Henry Hudson's routes are a significant chapter in the annals of exploration, marking a pivotal era in the quest for new commercial pathways and geographic discoveries. His voyages, primarily driven by the ambition to find an alternative route to Asia, inadvertently led to the exploration and mapping of parts of North America that would later play crucial roles in the continent's history. Hudson's expeditions not only expanded the geographical understanding of the time but also laid the groundwork for future explorations and the eventual colonization of the New World. His journeys are a testament to human curiosity, resilience, and the relentless pursuit of knowledge, despite the immense challenges posed by the unknown seas.
The tale of Henry Hudson is one of determination and exploration, with each voyage bringing its own set of challenges and discoveries. Hudson's routes are not merely lines on a map but represent the intersection of ambition, conflict, and adventure. His expeditions across the Atlantic Ocean and the Arctic waters were fueled by the desire to find the fabled Northwest Passage, a direct sea route to Asia that promised immense wealth and trade opportunities. Despite facing treacherous conditions and eventual mutiny, Hudson's voyages contributed significantly to the geographical knowledge of the time, and his legacy is deeply embedded in the history of exploration.
Understanding Henry Hudson's routes provides a window into the age of exploration, a time when the world was still largely uncharted and filled with endless possibilities. Hudson's voyages were instrumental in the European exploration of North America, leading to the establishment of new trade routes and settlements. His discoveries, although often fraught with peril, paved the way for future explorers and settlers, leaving an indelible mark on the course of history. As we delve into the details of Hudson's routes, we gain insight into the motivations, challenges, and outcomes of his historic journeys, enriching our understanding of this transformative period in history.
Table of Contents
Henry Hudson: The Man Behind the Compass
Henry Hudson, an English sea explorer, and navigator, was a pivotal figure during the Age of Exploration, known for his attempts to find a shorter route to Asia from Europe through the Arctic Ocean. His life, though shrouded in mystery and marked by a tragic end, was filled with remarkable achievements that significantly contributed to the geographic and commercial expansion of the time. Hudson's legacy is immortalized in the names of the Hudson River, Hudson Strait, and Hudson Bay, each a testament to his enduring impact on exploration.
Henry Hudson was born in the late 16th century, with the exact year remaining uncertain, adding to the enigmatic aura surrounding his life. Despite this ambiguity, Hudson's contributions to exploration are well-documented through his voyages, which were primarily sponsored by English and Dutch trading companies. His dedication to discovering new trade routes and his resilience in the face of adversity highlight his significance as an explorer.
Hudson's expeditions were instrumental in the European exploration of North America, particularly in the regions that would later become parts of Canada and the United States. His efforts to find the elusive Northwest Passage were driven by the promise of lucrative trade opportunities with Asia, a goal that remained unattainable but nonetheless led to significant discoveries that shaped the future of exploration and settlement in the New World.
| Personal Details | Information |
|---|---|
| Full Name | Henry Hudson |
| Birth Date | c. 1565 |
| Nationality | English |
| Occupation | Explorer, Navigator |
| Known For | Exploration of the Hudson River, Hudson Strait, and Hudson Bay |
| Spouse | Katherine Hudson |
| Children | John Hudson |
| Death | 1611 (presumed) |
Early Life and Inspirations
Henry Hudson's early life remains largely a mystery, with scant documentation available to paint a comprehensive picture of his formative years. Born into a time of great maritime exploration and burgeoning trade opportunities, Hudson's formative years were likely shaped by the spirit of adventure and discovery that characterized the late 16th and early 17th centuries. While little is known about his family background or early education, it is believed that Hudson came from a family with strong ties to maritime trade, which may have influenced his career path.
The era in which Hudson lived was marked by significant advancements in navigation and cartography, driven by the desire to expand trade networks and explore uncharted territories. The lure of discovering new trade routes to Asia was a powerful motivator for many explorers, including Hudson, whose expeditions were primarily focused on finding a more direct path to the riches of the East. This period of exploration was fueled by the economic and political ambitions of European nations, eager to establish dominance in global trade.
Hudson's inspirations likely stemmed from the achievements of earlier explorers, such as Christopher Columbus and John Cabot, whose voyages had opened new worlds and possibilities for European expansion. The tales of these explorers, coupled with the support of influential patrons and trading companies, would have ignited Hudson's passion for exploration and his determination to chart new courses across the seas.
The First Voyage: Searching for the Northeast Passage
Henry Hudson embarked on his first voyage in 1607, under the sponsorship of the Muscovy Company, with the ambitious goal of discovering a northeast passage to Asia. Setting sail from London aboard the ship Hopewell, Hudson and his crew ventured into the icy waters of the Arctic, exploring the region around Greenland and the North Pole. This expedition was marked by harsh conditions, including freezing temperatures, treacherous ice floes, and limited visibility, which ultimately hindered their progress.
