Waves are a fundamental aspect of physics, influencing various fields such as oceanography, acoustics, and even engineering. When discussing waves, one critical property that often comes into play is amplitude, which refers to the maximum extent of a vibration or oscillation, measured from the position of equilibrium. In this article, we will delve into waves with an amplitude of 3.5 m, exploring their properties, significance, and applications in real-world scenarios.
The concept of amplitude is crucial in understanding wave behavior, especially in contexts such as sound waves, seismic waves, and water waves. An amplitude of 3.5 m is significant, as it indicates a considerable level of energy and disturbance in the medium through which the wave travels. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of why amplitude matters, how it affects wave propagation, and its implications in various scientific and practical applications.
Moreover, we will explore the relationship between amplitude and other wave characteristics such as wavelength, frequency, and energy. By the end of this article, readers will have a thorough understanding of waves with an amplitude of 3.5 m and their relevance across different domains.
Table of Contents
What is Amplitude?
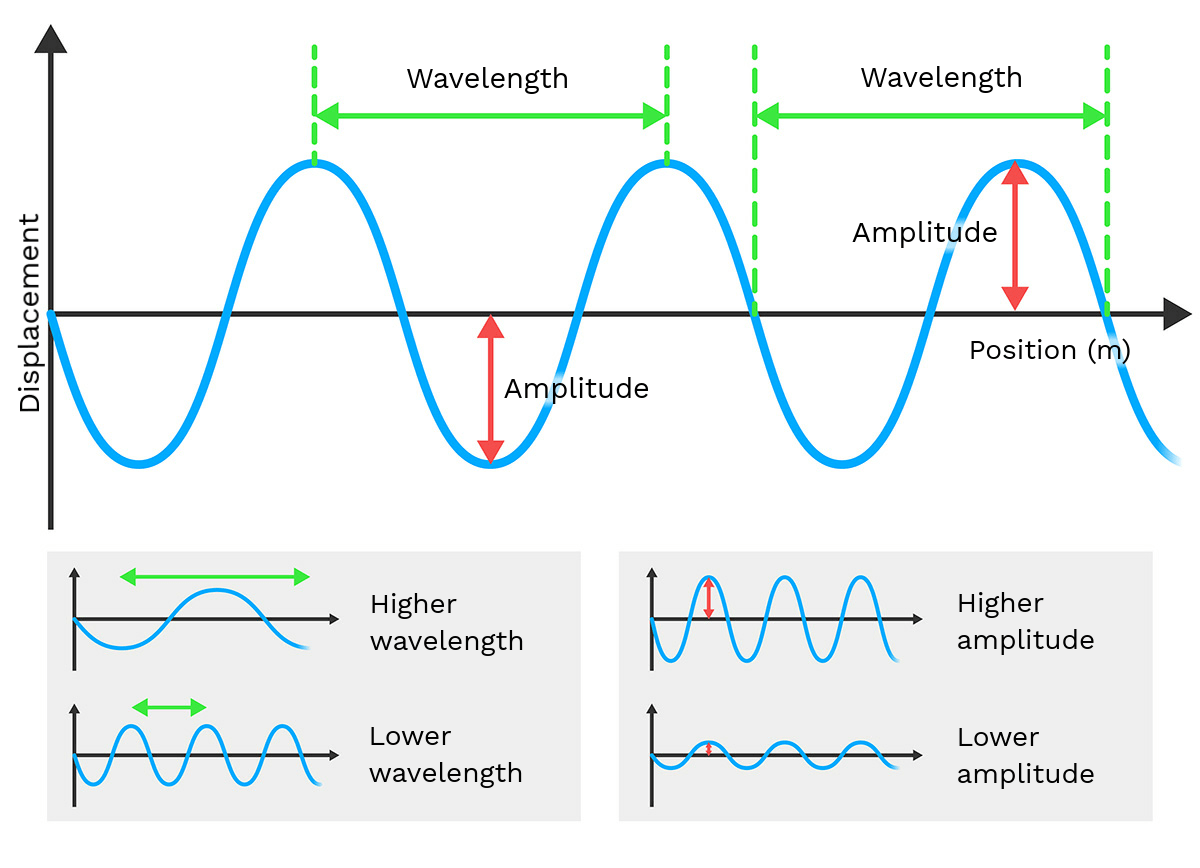
Amplitude is defined as the maximum displacement of points on a wave from its rest position. In simpler terms, it is the height of the wave measured from the equilibrium position to the crest. In waves with an amplitude of 3.5 m, this signifies that the wave can reach a maximum height of 3.5 meters above the equilibrium level.
