Burmese is not just a language; it is a gateway to understanding the rich culture and history of Myanmar. As the official language of Myanmar, Burmese serves as a crucial element of national identity and cultural heritage. In this article, we will explore the nuances of the Burmese language, its cultural significance, and its historical background, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this fascinating subject.
The Burmese language, also known as Myanmar language, is spoken by millions of people and is integral to the daily lives of those in Myanmar. The language itself is deeply intertwined with the country’s traditions, customs, and social fabric. Understanding Burmese goes beyond just learning a language; it encompasses appreciating the values, beliefs, and histories that shape the Myanmar people.
This article aims to provide in-depth knowledge about the Burmese language, from its linguistic characteristics to its cultural implications. We will delve into various aspects such as its grammar, vocabulary, and the historical context that has influenced its evolution. Whether you are a language enthusiast, a traveler, or someone looking to connect with Burmese culture, this article will serve as a valuable resource.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to the Burmese Language
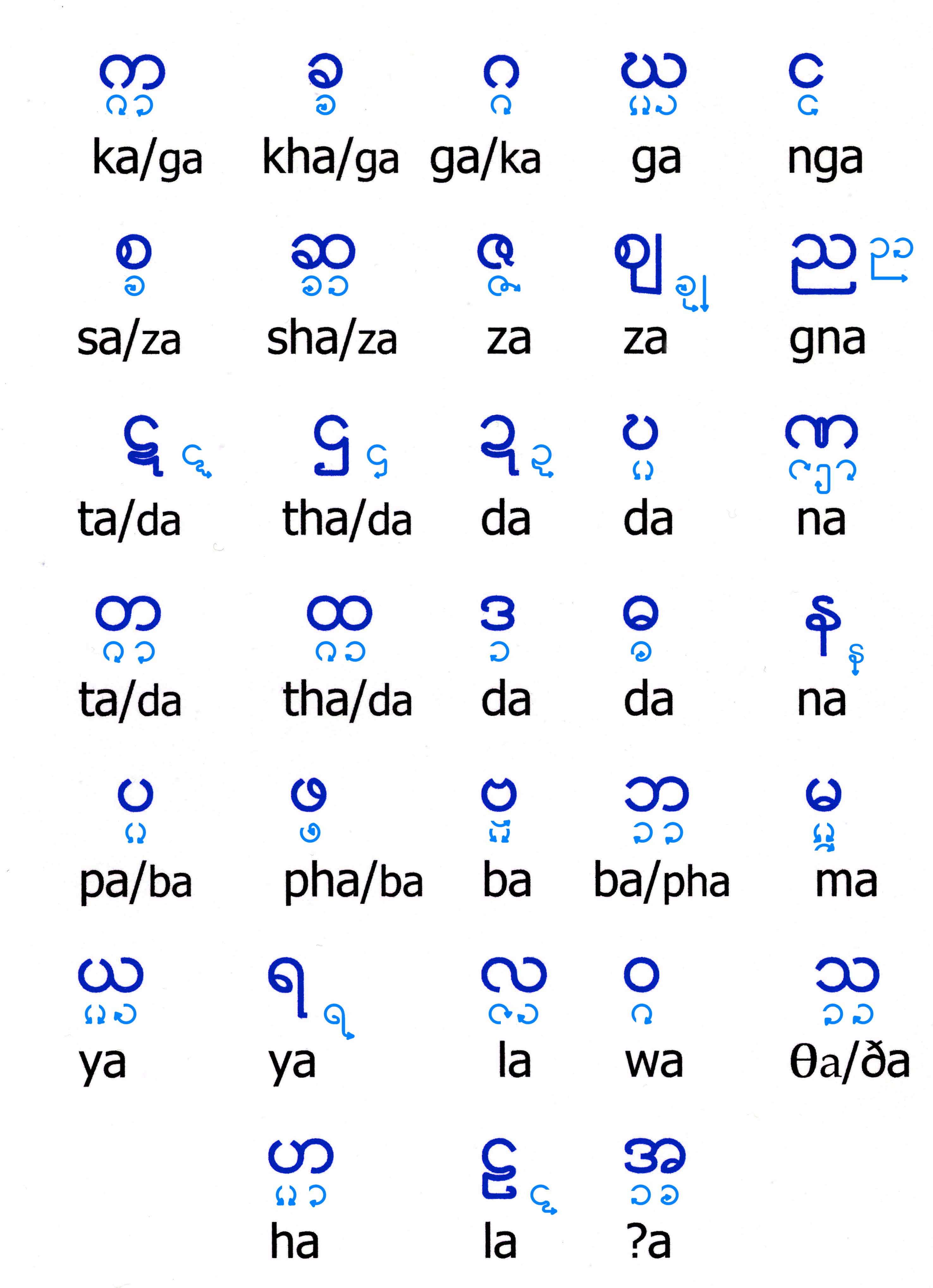
Burmese, or Myanmar language, is the official language of Myanmar and is spoken by approximately 33 million people. It belongs to the Sino-Tibetan language family and is the most widely spoken language in the country. The language is written using the Burmese script, which is an abugida, meaning that each character represents a consonant with an inherent vowel sound.
