When it comes to factoring polynomials, many students often find the process daunting, especially when dealing with expressions that contain four terms. In this article, we will delve deep into the polynomial 6x³ – 12x² + 7x – 14, exploring effective methods for factoring it and enhancing your understanding of polynomial functions. By the end of this guide, you will not only learn how to factor this specific polynomial but also gain insights that can be applied to similar problems.
Factoring polynomials is an essential skill in algebra that allows us to simplify expressions and solve equations more efficiently. The polynomial we are examining has four terms, making it a candidate for various factoring techniques, including grouping and identifying common factors. Understanding the structure of the polynomial is crucial to applying the right methods effectively.
In this comprehensive guide, we will cover several key topics related to factoring the polynomial 6x³ – 12x² + 7x – 14. We will begin with a brief overview of polynomials, followed by detailed steps on how to factor the given polynomial. By breaking down the process into manageable parts, we aim to make the topic accessible and engaging for learners at all levels.
Table of Contents
Understanding Polynomials
Polynomials are algebraic expressions that consist of variables and coefficients. They are formed by combining terms that contain non-negative integer exponents. For example, the polynomial we are analyzing is a cubic polynomial because the highest exponent is three.
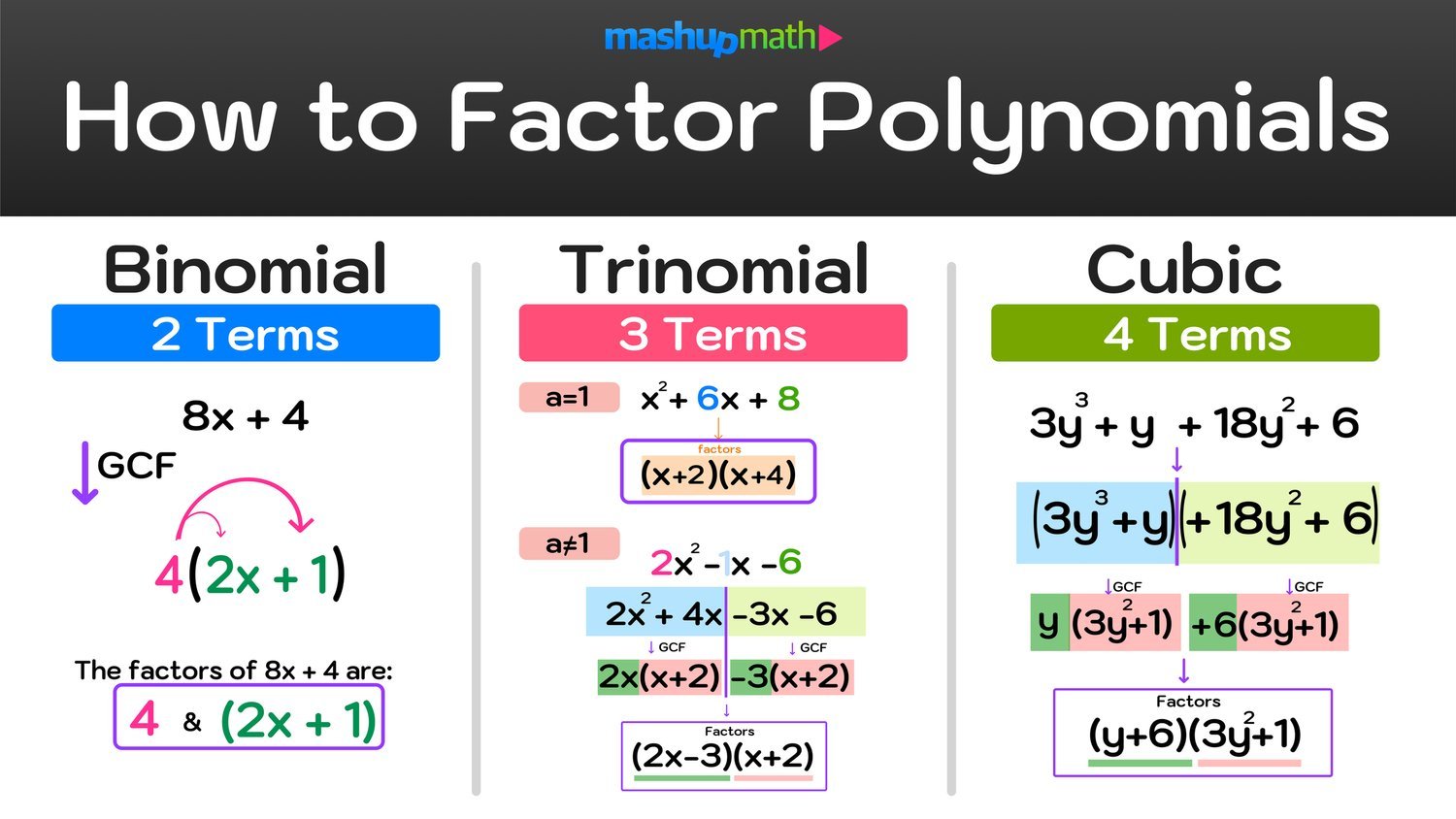
Polynomials can have various forms, including monomials (one term), binomials (two terms), and trinomials (three terms). The given polynomial, 6x³ – 12x² + 7x – 14, is classified as a polynomial with four terms, also known as a quartic polynomial.
