In today's rapidly evolving world, the concept of growth has taken on new dimensions, particularly in the context of businesses and economies. The phrase "involved to grow rapidly from early cycles to later cycles" encapsulates a crucial aspect of development that many organizations must navigate. In this article, we will explore the various factors contributing to this phenomenon, discussing the implications for businesses, economies, and societies. Additionally, we will provide actionable insights for stakeholders looking to harness the power of growth cycles effectively.
The journey of growth is not linear; it is a complex interplay of various elements that can either propel an organization forward or hinder its progress. Understanding these cycles is essential for anyone involved in strategic planning, investment, or management. As we delve into this topic, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of the stages of growth, the challenges faced, and the strategies employed to thrive in each cycle.
By examining real-world examples and drawing on data from credible sources, we hope to equip readers with a deeper understanding of how involvement in early cycles can lead to rapid growth in later cycles. This article will serve as a valuable resource for entrepreneurs, investors, and anyone interested in the dynamics of growth.
Table of Contents
Understanding Growth Cycles
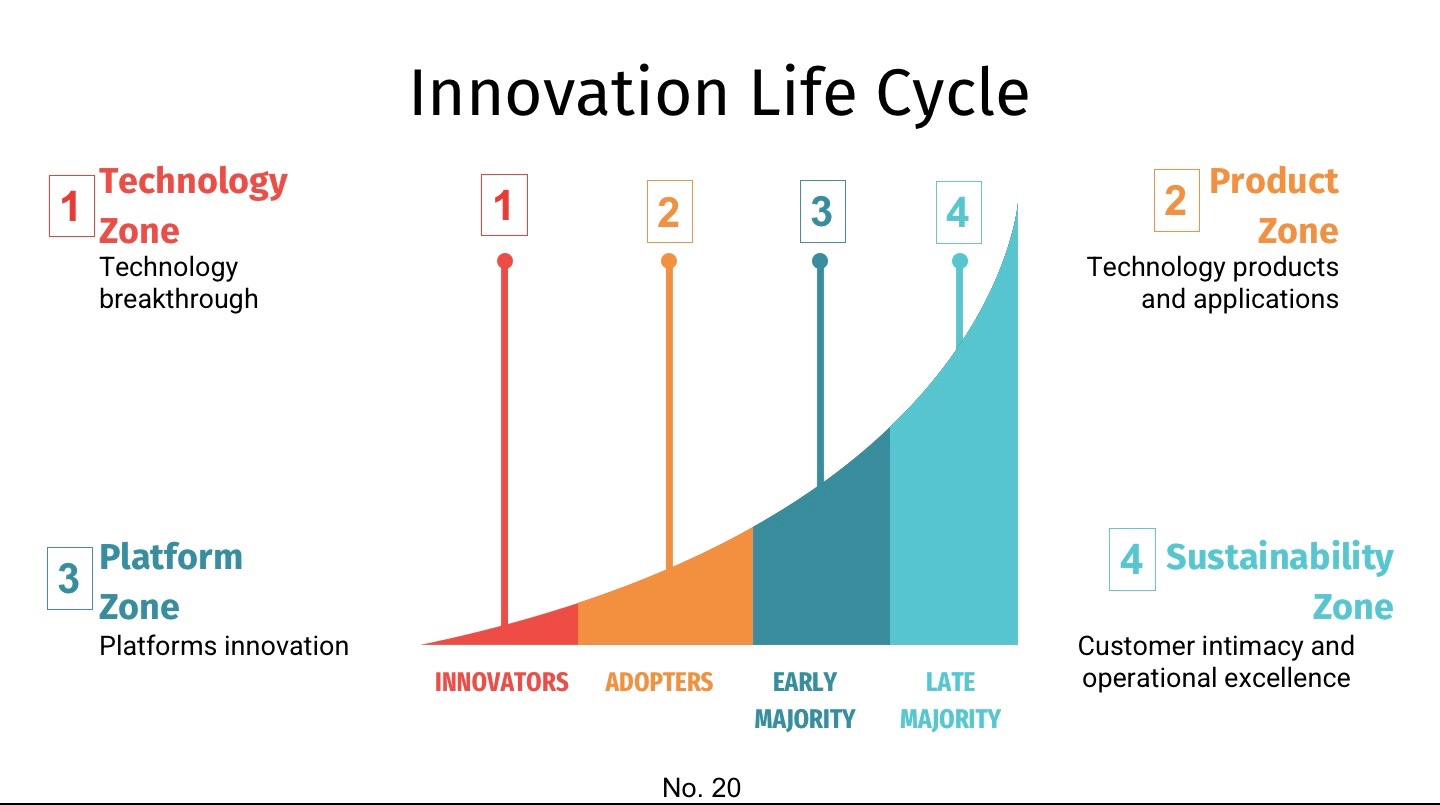
Growth cycles refer to the various stages an organization or economy goes through as it develops over time. Typically, these cycles can be divided into several phases, including:
- **Introduction**: This is the initial phase where a product or service is launched.