Despite the challenges faced during this first voyage, Hudson's journey provided valuable insights into the Arctic regions, contributing to the growing body of geographical knowledge of the time. While the northeast passage remained elusive, Hudson's observations and reports from the expedition were instrumental in shaping future exploration strategies and understanding the complexities of navigating Arctic waters.
This first voyage set the stage for Hudson's subsequent expeditions, establishing him as a determined and resourceful navigator. His ability to chart new territories and gather valuable information about the Arctic environment underscored his expertise and tenacity as an explorer, paving the way for future attempts to find alternative routes to Asia.
The Second Voyage: Encounters with the Arctic
Following the partial success of his first expedition, Henry Hudson embarked on a second voyage in 1608, once again seeking the elusive northeast passage to Asia. With the backing of the Muscovy Company, Hudson set sail aboard the Hopewell, determined to push further into the Arctic regions. This expedition took him to the vicinity of Novaya Zemlya, an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean, where he encountered even harsher conditions than before.
During this voyage, Hudson and his crew faced numerous challenges, including severe weather, navigational difficulties, and dwindling supplies. Despite these obstacles, Hudson's persistence and navigational skills allowed him to gather valuable data about the Arctic environment, further expanding the geographical understanding of the region. His observations during this expedition contributed to the growing body of knowledge about the Arctic, helping to inform future explorations and navigation strategies.
The second voyage, while ultimately unsuccessful in finding a passage to Asia, reinforced Hudson's reputation as a skilled navigator and explorer. His determination to overcome the formidable challenges posed by the Arctic environment demonstrated his commitment to exploring new frontiers, setting the stage for his subsequent voyages and discoveries.
The Third Voyage: The Discovery of the Hudson River
In 1609, Henry Hudson embarked on what would become his most famous voyage, leading to the discovery of the river that now bears his name. This expedition, sponsored by the Dutch East India Company, marked a significant turning point in Hudson's career, as he shifted his focus from the northeast to the northwest in search of a passage to Asia. Aboard the ship Half Moon, Hudson set sail across the Atlantic, navigating the treacherous waters of the North Atlantic Ocean.
Hudson's journey took him along the eastern coast of North America, where he explored various bays and estuaries, searching for a navigable route to the Pacific. During this expedition, Hudson and his crew navigated the waters of what is now known as the Hudson River, traveling as far inland as present-day Albany, New York. This discovery was a monumental achievement, as it provided valuable insights into the geography of the region and opened new possibilities for trade and settlement.
The discovery of the Hudson River had far-reaching implications, contributing to the eventual establishment of Dutch settlements in the region and the expansion of European influence in North America. Hudson's exploration of the river laid the groundwork for future exploration and colonization, highlighting the strategic importance of the area for trade and navigation.
The Fourth Voyage: Tragedy in the Hudson Bay
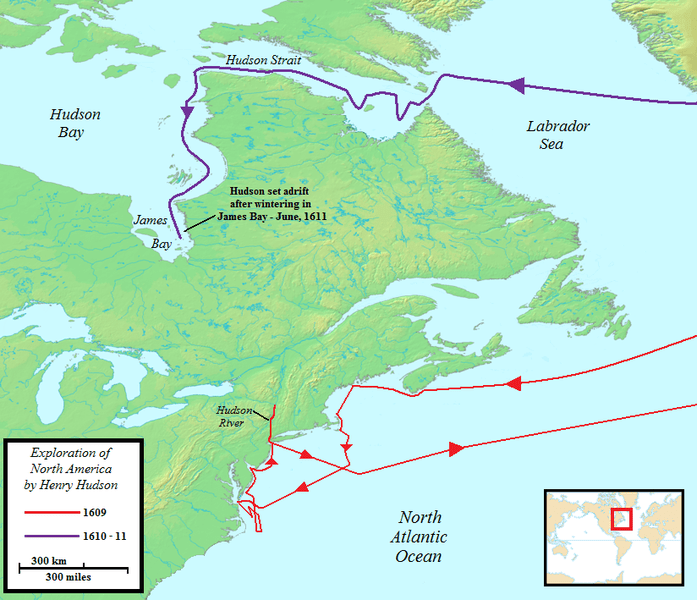
Henry Hudson's fourth and final voyage, undertaken in 1610-1611, was a perilous journey that ultimately ended in tragedy. Sponsored by English merchants eager to find the Northwest Passage, Hudson set sail aboard the Discovery, navigating the treacherous waters of the North Atlantic once again. This time, his journey led him into the vast expanse of the Hudson Bay, a region that would prove both promising and perilous.
