In a perfectly competitive industry, each firm operates under conditions that define the market dynamics and consumer choices. Understanding how these firms interact, respond to market changes, and sustain their operations is crucial for both new entrants and existing players in the market. This article delves into the characteristics of perfect competition, the role of individual firms, and the broader implications for the economy.
The concept of perfect competition serves as a foundational theory in economics, illustrating an idealized market structure where numerous small firms compete against one another. Each firm is a price taker, meaning they accept the market price as given and cannot influence it. This article will explore various aspects of perfect competition, focusing on how each firm operates within this framework and the implications for consumers and the economy as a whole.
As we navigate through this topic, we will cover essential aspects such as the characteristics of perfectly competitive markets, the role of supply and demand, firm behavior, and the long-term sustainability of firms in such an environment. By the end of this article, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of the dynamics at play in a perfectly competitive industry.
Table of Contents
Characteristics of Perfectly Competitive Markets
Perfectly competitive markets exhibit several distinct characteristics:
- Many Buyers and Sellers: The market consists of a large number of buyers and sellers, ensuring that no single entity can control the market price.
- Homogeneous Products: The products offered by different firms are identical, making them perfect substitutes for consumers.
- Free Entry and Exit: Firms can easily enter or exit the market without significant barriers, promoting competition and innovation.
- Perfect Information: All market participants have access to complete information about prices and products, facilitating informed decision-making.
Role of Each Firm in the Market
In a perfectly competitive industry, each firm plays a crucial role in maintaining the market equilibrium:
- Price Takers: Firms cannot influence prices due to their small size relative to the market. They accept the market-determined price.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Firms strive to minimize production costs and maximize efficiency, leading to optimal resource allocation.
- Innovation and Quality: While products are homogeneous, firms compete on factors like quality and customer service to attract consumers.
Impact on Consumers
The competitive nature of the market benefits consumers through:
- Lower prices due to competition.
- Increased product quality and variety.
- Better customer service as firms strive to retain customers.