- **Growth**: In this phase, sales begin to increase rapidly as the market begins to recognize the value of the offering.
- **Maturity**: Growth stabilizes as the market becomes saturated.
- **Decline**: Sales begin to decrease as new competitors enter the market or consumer preferences shift.
Understanding these stages is crucial for stakeholders, as each phase presents unique opportunities and challenges.
The Role of Involvement in Early Cycles
Involvement in early cycles is critical for setting the foundation for future growth. This involvement can take many forms, including:
- **Investment**: Early financial backing can provide the necessary resources for development.
- **Networking**: Building relationships with key stakeholders can enhance credibility and open doors to new opportunities.
- **Market Research**: Understanding consumer needs early on can guide product development and marketing strategies.
Through active involvement in these areas, organizations can position themselves favorably for later growth cycles.
Challenges in Early Growth Cycles
While early growth cycles present opportunities, they are also fraught with challenges. Common obstacles include:
- **Cash Flow Management**: Many startups struggle with managing cash flow effectively.
- **Market Competition**: Entering a competitive market can be daunting for new entrants.
- **Resource Allocation**: Deciding where to allocate resources for maximum impact can be challenging.
Understanding these challenges is essential for developing effective strategies to overcome them.
Strategies for Success in Later Cycles
To ensure sustained growth in later cycles, organizations should consider the following strategies:
- **Diversification**: Expanding product lines or markets can reduce risk.
- **Continuous Innovation**: Regularly updating offerings can keep the brand relevant.
- **Customer Engagement**: Building strong relationships with customers can enhance loyalty.
Implementing these strategies can help organizations transition smoothly from early to later growth cycles.
Case Studies of Rapid Growth
Examining real-world examples can provide valuable insights into successful growth strategies. Some notable case studies include:
- **Company A**: This company leveraged early involvement in technology to dominate the market.
- **Company B**: By focusing on customer engagement, this firm turned challenges into opportunities for growth.
These case studies illustrate how strategic involvement in early cycles can lead to rapid growth in later cycles.
The Impact of Technology on Growth Cycles
Technology plays a pivotal role in shaping growth cycles. Key impacts include:
- **Increased Efficiency**: Technology can streamline processes, reducing operational costs.
- **Market Reach**: Digital platforms enable businesses to reach a global audience.
- **Data-Driven Decisions**: Technology allows for better data analysis, leading to informed decision-making.
Organizations that embrace technology are better positioned to navigate growth cycles effectively.
The Global Perspective on Growth
Growth is not limited to individual organizations; it has global implications. Factors influencing global growth include:
- **Economic Policies**: Government regulations can either facilitate or hinder growth.
- **Globalization**: The interconnectedness of markets can create new opportunities.
- **Cultural Shifts**: Changing consumer preferences can influence market dynamics.
Understanding these global factors is essential for organizations looking to expand their reach.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, involvement in early cycles is a crucial determinant of success in later growth cycles. By understanding the dynamics of growth, organizations can develop effective strategies to navigate challenges and seize opportunities. We encourage readers to share their thoughts on this topic in the comments section and explore our other articles for more insights on growth strategies.
Thank you for taking the time to read this article! We look forward to welcoming you back for more engaging content in the future.
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8qrrVqKOvnZRiwbB5xqumsGWilr2qsMuyZJ%2Bqn6J6pq3RpbBmm6mYuaa%2FjK2mZqSRqbKzecKymqWdo2K7sLrEZqafZaSdsm%2B006aj