Cell's plasma membrane plays a crucial role in regulating what enters and exits the cell, which is vital for maintaining homeostasis and facilitating various biochemical processes. One of the significant functions of this membrane is to allow enzymes to enter the cell, enabling them to fragment specific targets within. This article delves into the structure and function of the plasma membrane, the mechanisms that allow enzyme entry, and the implications for cellular function and health.
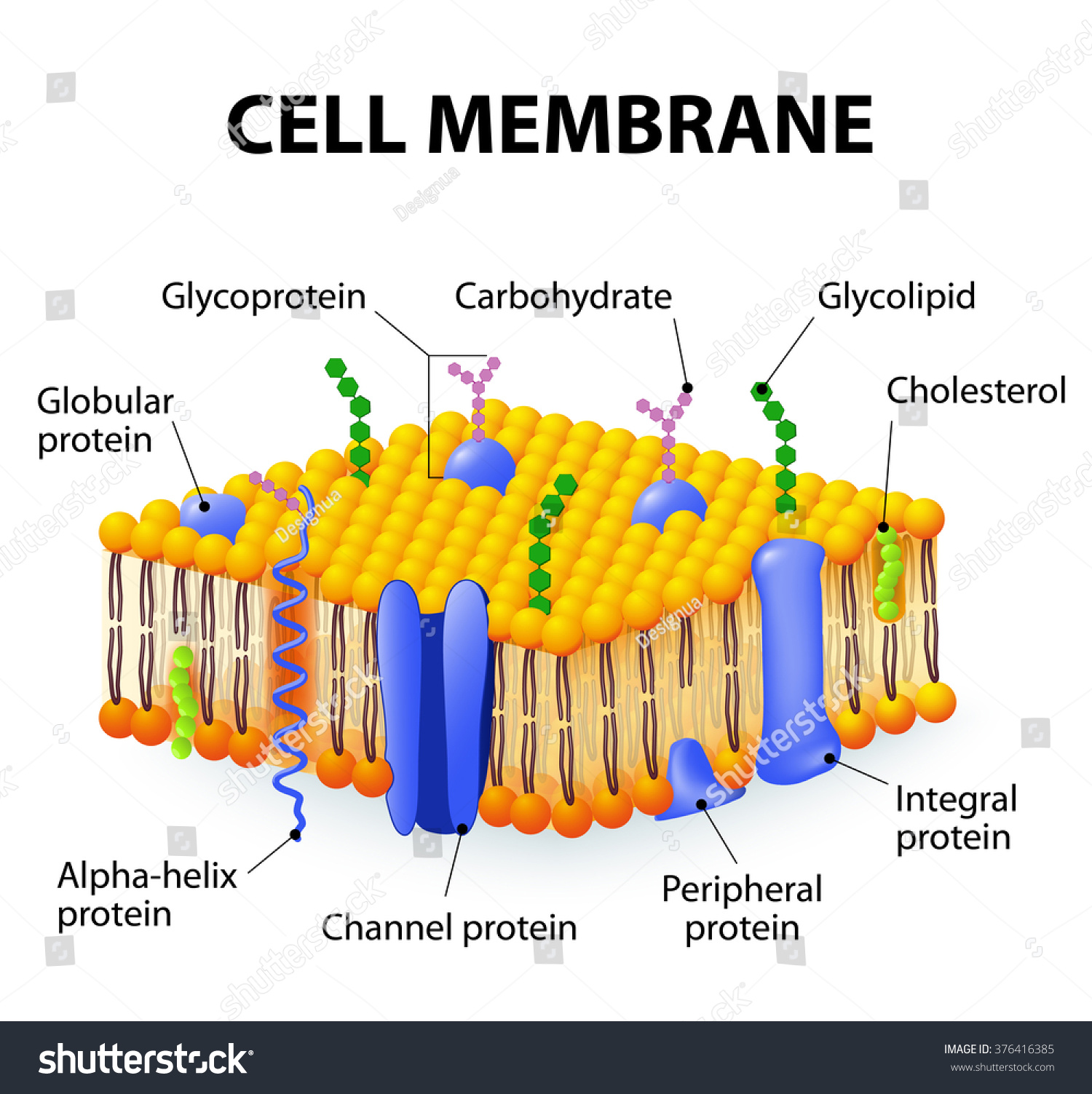
The plasma membrane, often referred to as the cell membrane, is a dynamic structure composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. This unique arrangement not only provides a barrier but also creates a selective environment that can control the flow of substances. Understanding how enzymes can penetrate this barrier is crucial for insights into cellular metabolism and therapeutic interventions.