The Burmese language is an essential part of the country's identity and is used in government, education, and media. It is also the medium through which the rich literary traditions of Myanmar are expressed. Understanding Burmese opens the door to exploring the country's folklore, poetry, and historical texts.
2. Historical Background of Burmese
The history of the Burmese language can be traced back to ancient times, with its roots embedded in the Pyu and Mon languages. The first recorded use of the language dates back to the 11th century, during the Bagan Dynasty. Over the centuries, Burmese has absorbed influences from Pali, Sanskrit, and English, reflecting the historical interactions of Myanmar with neighboring cultures and colonial powers.
During the British colonial period, the language underwent significant changes, leading to the development of modern Burmese. The impact of colonialism introduced new vocabulary and grammatical structures, which have continued to evolve in contemporary usage.
3. Linguistic Features of Burmese
Burmese is a tonal language, meaning that the tone in which a word is spoken can change its meaning. There are three primary tones in Burmese: high, low, and creaky. This tonal aspect makes pronunciation particularly important for learners.
Additionally, Burmese grammar is characterized by its use of particles to indicate tense, mood, and aspect. Unlike many Indo-European languages, Burmese does not use inflections to convey grammatical relationships. Instead, word order and context play crucial roles in understanding meaning.
3.1 Pronunciation and Phonetics
The phonetic system of Burmese consists of a range of consonants and vowels, with distinct sounds that may not exist in other languages. Mastering the pronunciation is essential for effective communication and comprehension.
3.2 Vocabulary
The vocabulary of Burmese is rich and diverse, influenced by historical events and cultural exchanges. Common words and expressions often reflect the everyday life and traditions of the Myanmar people.
4. The Cultural Significance of Burmese
The Burmese language is deeply intertwined with the cultural identity of Myanmar. It serves as a vessel for expressing the values, beliefs, and customs of the people. Traditional songs, poems, and stories are often conveyed through the Burmese language, preserving the cultural heritage for future generations.
Moreover, understanding Burmese is crucial for appreciating the country's festivals, rituals, and social practices. The language embodies the essence of Myanmar's cultural fabric, making it a vital aspect of any cultural exploration.
5. Learning Burmese: Tips and Resources
For those interested in learning Burmese, there are several effective strategies and resources available. Here are some tips to get started:
- Enroll in language courses, either online or in-person, to receive structured learning.
- Utilize language learning apps that focus on vocabulary and pronunciation.
- Practice speaking with native speakers to improve conversational skills.
- Immerse yourself in Burmese media, such as films, music, and literature.
6. Common Phrases in Burmese
Here are some common phrases in Burmese that can be useful for travelers and language learners:
- မင်္ဂလာပါ (Mingalaba) - Hello
- ကျေးဇူးတင်ပါတယ် (Kyaayyzuu tin par tal) - Thank you
- ဘာသာပြန်ပေးပါ (Batha pyann pay par) - Please translate
- သင်ဘယ်လိုရှိသလဲ (Thin behlo shi tal) - How are you?
7. The Role of Burmese in Myanmar Society
Burmese plays a pivotal role in the social and political landscape of Myanmar. As the national language, it is used in government, education, and media, serving as a unifying factor among the diverse ethnic groups in the country.
In recent years, the importance of preserving the Burmese language has gained recognition, especially in the context of globalization and the influence of foreign languages. Efforts are being made to promote the use of Burmese in various domains to ensure that the language continues to thrive.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, the Burmese language is a vital component of Myanmar's cultural identity and history. Understanding Burmese provides insight into the values, beliefs, and traditions of the Myanmar people. Whether you are a language learner or simply interested in the culture, exploring the Burmese language can be a rewarding experience.
We encourage you to share your thoughts in the comments section below and explore more articles on our site to deepen your understanding of Burmese culture and language.
References
- Smith, J. (2020). "The Linguistic Heritage of Myanmar." Language and Culture Journal.
- Johnson, L. (2019). "Understanding Burmese: A Guide for Learners." Myanmar Language Studies.
- World Bank. (2021). "Education in Myanmar: A Country Report."
Thank you for reading! We hope to see you back for more insightful content.
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmmqaUpH53e8Guqaado5p7qcDMpQ%3D%3D