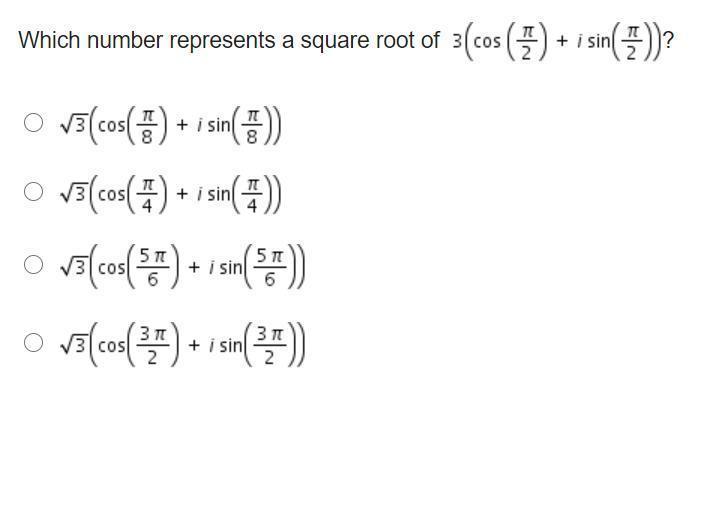
Mathematics is a vast field that encompasses various concepts and terminologies, and one of the intriguing aspects of it is understanding complex numbers and their applications. In this article, we will explore the equation (endfraction) + i sine (startfraction 3 pi over 4 endfraction) and z 2, breaking down the components and their relevance in mathematical theory. We aim to provide clarity on these concepts, making them accessible to readers who may find mathematics daunting.
We will discuss the importance of complex numbers, their representation in the polar form, and how sine functions play a vital role in this context. Additionally, we will examine the implications of these mathematical expressions in real-world scenarios, showcasing their importance in various fields such as engineering and physics.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the mathematical expression we are analyzing, as well as insights into its practical applications. Let us embark on this mathematical journey together!
Table of Contents
1. Understanding Complex Numbers
Complex numbers are numbers that consist of a real part and an imaginary part. The standard form of a complex number is expressed as:
z = a + bi
Where:
- z represents the complex number
- a is the real part
- b is the imaginary part
- i is the imaginary unit, defined as i² = -1
Complex numbers can be represented graphically on a plane known as the complex plane, where the x-axis represents the real part and the y-axis represents the imaginary part.
2. Introduction to Polar Form
Polar form is an alternative way to express complex numbers. Instead of using the rectangular form (a + bi), we can represent complex numbers in terms of their magnitude and angle:
z = r (cos θ + i sin θ)
Where:
- r is the magnitude of the complex number, calculated as r = √(a² + b²)
- θ is the argument or angle, which can be found using the arctan function: θ = arctan(b/a)
This representation is particularly useful in multiplication and division of complex numbers, as it simplifies the calculations.
3. The Role of Sine in Complex Numbers
The sine function plays a crucial role in the representation of complex numbers in polar form. The expression i sin θ signifies the imaginary component of the complex number. The sine function is periodic and oscillates between -1 and 1, which is essential in analyzing waveforms in engineering and physics.
Furthermore, using Euler's formula, we can express complex numbers in a more compact form:
e^(iθ) = cos θ + i sin θ
This elegant formula connects exponential functions with trigonometric functions and is foundational in many areas of mathematics.
4. Analyzing the Expression
Now, let us delve deeper into the specific expression (endfraction) + i sin(startfraction 3 pi over 4 endfraction). This expression can be interpreted as a complex number where:
- The real part is endfraction
- The imaginary part is given by i sin(3π/4)
To evaluate sin(3π/4), we use the sine value for the angle:
sin(3π/4) = √2 / 2
Thus, we can rewrite the expression as:
(endfraction) + i(√2 / 2)
This representation provides insight into how complex numbers can be broken down into their real and imaginary components.
5. Real-world Applications of Complex Numbers
Complex numbers have practical applications in various fields, including:
- Electrical Engineering: Used in analyzing alternating current (AC) circuits.
- Signal Processing: Essential in Fourier transforms for analyzing signals.
- Control Theory: Applied in designing control systems and stability analysis.
- Fluid Dynamics: Used to model fluid flow and potential flow theory.
These applications highlight the relevance and utility of complex numbers in solving real-world problems.
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, we have explored the mathematical expression (endfraction) + i sin(startfraction 3 pi over 4 endfraction) and its components. Understanding complex numbers, their polar form, and the significance of trigonometric functions like sine is crucial for grasping advanced mathematical concepts.
We encourage readers to delve deeper into the world of mathematics and explore more about complex numbers and their applications. If you found this article helpful, please leave your comments below and share it with others who may benefit from this knowledge.
7. References
- Brown, J. W. (2018). *Complex Variables and Applications*. McGraw-Hill Education.
- Stewart, J. (2015). *Calculus: Early Transcendentals*. Cengage Learning.
- Friedman, A. (2016). *A Guide to Complex Variables*. Springer.
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8prrDn6mam6SevK95yGaqoqaVYsC1rdGtnauZk6m2sLqMbGSpoV2kw6a%2BjG1knqaUm7%2Bir9OipqdlkaOxbsaMa2WhrJ2h