Initially, Hudson and his crew were hopeful that they had found the long-sought passage to Asia, but as they explored the bay, it became clear that it was a dead end. The harsh winter conditions, combined with dwindling supplies and mounting tensions among the crew, created a volatile situation aboard the Discovery. As the months passed, discontent grew, leading to a mutiny in June 1611, where Hudson, his son, and several loyal crew members were cast adrift in a small boat, never to be seen again.
The tragic end of Hudson's final voyage marked a somber conclusion to his storied career as an explorer. Despite the challenges and ultimate failure of the expedition, Hudson's exploration of the Hudson Bay region provided valuable geographical insights and laid the groundwork for future explorations in the area. His legacy as a determined and visionary explorer endures, serving as a reminder of the trials and triumphs of early exploration.
Mapping the Routes: A Cartographer's Dream
Henry Hudson's expeditions significantly contributed to the cartographic knowledge of the time, providing valuable data and insights that helped shape the maps of the New World. The routes he charted during his voyages were instrumental in expanding the geographical understanding of North America, particularly in the regions surrounding the Hudson River, Hudson Strait, and Hudson Bay.
Hudson's meticulous observations and documentation of the landscapes, waterways, and climatic conditions encountered during his journeys provided cartographers with crucial information for creating more accurate maps. His discoveries and routes were carefully recorded and shared with other explorers and navigators, enhancing the collective knowledge of the time and paving the way for future explorations.
The maps created from Hudson's voyages were vital tools for subsequent explorers, traders, and settlers, guiding them through the uncharted territories of North America. These maps played a crucial role in the expansion of European influence in the New World, facilitating trade, colonization, and the establishment of new settlements. Hudson's contributions to cartography remain a testament to his enduring impact on the field of exploration and navigation.
Impact on Exploration and Trade
Henry Hudson's routes had a profound impact on the exploration and trade dynamics of the early 17th century, shaping the course of European expansion in the New World. His voyages opened new avenues for trade and exploration, providing European powers with valuable insights into the geography and resources of North America.
Hudson's discovery of the Hudson River, in particular, had significant implications for trade and settlement. The river served as a vital waterway for transporting goods and people, facilitating the establishment of Dutch settlements in the region. These settlements, including the city of New Amsterdam (modern-day New York City), became key centers of trade and commerce, contributing to the economic growth and development of the area.
Moreover, Hudson's exploration of the Hudson Bay region and the surrounding areas provided valuable information about the natural resources and potential trade opportunities in the region. These discoveries spurred further exploration and the eventual establishment of trade networks that connected the New World with Europe, Asia, and beyond.
Cultural Significance and Legacy
The cultural significance of Henry Hudson's routes extends beyond their geographic and economic impact. His voyages are emblematic of the spirit of exploration and discovery that characterized the Age of Exploration, a period that transformed the world's understanding of geography and expanded the horizons of human knowledge.
Hudson's legacy is preserved in the names of the Hudson River, Hudson Strait, and Hudson Bay, each a testament to his enduring impact on exploration and navigation. These waterways continue to hold cultural and historical significance, serving as reminders of the challenges and triumphs of early exploration.
In addition to their historical importance, Hudson's routes have inspired countless stories, myths, and legends, reflecting the enduring fascination with exploration and the unknown. His journeys have been the subject of numerous books, films, and artistic works, highlighting the timeless allure of discovery and the quest for new frontiers.
Challenges Faced During the Expeditions
Henry Hudson's expeditions were fraught with numerous challenges, both environmental and human, that tested his skills as a navigator and leader. The harsh conditions of the Arctic and North Atlantic regions posed significant obstacles, including extreme weather, treacherous ice floes, and limited visibility, which made navigation difficult and dangerous.
In addition to the environmental challenges, Hudson faced logistical difficulties, such as dwindling supplies, inadequate equipment, and the constant threat of mutiny among his crew. The isolation and uncertainty of long sea voyages often led to tensions and conflicts aboard the ships, requiring Hudson to exercise strong leadership and decision-making skills to maintain order and morale.
Despite these formidable challenges, Hudson's determination and resilience enabled him to persevere and make significant contributions to the field of exploration. His ability to navigate the unknown and adapt to changing circumstances underscored his expertise and commitment to his goals, leaving a lasting legacy of discovery and exploration.
Scientific Contributions and Discoveries
Henry Hudson's expeditions were not only significant for their geographical discoveries but also for their contributions to the scientific understanding of the time. His voyages provided valuable data on the Arctic and North Atlantic regions, including information about the climate, wildlife, and natural resources encountered during his journeys.
Hudson's meticulous observations and documentation of the environments he explored contributed to the growing body of scientific knowledge about the Earth's geography and ecosystems. His reports and findings were shared with other explorers, scientists, and navigators, helping to inform future exploration efforts and advance the understanding of the natural world.