Amplitude is a critical factor in determining the energy and intensity of a wave. The higher the amplitude, the more energy the wave carries. This property is particularly important in various fields, including:
- Seismology: Understanding earthquake waves.
- Acoustics: Determining sound intensity.
- Hydrodynamics: Analyzing water waves.
Properties of Waves
Waves display several key properties, including:
- Wavelength: The distance between consecutive crests or troughs.
- Frequency: The number of waves that pass a point in a given time period.
- Speed: How fast the wave travels through a medium.
- Amplitude: The maximum height of the wave.
Understanding these properties is essential for analyzing wave behavior, especially in contexts involving high amplitudes like 3.5 m.
Types of Waves
Waves can be classified into two main categories: mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves.
Mechanical Waves
Mechanical waves require a medium (solid, liquid, or gas) to travel through. Examples include:
- Sound Waves: Vibrations that travel through air or other media.
- Water Waves: Oscillations on the surface of water bodies.
- Seismic Waves: Waves generated by earthquakes.
Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium and can travel through a vacuum. Examples include:
- Radio Waves: Used in communication systems.
- Light Waves: Visible light traveling from the sun.
- X-rays: Used in medical imaging.
Significance of Amplitude
The amplitude of a wave is a crucial parameter that affects various characteristics:
- Energy: Greater amplitude equates to higher energy. For example, an ocean wave with an amplitude of 3.5 m carries significant energy that can lead to coastal erosion.
- Intensity: In sound waves, a higher amplitude results in louder sounds, impacting hearing and acoustics.
- Impact on Structures: In engineering, understanding wave amplitudes is vital for designing buildings and structures that can withstand seismic activity.
Calculating Energy in Waves
The energy carried by a wave is directly proportional to the square of its amplitude. The formula for the energy (E) of a wave can be expressed as:
E = k * A²
Where:
- E: Energy of the wave
- A: Amplitude of the wave
- k: Constant depending on the type of wave
For waves with an amplitude of 3.5 m, this equation allows for the calculation of the energy carried by such waves, providing insights into their potential impacts.
Real-World Applications of Waves with Amplitude of 3.5 m
Waves with significant amplitudes, such as 3.5 m, have various practical applications, including:
- Coastal Engineering: Understanding wave behavior helps design sea walls and coastal defenses.
- Seismology: Predicting the impact of earthquakes based on wave amplitudes.
- Acoustic Engineering: Designing auditoriums and public spaces for optimal sound quality.
Environmental Impact of High Amplitude Waves
High amplitude waves can have both positive and negative environmental impacts:
- Coastal Erosion: Powerful waves can erode beaches and cliffs, altering landscapes.
- Habitat Disruption: Strong waves can disrupt marine habitats, affecting biodiversity.
- Wave Energy: Harnessing wave energy can provide renewable energy sources.
Future Research Directions
Future research on waves with amplitudes like 3.5 m may include:
- Wave Energy Conversion: Developing more efficient systems to convert wave energy into usable power.
- Climate Change Studies: Understanding how changing sea levels affect wave behavior.
- Advanced Modeling Techniques: Using computer simulations to predict wave patterns and impacts.
Conclusion
In summary, waves with an amplitude of 3.5 m represent a fascinating area of study within the field of physics. Understanding their properties, significance, and real-world applications can provide valuable insights into various domains, including environmental science, engineering, and acoustics. We encourage readers to explore further, leave comments, and share this article with others interested in wave phenomena.
Penutup
Kami berharap artikel ini memberikan pemahaman yang lebih dalam tentang gelombang dengan amplitudo 3.5 m. Silakan kembali ke situs kami untuk artikel menarik lainnya dan berbagi pemikiran Anda di kolom komentar di bawah!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8uLXToWSapl2WurG4yK2snZ1dpLNuf5RmpGegpKK5