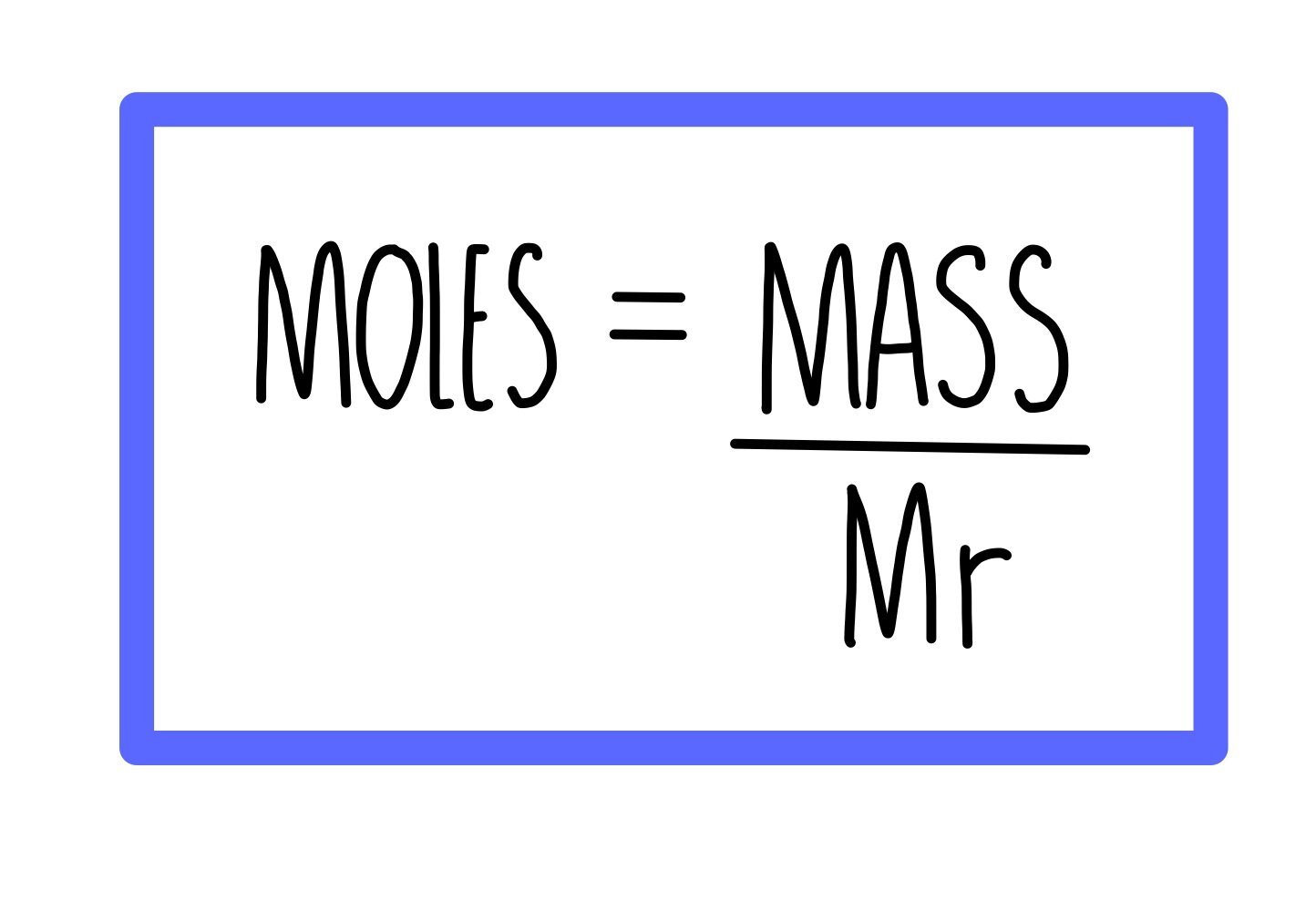
Understanding how to find the mass of 1 mole of xenon tetrafluoride (XeF₄) is crucial for students and professionals in chemistry. This knowledge not only helps in various chemical calculations but also enhances our understanding of molecular compounds and their properties. In this article, we will explore the process of determining the molar mass, the significance of xenon tetrafluoride in chemical reactions, and practical applications in real-world scenarios.