In this article, we will explore the components of the plasma membrane, the processes by which enzymes gain access to the cell, and the subsequent fragmentation of targets. We will also look at the implications of these processes in various biological contexts, including metabolism, cell signaling, and disease states. Let’s dive deeper into the fascinating world of cellular membranes and their vital functions.
Table of Contents
1. Structure of the Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane is primarily composed of a phospholipid bilayer, which forms a semi-permeable barrier around the cell. This bilayer consists of hydrophilic (water-attracting) heads and hydrophobic (water-repelling) tails. The arrangement of these molecules allows the membrane to be fluid and flexible, accommodating various cellular functions.
Additionally, the plasma membrane contains proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates, each contributing to its overall function:
- Proteins: Integral and peripheral proteins facilitate communication and transport across the membrane.
- Cholesterol: Maintains membrane fluidity and stability, especially in varying temperatures.
- Carbohydrates: Play a role in cell recognition and signaling.
2. Functions of the Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane serves several essential functions that are critical for cell survival and communication:
- Selective Permeability: Controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell, allowing essential nutrients to enter while keeping harmful substances out.
- Cell Signaling: Membrane proteins act as receptors for signaling molecules, triggering cellular responses.
- Cell Adhesion: Carbohydrates on the membrane surface assist in cell recognition and adhesion to other cells.
- Transport: Facilitates the movement of ions and molecules through various transport mechanisms.
3. Mechanisms for Enzyme Entry
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions, and their entry into the cell is vital for numerous metabolic processes. There are several mechanisms by which enzymes can enter the cell:
a. Passive Transport
This process does not require energy as enzymes move along their concentration gradient. Small, non-polar enzymes can diffuse directly through the phospholipid bilayer.
b. Active Transport
In contrast, active transport requires energy (ATP) to move enzymes against their concentration gradient. This process often involves specific transport proteins.
c. Endocytosis
Endocytosis is a mechanism that allows cells to engulf large molecules or particles, including enzymes. This process involves the invagination of the plasma membrane, forming a vesicle that transports the enzyme into the cell.
4. Enzymatic Fragmentation of Targets
Once inside the cell, enzymes can interact with various substrates to facilitate fragmentation. This process is essential for numerous cellular functions, including:
- Metabolism: Enzymes break down macromolecules into smaller units for energy production.
- Signal Transduction: Fragmentation of signaling molecules can modulate cellular responses.
- Cell Cycle Regulation: Enzymatic processes are involved in cell division and growth regulation.
5. Biological Implications
The ability of enzymes to enter cells and fragment targets has significant implications in various biological contexts:
- Cellular Metabolism: Enzyme functionality is crucial for energy production and nutrient processing.
- Immune Response: Enzymes play a role in breaking down pathogens and signaling immune responses.
- Neurotransmission: Enzymatic fragmentation of neurotransmitters regulates synaptic activity.
6. Clinical Relevance
Understanding how enzymes interact with the plasma membrane and their fragmentation processes is vital for developing therapeutic strategies:
- Drug Delivery: Designing drugs that can efficiently cross the plasma membrane can enhance treatment outcomes.
- Enzyme Replacement Therapy: For conditions like enzyme deficiencies, ensuring proper enzyme entry can be crucial for effective treatment.
- Targeted Cancer Therapies: Manipulating enzyme activity can provide new avenues for cancer treatment.
7. Future Research Directions
The ongoing exploration of plasma membrane dynamics and enzyme interactions holds promise for numerous fields:
- Nanotechnology: Developing nanoparticles that can facilitate enzyme delivery.
- Gene Therapy: Utilizing enzymes to modulate gene expression and repair.
- Biotechnology: Engineering enzymes for industrial applications.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, the cell's plasma membrane serves as a critical gateway for enzymes, enabling them to enter and fragment targets essential for numerous biological processes. Understanding the mechanisms of enzyme entry and their implications for cellular function is vital for advancing our knowledge in cell biology and developing novel therapeutic strategies. We encourage readers to reflect on the importance of these processes and explore related topics further.
We invite you to leave your comments below, share this article with others who may find it informative, or read more articles on our site to enhance your understanding of cellular biology.
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you again soon!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8pLHLpapmqJyWwK6tjKacppqilrumedKoZK2gkal6prrZsqSeq12Yrq95xKernqpdlrulecWrmKCllaPBbsDHnmStmaKcsrV6x62kpQ%3D%3D