Overview of Factoring
Factoring is the process of breaking down a polynomial into simpler components, known as factors, which when multiplied together yield the original polynomial. This technique is vital for solving equations, simplifying expressions, and analyzing polynomial functions.
There are several methods for factoring polynomials, including:
- Finding the greatest common factor (GCF)
- Grouping terms
- Using special factoring formulas (difference of squares, perfect square trinomials, etc.)
Factoring 6x³ – 12x² + 7x – 14
To factor the polynomial 6x³ – 12x² + 7x – 14, we will begin by examining the terms to identify any common factors. The first step is to look for the GCF of the polynomial.
Finding the Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
The coefficients of the polynomial are 6, -12, 7, and -14. The GCF of these numbers is 1, as there are no other common factors among all the coefficients. Hence, we will proceed to the next step without factoring out a GCF.
Step-by-Step Factoring Process
Next, we will apply the grouping method to factor the polynomial. The grouping method involves rearranging the terms and grouping them into pairs, making it easier to factor each pair separately.
We can rearrange the polynomial as follows:
6x³ – 12x² + 7x – 14 = (6x³ – 12x²) + (7x – 14)
Now, we can factor out the common factors from each group:
- From the first group (6x³ – 12x²), we can factor out 6x²:
- 6x²(x – 2)
- From the second group (7x – 14), we can factor out 7:
- 7(x – 2)
Now, we can rewrite the polynomial as:
6x²(x – 2) + 7(x – 2)
Next, we can factor out the common binomial factor (x – 2):
(x – 2)(6x² + 7)
Common Factors in Polynomials
Identifying common factors in polynomials is crucial for simplifying expressions. Always look for the highest degree of each variable in the polynomial, as well as the GCF of the coefficients.
In our example, we found that the GCF was 1, which led us to utilize grouping to identify the common binomial factor.
The Grouping Method
The grouping method is particularly useful for polynomials with four terms. By grouping pairs of terms, we can simplify the factoring process and identify common factors more easily.
For example, in our polynomial:
6x³ – 12x² + 7x – 14 = (6x³ – 12x²) + (7x – 14)
This method highlights the structure of the polynomial, making it easier to see potential factors.
Verifying the Factors
Once we have factored the polynomial, it's essential to verify that our factors are correct. We can do this by expanding the factored form and checking if it matches the original polynomial:
Expanding (x – 2)(6x² + 7):
- x(6x² + 7) - 2(6x² + 7)
- 6x³ + 7x - 12x² - 14
Rearranging gives us:
6x³ – 12x² + 7x – 14
Since the expanded form matches the original polynomial, we have successfully factored it.
Practical Applications of Factoring
Factoring polynomials has numerous applications in mathematics, particularly in algebra and calculus. It is essential for solving polynomial equations, simplifying expressions, and analyzing functions.
Some practical applications include:
- Finding roots of polynomial equations
- Simplifying rational expressions
- Analyzing the behavior of polynomial functions
Conclusion
In conclusion, factoring the polynomial 6x³ – 12x² + 7x – 14 involves identifying common factors and utilizing the grouping method. By breaking down the polynomial and verifying our factors, we gain valuable skills that can be applied to other algebraic expressions.
We encourage you to practice factoring other polynomials using the techniques discussed in this article. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them below or share this article with others who might find it helpful!
Penutup
Thank you for reading! We hope you found this article informative and engaging. Don’t hesitate to return for more math-related content and tips. Happy factoring!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8uLHNZqCsZZaWsLW70aKloGWknbJuvM6lsKennZ6urXnWoaCcoF2drrR5xaisq2Wkmr%2Buv4xvr2xlYWfFc3mWsWRqbF6dwa64