In today's complex society, a stratification system plays a crucial role in determining the position of each individual within various social, economic, and political contexts. Understanding this system is essential for comprehending how social mobility works and the implications it has for individuals and communities. This article delves into the intricacies of social stratification, exploring its definitions, types, and the impact it has on people's lives.
Stratification refers to the hierarchical arrangement of individuals in a society based on various factors such as wealth, income, race, education, and power. The concept of social stratification implies that not all individuals have equal access to resources, opportunities, and privileges, which significantly affects their life chances. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of stratification systems, their characteristics, and their implications on individual positioning within society.
Moreover, we will discuss the various theories of stratification, the impact of globalization on social hierarchies, and the role of education in facilitating upward mobility. By the end of this article, readers will gain insight into the importance of addressing social inequalities and the need for a more equitable society.
Table of Contents
What is Stratification?
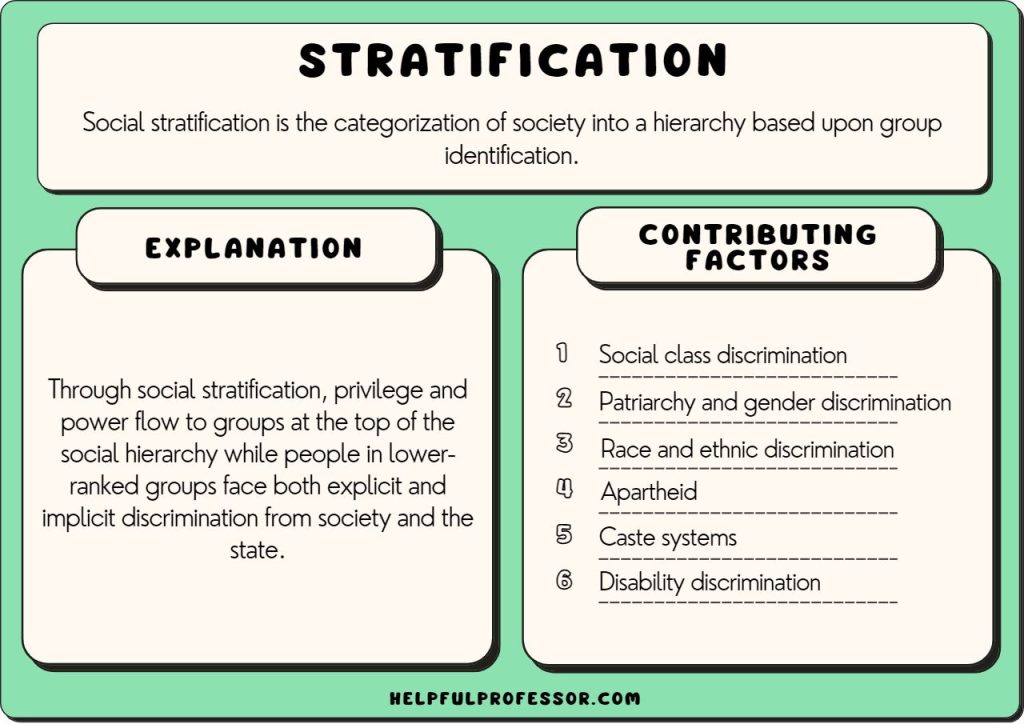
Social stratification is a system by which a society ranks categories of people in a hierarchy. This stratification can be based on several factors, including:
- Wealth and income
- Education and occupation
- Race and ethnicity
- Gender
- Social status and prestige
These factors create a layered structure that dictates the level of access individuals have to resources and opportunities. Stratification influences every aspect of life, from the opportunities available to individuals to their social interactions and relationships.
Types of Stratification
There are several types of social stratification, including:
1. Caste System
The caste system is a form of social stratification found primarily in India, where individuals are born into a specific social group. This system is rigid, with little opportunity for mobility between castes.
2. Class System
The class system is more fluid than the caste system, allowing for social mobility based on factors such as education and income. In this system, individuals are categorized into classes, typically upper, middle, and lower classes.
3. Meritocracy
In a meritocratic system, individuals are rewarded based on their abilities, talents, and efforts. This system is grounded in the belief that everyone has an equal opportunity to succeed, although this is often not the case in reality.
Theories of Stratification
Several theories explain the dynamics of social stratification:
- Functionalist Theory: This theory posits that stratification is necessary for the functioning of society, as it ensures that the most qualified individuals fill the most important roles.
- Conflict Theory: In contrast, conflict theory argues that stratification results from the unequal distribution of resources and power, leading to social conflict.
- Weberian Theory: Max Weber expanded on the concept of stratification by introducing additional dimensions such as status and party, which interact with class to create a more nuanced understanding of social hierarchies.
Impact of Globalization on Stratification
Globalization has significantly impacted social stratification by altering economic structures, cultural exchanges, and political dynamics. Some of the effects include:
- Increased economic inequality as wealth becomes concentrated in certain regions.
- The rise of a global elite class, while many remain in poverty.
- Changes in labor markets and job availability due to outsourcing and technological advancements.
Education and Social Mobility
Education plays a pivotal role in social mobility, serving as a primary pathway for individuals to improve their socioeconomic status. Key points include:
- Access to quality education is often stratified based on income and geography.
- Higher education is correlated with better job opportunities and higher income levels.
- Educational attainment can break the cycle of poverty for individuals and families.
Effects of Stratification on Individuals
Social stratification has profound effects on individuals, including:
- Access to healthcare and social services.
- Opportunities for personal and professional development.
- Impact on mental health and well-being.
Case Studies of Stratification
Analyzing real-world examples of stratification can provide insights into its implications. Case studies may include:
- The impact of the class system in the United States.
- The implications of the caste system in India.
- Global disparities in education and income across different countries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the stratification system is vital for recognizing the complexities of social hierarchies and their impact on individuals. It is essential to address these inequalities to foster a more equitable society. We encourage readers to reflect on their own positions within this system and consider ways to contribute to social change. For further discussion, feel free to leave a comment, share this article, or explore more content on our site.
Thank you for taking the time to read this article. We hope to see you again for more insights and discussions on social issues!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8onnSramarJmbtqSt06Kmp2WjrsC1scxmq6GZpGK2rrzLopysZaSdrrV506GcZqifqLa1tc6nZKieXZqupLSMoqWdoaaesbaty2efraWc