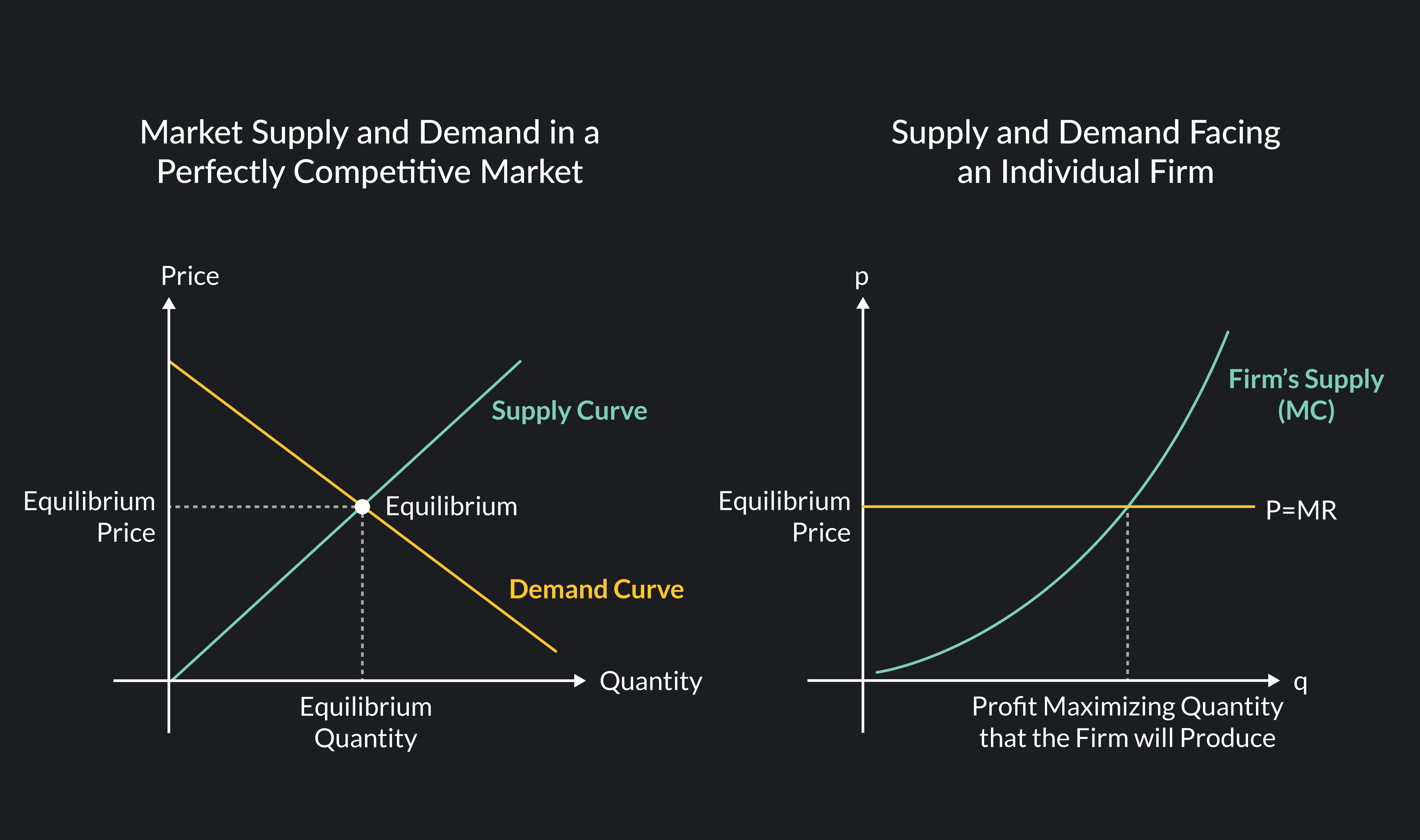
Supply and Demand Dynamics
The interaction of supply and demand is fundamental in a perfectly competitive market:
- Market Equilibrium: The price is determined at the point where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded.
- Shifts in Supply and Demand: Changes in consumer preferences or production costs can shift the supply and demand curves, impacting equilibrium prices.
Behavior of Firms in Perfect Competition
Firms in a perfectly competitive market exhibit specific behaviors to survive and thrive:
- Cost Minimization: Firms focus on reducing production costs to maintain profitability at the market price.
- Output Decisions: Firms determine their optimal output level where marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
- Market Entry Strategies: New firms may enter the market if existing firms are making profits, leading to increased competition.
Long-Term Viability of Firms
In the long run, perfectly competitive firms tend to achieve:
- Normal Profits: Firms earn just enough to cover their costs, including opportunity costs.
- Market Equilibrium: Over time, the market reaches an equilibrium where supply equals demand, stabilizing prices.
Challenges Faced by Firms
Despite the benefits of perfect competition, firms face several challenges:
- Price Wars: Intense competition can lead to price wars, eroding profit margins.
- Market Saturation: As new firms enter, markets can become saturated, leading to fierce competition.
Case Studies of Perfectly Competitive Industries
Several industries exemplify characteristics of perfect competition:
- Agricultural Products: Many agricultural markets display perfect competition, with numerous farmers selling identical products.
- Stock Market: The exchange of stocks also reflects perfect competition, where numerous buyers and sellers interact.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
Understanding the dynamics of a perfectly competitive industry is essential for firms and consumers alike. Each firm operates under unique constraints while contributing to the overall market structure. The principles of perfect competition emphasize the importance of efficiency, innovation, and consumer welfare. As markets evolve, firms must adapt to changing conditions to maintain their viability and relevance. We encourage readers to share their insights and experiences regarding competition in their industries.
For further reading or to engage in discussions about market dynamics, feel free to leave a comment or explore more articles on our site!
Thank you for visiting, and we hope to see you again soon!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8qrqMmmSpnaKbsqTAy7JknKedpbK1tdOirZ5lmaOxtr%2FTq7BmnZGYtW6yyKukZ6Ckork%3D