The scientific contributions of Hudson's expeditions extended beyond their immediate impact, influencing the development of navigation techniques, cartography, and the study of the Earth's climate and ecosystems. His legacy as a pioneer of exploration and scientific discovery continues to inspire future generations of explorers and scientists.
The Mutiny and the Mystery of Hudson's Fate
The mutiny that marked the tragic end of Henry Hudson's final voyage remains one of the most enigmatic and compelling aspects of his legacy. In June 1611, as tensions aboard the Discovery reached a boiling point, Hudson and several loyal crew members were set adrift in a small boat in the Hudson Bay, never to be seen again. The circumstances surrounding the mutiny and Hudson's fate have been the subject of speculation and intrigue for centuries.
While the exact details of the mutiny remain unclear, it is believed that the harsh conditions, dwindling supplies, and Hudson's leadership style contributed to the crew's discontent and eventual rebellion. The fate of Hudson and his companions remains a mystery, with no definitive evidence of their survival or demise.
The mystery of Hudson's fate has captured the imagination of historians, writers, and explorers, inspiring countless theories, stories, and legends. Despite the uncertainty surrounding his final days, Hudson's legacy as a determined and visionary explorer endures, serving as a reminder of the risks and rewards of exploration.
A Modern Perspective on Hudson's Routes
In the modern era, Henry Hudson's routes continue to hold significance for historians, geographers, and explorers, offering valuable insights into the history of exploration and the development of global trade networks. The waterways and regions explored by Hudson remain important for their strategic and economic value, serving as vital transportation routes and centers of commerce.
Hudson's legacy as an explorer is celebrated through various commemorations, including monuments, museums, and educational programs that highlight his contributions to the field of exploration. These efforts serve to preserve the memory of Hudson's achievements and inspire future generations to explore and discover new frontiers.
The story of Henry Hudson and his routes is a testament to the enduring human spirit of exploration, curiosity, and the desire to understand and connect with the world. As we continue to explore and learn about our planet, Hudson's legacy serves as a reminder of the importance of perseverance, innovation, and the quest for knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions
What were the main goals of Henry Hudson's expeditions?
The primary goal of Henry Hudson's expeditions was to find a shorter sea route to Asia, known as the Northwest Passage, which would facilitate trade and commerce. Despite not finding the passage, Hudson's voyages contributed to the exploration and mapping of parts of North America.
How did Hudson's discoveries impact European colonization?
Hudson's discoveries, particularly the Hudson River, played a significant role in European colonization by providing strategic trade routes and facilitating the establishment of settlements, such as New Amsterdam, which later became New York City.
What challenges did Hudson face during his voyages?
Hudson faced numerous challenges, including harsh weather conditions, treacherous ice floes, limited supplies, and the threat of mutiny among his crew. These challenges tested his navigational skills and leadership abilities throughout his expeditions.
Is there any evidence of Hudson's fate after the mutiny?
The fate of Henry Hudson after the mutiny remains a mystery, as there is no definitive evidence of his survival or demise. Hudson and his loyal crew members were set adrift in a small boat in the Hudson Bay and were never seen again.
How did Hudson's voyages contribute to scientific knowledge?
Hudson's meticulous observations and documentation of the Arctic and North Atlantic regions provided valuable data on climate, wildlife, and natural resources, contributing to the scientific understanding of the Earth's geography and ecosystems.
What is the cultural significance of the Hudson River today?
The Hudson River holds cultural and historical significance as a symbol of exploration and discovery. It continues to serve as an important transportation route and center of commerce, while also inspiring stories, artworks, and educational programs that celebrate Hudson's legacy.
Conclusion: The Legacy of Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson's routes represent a pivotal chapter in the history of exploration, marking a period of significant geographical discoveries and advancements in navigation. His voyages, driven by the ambition to find new trade routes, inadvertently led to the exploration and mapping of parts of North America, contributing to the expansion of European influence in the New World.
Hudson's legacy as an explorer is immortalized in the names of the Hudson River, Hudson Strait, and Hudson Bay, each a testament to his enduring impact on exploration and navigation. His contributions to cartography, trade, and scientific knowledge continue to be recognized and celebrated, inspiring future generations to explore and discover new frontiers.
As we reflect on Henry Hudson's routes and their significance, we are reminded of the enduring human spirit of exploration and the quest for knowledge. Hudson's journeys serve as a testament to the challenges and triumphs of early exploration, highlighting the importance of perseverance, innovation, and the desire to connect with the world. His legacy endures, enriching our understanding of history and inspiring us to continue exploring the unknown.
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmrK2TmLK0v4yepaChnpp8qbHNq7BmoKWZwLC6jKumrqyVqHupwMyl