The concept of moles is a fundamental aspect of chemistry, as it allows chemists to quantify substances and predict the outcomes of chemical reactions. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how to calculate the mass of 1 mole of XeF₄ and why it matters in the broader context of chemistry. Let's dive into the details!
We will break down the calculation process, examine the molecular structure of XeF₄, and discuss its applications in various fields. The journey through this topic will provide you with a solid foundation in both theoretical and practical aspects of xenon tetrafluoride.
Table of Contents
Understanding Molecular Weight
Molecular weight, often expressed in grams per mole (g/mol), is a critical concept in chemistry that refers to the mass of a molecule. It is calculated by summing the atomic weights of all atoms present in the molecule. The atomic weight of an element can be found on the periodic table.
For xenon tetrafluoride, the molecular formula is XeF₄, which indicates it contains one xenon atom and four fluorine atoms. To find the molar mass, we will need the atomic weights of xenon and fluorine.
Xenon Tetrafluoride (XeF₄): An Overview
Xenon tetrafluoride is a colorless, odorless gas at room temperature and is a member of the noble gas family. It was first synthesized in 1962 and is notable for its unique properties and reactivity. Xenon tetrafluoride is commonly used in various chemical syntheses and has applications in the semiconductor industry.
Data and Personal Information
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | XeF₄ |
| Molar Mass | 130.30 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless gas |
| Melting Point | -63.2 °C |
| Boiling Point | -40.0 °C |
Calculating the Molar Mass of XeF₄
To calculate the molar mass of xenon tetrafluoride, we will use the following steps:
- Xenon (Xe): 131.29 g/mol
- Fluorine (F): 19.00 g/mol
- Molar Mass of XeF₄ = (1 × Atomic Weight of Xe) + (4 × Atomic Weight of F)
- Molar Mass of XeF₄ = (1 × 131.29 g/mol) + (4 × 19.00 g/mol) = 131.29 g/mol + 76.00 g/mol
- Molar Mass of XeF₄ = 207.29 g/mol
Biographical Insight on Xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a colorless, heavy noble gas that occurs in trace amounts in the Earth's atmosphere. Xenon is used in various applications, including lighting, anesthesia, and as a propellant in ion engines.
Chemical Properties of XeF₄
Xenon tetrafluoride exhibits unique chemical properties that make it a subject of interest in advanced chemistry. Here are some key properties:
- Reacts with water to form hydrofluoric acid and xenon gas.
- Can act as a fluorinating agent in organic synthesis.
- Undergoes hydrolysis to form xenon oxides.
Applications of Xenon Tetrafluoride
Xenon tetrafluoride has a variety of applications across different fields:
- Chemical Synthesis: Used as a fluorinating agent.
- Semiconductor Industry: Used in the production of specialized materials.
- Research: Investigated for potential applications in nuclear medicine.
Safety Precautions When Handling XeF₄
Due to its reactive nature, handling xenon tetrafluoride requires strict safety measures:
- Always work in a well-ventilated area.
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Store in a cool, dry place away from incompatible materials.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how to find the mass of 1 mole of xenon tetrafluoride (XeF₄) is essential for both academic and practical applications in chemistry. By comprehending the calculation of molar mass and the properties of XeF₄, chemists can effectively utilize this compound in various chemical reactions and industrial applications. We encourage you to share your thoughts in the comments below, explore more articles on our site, and deepen your understanding of chemistry!
Thank you for reading! We hope you found this article informative and engaging. Don't hesitate to return for more insightful content on chemistry and related topics.
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8p7XNnWStoJViuqK%2F0mamn2VhYrqwuMRmr56ej2l7qcDMpQ%3D%3D